We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Efficient Food Safety is a major concern for the food industry, and it is associated with both businesses and consumers. These dangers range from biological origins, like different types of bacteria and viruses. They also include chemicals such as pesticides or food additives and the physical involvement of foreign objects in foods. Therefore, the right Food Safety practices are important to avoid the likelihood of Food Safety Hazards during food processing, production or distribution.
The statistical analysis of the Food Standards Agency shows that the UK is registering around 2.4 million cases of foodborne diseases annually. That would certainly worsen conditions to the extent of allergies and even fatal food poisoning in the long run, and therefore, ignorance or negligence should not be practised. Continue reading to get a better understanding of the main Food Safety Hazards, including their most common sources for food contamination.
Table of Contents
1) What are Food Safety Hazards?
2) Types of Food Safety Hazards
3) Common Sources of Food Contamination
4) Recognising and Preventing Biological Hazards
5) Understanding and Mitigating Chemical Hazards
6) Physical Hazards: Identification and Prevention
7) Digital Solutions to Control Hazards
8) Maintaining Food Safety at Home
9) Conclusion
What are Food Safety Hazards?
Food Safety risks are the environmental factors or the substances in food that can influence consumers negatively. They are classified into three types: Organic, chemical, and physical.
Biological Hazards are bacteria, viruses or germs that cause disease. Chemical risk is a kind of dangerous compound that can include pesticides or some chemical additives that are harmful or toxic. The word Physical Hazard is used to describe objects like stones or metal pieces, which can result in injury.
The identification and prevention of these dangers play a key role in guaranteeing Food Safety product level and public health. Achieving good Food Safety practices includes correct portioning, cooking, and storage. It is important to prevent risks posed by these hazards and keep food safe.

Types of Food Safety Hazards
To understand Food Safety Hazards, one must first understand the three common categories: biological, chemical, and physical. Some of them are riskier than others, so, it is important to address them in order to ensure Food Safety.
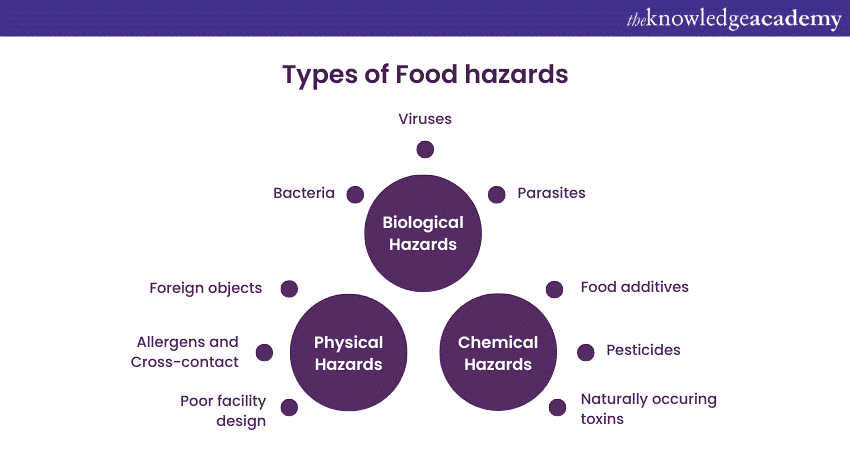
1) Biological Hazards
Biological Hazards are those microorganisms that heavily threaten Food Safety which brings on Foodborne illnesses. These single cell animals with sizes below human eyes’ capabilities multiply fast in favourable conditions, causing diseases when ingested. Amongst the notable three Biological Hazards are bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
a) Bacteria: Such ones are different unicellular microorganisms that can live in various spaces, one of which is food. However, the majority of bacteria are not dangerous, while others can bring about life threatening diseases.
Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria are examples of bacteria that can be transmitted to food. These pathogens can cause symptoms such as diarrhoea, vomiting, nausea, and potentially life-threatening complications.
b) Viruses: They are 500 times smaller than bacteria. They have to have a host for nutrition as well as an environment for well-divided and multiplied growth. Illness-causing microbes, e.g. the Norovirus, hepatitis A virus, etc., can be spread through the contamination of water, food and surfaces. A patient can have symptoms indicating viral contamination that are digestive in nature. These symptoms can range from mild discomfort in the gastrointestinal system to serious infections.
c) Parasites: As opposed to other microorganisms, these microorganisms stay in or on host organisms or get them as a nutrition source. Certain parasites may contaminate food, and subsequently, parasitic infections may develop in humans. Examples such as Cryptosporidium and Giardia. Such illnesses occur after consuming contaminated water or thoroughly uncooked meat.
2) Chemical Hazards
Chemical risks originate from numerous chemical components. These components have the potential to contaminate foods and be transmitted to consumers. This may arise from a large number of possible sources such as food additives, pesticide residues even natural toxins.
a) Food Additives: These are the compounds added to food products to increase shelf life, improve appearance, or enhance taste. For example, they can make food look better, taste more favourable, or increase durability. Meanwhile, a large dose or the abuse of any additive may also impair your health. Use labels as your guiding light and know the additive limits. Prioritise minimally processed foods on your shopping list.
b) Pesticides: Insect repellents such as these have various uses in agribusiness to protect crops from insects. Carcinogenic residues of the toxic substances can be found on foods, including fruit, vegetables, and grain, although they are washed.
c) Naturally Occurring Toxins: Certain foodstuffs have natural toxins in them, which can turn toxic if they are taken in greater amounts. For example, a few mushrooms might induce some poisons that can result in serious ailments or even fatalities.
We must clearly identify edible mushrooms and purchase seafood from reliable suppliers to avoid mercury and other toxins. Additionally, learning to recognise food poisoning symptoms is essential to maintain our health.
3) Physical Hazards
Physical Hazards in Food Safety refer to foreign objects that inadvertently find their way into food products, posing risks to consumers. These Hazards can include glass, metal, plastic, wood, or any other material not naturally present in the food.
a) Foreign Objects: These objects can enter food during various stages of production, packaging, and handling. Contaminated raw materials, improper equipment maintenance, or poor facility design can contribute to the presence of foreign objects. Implementing quality control measures, using appropriate food-grade materials, and regularly inspecting equipment can help prevent foreign object contamination.
b) Poor Facility Design: Inadequate facility design can create opportunities for Physical Hazards to contaminate food. For example, improper food packaging sealing can allow foreign objects to enter. To avoid such hazards, it is essential to design facilities with Food Safety in mind. Conducting routine maintenance and training staff in proper handling and packaging procedures are also crucial.
c) Allergens and Cross-contact: Cross-contact occurs when allergenic proteins from one food meet with another food, leading to unintended allergen presence. This can happen during food processing, preparation, or storage.
Register for our Food Safety and Hygiene Course and learn how to safeguard yourself and your workplace.
Common Sources of Food Contamination
Food contamination can occur from various sources, compromising the safety of what people eat. Here are three familiar sources of food contamination to help you safeguard yourselves and take precautions:
1) Contaminated water and ice
Water or ice, commonly used in food preparation, can transmit pathogens if sourced from unclean areas and handled improperly. Contaminated water can introduce active bacteria and viruses into foods, leading to diseases. Washing salads with polluted water or using it to make drinks can pose hidden dangers. Therefore, selective and high-quality water treatment is essential.
2) Cross-contamination
Often problems arise regarding cross contamination which refers to when microorganisms from raw foods move to ready to eat foods or surfaces. It is almost sure to happen if people use shared utensils, cutting boards or bare hands.
These bacteria can be transferred from raw chicken onto a cutting board that is not properly sanitised. From there, they can further spread onto chopped vegetables using the same board. Saving cross-contamination is only possible with strict separation of raw and ready-to-eