We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Is managing containers slowing down your development? You probably haven’t encountered Docker Hub. Docker Hub has revolutionised how applications are built, shipped, and functions. It acts as a pivotal player in the world of containerisation and forms a useful platform for software developers on a global scale. Based on a report, Docker Hub is utilised by over 5 million developers, indicating a large and active user base. In this blog, we will learn about what is Docker Hub, its vast applications, key features, and best practices. Let’s continue diving into this enthralling journey!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding what is Docker Hub
2) Key Features of Docker Hub
3) What is Docker Hub Used For?
4) 4 Best Practices for Docker Hub Security
5) Getting Started With Docker Hub
6) Conclusion
Understanding What is Docker Hub
Docker Hub is a cloud-based registry service where one can store, share, and manage Docker container images. It serves as a central hub for container images and forms a vital component of the Docker ecosystem. It offers numerous features, which are designed to simplify the containerisation process and enhance developer productivity. One of the most significant advantages of Docker Hub is its vast collection of official and verified images. Out of these, official images are maintained by Docker and the software's original creators to ensure authenticity and trustworthiness.
Moreover, it provides an intuitive web interface, making browsing, searching, and discovering repositories effortless. It's essential to understand the key aspects that make Docker Hub an indispensable tool for developers and organisations to grasp its complexities in-depth.
Key features of Docker Hub
Docker Hub offers essential features that help developers manage and share their container images easily. Let’s look at the key features that make Docker Hub a valuable tool for building and deploying applications.
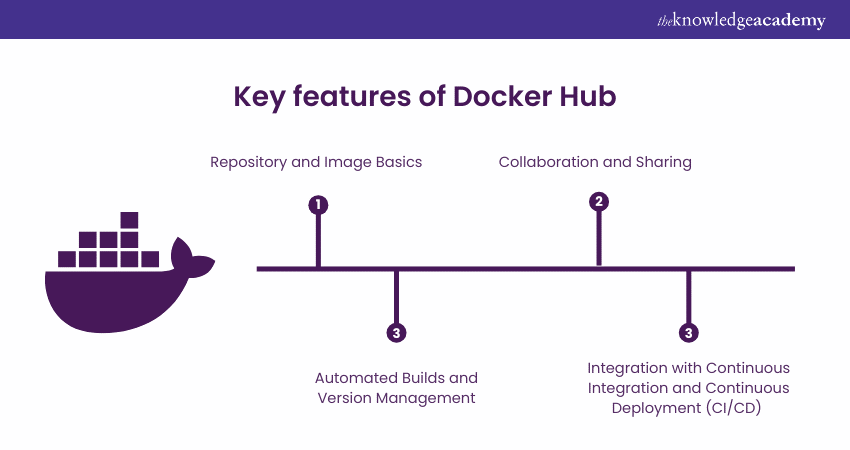
Repository and Image Basics
At the core of Docker Hub lies the concept of repositories and images. A repository is a collection of related container images, each representing a packaged application or software.
These images act as the building blocks of containerisation, containing all the necessary code, dependencies, and libraries for seamless application running. Docker Hub allows users to create public and private repositories (available on paid plans).
Docker Hub houses a vast library of container images that cater to several needs, ranging from popular software stacks to niche development tools. These repositories are not only managed by Docker itself but are also enriched by contributions from the active Docker community. This collaborative approach ensures the development team creates a rich and ever-growing, ready-to-use selection of images.
Collaboration and Sharing
Docker Hub's collaborative nature fosters sharing and collaboration among developers worldwide. It greatly benefits open-source projects where developers can contribute their images to public repositories, enabling others to use and build upon their work.
Furthermore, it facilitates collaboration within organisations through private repositories. Using its applications, businesses can easily maintain their container images, controlling access and ensuring the security of sensitive applications. This level of flexibility caters to both individual developers and enterprises, making Docker Hub a versatile solution for every situation.
Kickstart your Docker journey today with our Certified Agile DevOps Professional (CADOP) Course - sign up now!
Automated Builds and Version Management
Docker Hub streamlines image creation and maintenance through automated builds. Whenever changes are made to a codebase or a repository, it can automatically trigger image rebuilds, ensuring that the latest version is always available when needed. Moreover, this automation significantly reduces manual overhead and guarantees up-to-date and consistent container images.
Version management is also made seamless with Docker Hub. It allows developers to control and organise different versions of their images efficiently. Users can easily tag images with specific version numbers or labels, making it easy to keep track of the changes and revert back to previous states if needed.
Integration with Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Docker Hub's integration with CI/CD pipelines enhances the overall Software Development lifecycle (SDLC). Developers can incorporate its automated builds into their CI/CD workflows, enabling a smooth and efficient process, ranging from code changes to deployment.
CI/CD pipelines can automatically trigger image builds on Docker Hub whenever new code is committed to the repository. This ensures that any changes are rapidly reflected in the container images. This tight integration streamlines development practices and supports agile methodologies, where rapid iteration and deployment are key.
How a Docker Hub Works?
Understanding how Docker Hub works is essential for effectively utilising its features. This platform simplifies the process of managing container images and fosters collaboration among developers. Below are key components of Docker Hub that illustrate its functionality:
1) Cloud-Based Registry: Docker Hub serves as a cloud-based registry for storing and sharing Docker container images. It enables developers to pull images for their applications or push their own images to share with others.
2) Account Creation and Login: To start using Docker Hub, users create an account and log in through the Docker CLI or the Docker Hub website. This step is important for accessing and managing images.
3) Image Search and Upload: Once logged in, users can search for public images or upload their own custom images to the registry. This makes it easy to manage and access containerised applications.
4) Pulling Images: When a developer wants to use a specific image, they can pull it from Docker Hub using the command docker pull
5) Vast Image Library: Docker Hub hosts a vast library of official and community-contributed images, covering various software applications and services. Users can browse and search for these images on the Docker Hub website.
6) Version Control with Tagging: Docker Hub supports version control through tagging, which allows users to maintain multiple versions of their images. When pushing an image, developers can assign tags to specify the version, making it easy to assess changes and revert to previous versions if needed.
7) Collaboration Features: Collaboration is a key aspect of Docker Hub. Developers can create teams and share their repositories with other users, facilitating seamless teamwork and project management.
8) CI/CD Integration: Docker Hub integrates with continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) tools, enabling automated workflows. This integration streamlines the development process and improves productivity.
What is Docker Hub Used For?
Docker Hub provides several benefits that make managing container images easier. There are various advantages of using Docker Hub, which are discussed below:
1) Verified Publisher Images: Images from software vendors are verified by Docker.
2) Docker Certified Images: Docker ensures that these images follow best practices and don't fall for any kind of external vulnerabilities.
3) Official Images: These are handpicked by Docker and help to build a strong base for your projects since they follow best practices and are based on essential base images.
4) Docker’s Free Plan: Docker Hub's free plan offers some useful features for container repositories that are listed below:
a) You can have as many public repositories as you want.
b) You get one private repository, and up to three people can work on it with you.
c) You can do some basic testing with this free plan to understand how Docker Hub works.
4 Best Practices for Docker Hub Security
Ensuring security on Docker Hub is crucial for protecting your container images and maintaining the integrity of your applications. By following best practices, you can minimise risks and safeguard your resources. Listed below are the four main best practices for Docker Hub security:
Select the Right Base Image
When selecting a base image for your Docker project, you must consider the following two important tips:
a) Pick a Trusted Source: Docker Hub has various image classifications; however, its recommended to choose images from trusted sources like the official images. If not the official images, you can use Docker Certified and Verified Publisher images.
b) Choose the Smallest Image That Meets Your Needs: It's important to choose the smallest base image that easily meets your project's requirements. In comparison, smaller images are easier to work with, faster to download, space-efficient, and reduce the chances of security issues since they have fewer dependencies that could be vulnerable.
Use Multi-Stage Builds
Multi-stage builds are used to create a Docker file that is easily understandable and requires less maintenance. Here, you can use different images, including artifacts, which are necessary for that particular stage of the development process.
Scan Images During Development
Creating and rebuilding Docker images from a Dockerfile can cause potential security vulnerabilities in your system. For this reason, it’s important to conduct periodic image scanning to ensure the early detection of vulnerabilities.
Scan Images During Production
Analyse your container images regularly to identify potential security threats. Failure to follow this step can bring various security threats to your operational system. It’s also important to perform a scan twice, as the security of that image can change over time with the emergence of new vulnerabilities.
Getting Started With Docker Hub
The first step to getting started with Docker Hub is to create an account. The registration process is simple, requiring only a few simple steps, which are as follows:
Setting up an Account
a) Open your web browser and navigate to the Docker Hub website: https://hub.docker.com/.
b) Click on the "Sign Up" option placed at the top right corner of the page. You must enter your email id, username, and password.
c) After submitting your details, Docker Hub will send a verification message to your registered email id. Check your inbox and click on the verification link to complete the registration process.
d) Once verified, you will be greeted with a warm welcome to Docker Hub. Also, the account is now active and ready to use.
Navigating the Docker Hub Interface
Upon logging into Docker Hub, you will be presented with a user-friendly interface that offers easy navigation and access to a wealth of container images and repositories. Here are the main components of the Docker Hub interface:
a) Dashboard: The Dashboard is your personalised landing page that displays recommended images, repositories you have interacted with and relevant updates from the Docker community.
b) Search Bar: The search bar allows you to explore Docker Hub's vast collection of container images. You can also search by keywords and categories and even filter results based on popularity and official status.
c) Featured Images: Docker Hub often highlights featured images on the homepage. These images are popular, high-quality container images and are recommended by Docker or the community.
d) Repositories: You can access your repositories and manage them from the "Repositories" tab. Here, you can easily create new repositories, upload images and organise your existing containers.
e) Explore: The "Explore" section allows you to browse images by categories, including programming languages, databases, operating systems, etc, making it easy to discover new tools and applications for your projects.
f) Official Images: Docker Hub's "Official Images" section displays images officially maintained by software vendors. These images have undergone rigorous testing to ensure their reliability and safety.
g) Verified Images: In the "Verified Images" section, you will find images that have been verified by Docker. This indicates that they meet the company's quality standards and security requirements.
h) Your Profile: Click on your profile picture to access your account settings, manage your repositories, and review your activity on Docker Hub.
Searching and Pulling Images to Your Local Machine
Getting the right container images is essential for effective development. Let's explore how to find and pull container images to your local machine:
a) Search for Images: Use the search bar to find images related to your project. For example, if you are developing a web application using Node.js, you can search for "Node.js" to find relevant images.
b) Choose the Image: Browse the search results and select the image that best suits your needs. Click on the image to view its details, including the available tags and descriptions.
c) Pull the Image: Once you have chosen the image and identified the specific version you want, copy the "pull" command provided on the image page. Open the terminal or command prompt and paste the command to start pulling the image.
d) Monitor Progress: The image will start downloading to your local machine. You will see progress updates in the terminal, indicating the download status.
e) Verify the Pull: Once the pull is complete, you can verify that the image is now available on your local system using the "Docker Images" command. This will display a list of images stored on your machine.
Docker Hub vs Other Docker Registries
When choosing a Docker registry, it's important to understand the differences in features and integrations. Below are key comparisons between Docker Hub and other popular Docker registries:
1) Integration and Management: Docker Hub offers seamless integration with Docker CLI, enabling easy image management and version control. This makes it straightforward for developers to handle their container images.
2) Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR): Amazon ECR integrates closely with Amazon Web Services (AWS), offering enhanced security features like IAM-based access controls and image scanning for vulnerabilities. It is ideal for teams already using AWS.
3) Google Container Registry (GCR): Google GCR provides robust integration with Google Cloud Platform (GCP), emphasising secure storage and efficient image management. It caters to organisations looking for cloud-based solutions that enhance their infrastructure.
4) Self-Hosted Registries: Self-hosted registries like Harbor and Nexus offer complete control over Docker images. These are appealing for enterprises with strict compliance and security requirements, allowing deployment on-premises or within private clouds.
5) Customisation and Flexibility: Self-hosted registries allow for customisation, enabling teams to tailor features to their specific workflows. This flexibility is crucial for organisations with unique needs.
6) Choosing the Right Registry: The choice between Docker Hub and other registries depends on project needs and organisational goals. Docker Hub excels in community support and accessibility, while alternatives like ECR and GCR offer advanced features for cloud-centric applications. Self-hosted registries provide the control and customisation some organisations require.
Webhooks
Webhooks are a way for one computer to notify another to perform a specific operation and receive a response without waiting. You can think of them as a POST request sent to an API URL, which can be configured in Docker Hub. Here's how it is used:
a) To configure webhooks, select the ‘Webhooks’ tab on the Docker Hub repository which is shown in the image below:
b) Now, put a name for the Webhooks.
c) Give a desired destination webhook URL link where webhook POST requests will be delivered:
Docker Hub Pricing
Understanding the pricing structure is essential for choosing the right plan that fits your needs. Discussed below are the pricing options of Docker Hub:
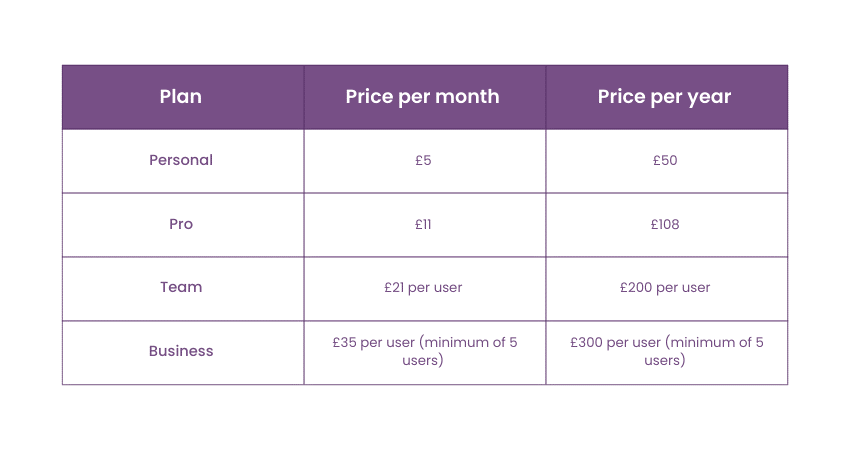
1) Personal Plan: This plan is suited for individual developers who want a basic Docker Hub account. You can have as many private repositories as you need, up to 100 public repositories, and you get 1 GB of monthly bandwidth.
2) Pro Plan: This plan is designed for teams and small businesses that need more features and bandwidth. It offers unlimited private and public repositories, 10 GB of monthly bandwidth, and priority support.
3) Team Plan: The team plan is well-suited for larger teams and businesses, requiring more users and bandwidth. It has all the Pro plan features and offers 50 GB of monthly bandwidth per user.
4) Business Plan: It includes everything in the Team plan 200 GB of monthly bandwidth per user, dedicated support, and image scanning.
Conclusion
We hope you understood What is Docker Hub. Understanding Docker Hub is crucial for every aspiring developer to harness the power of containerisation effectively and quickly. Additionally, it serves as an indespensible tool for developers and organisations who are looking to optimise their application development and deployment processes. So, cherish its power and unlock a world of innovative possibilities to innovate and deliver software development faster and more efficiently.
Level up your potential for programming with our Certified DevOps Security Professional Course - join now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Yes, Docker Hub hosts open-source images through its Docker Trusted Open-Source program. These images are of high quality, maintained by trusted open-source communities, and provide access to popular software and libraries.

Yes, Docker Hub offers private repositories that allow you to store and manage container images securely. These private repositories provide full control over who can access your images, making it ideal for managing sensitive projects or proprietary software.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various DevOps Certification Courses, including Certified DevOps Professional (CDOP), Docker Course, and Certified DevOps Security Professional (CDSOP). These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into DevOps Engineer Salary.
Our Programming & DevOps Blogs cover a range of topics related to Earned Value Management, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Programming & DevOps Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Docker Course
Docker Course
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


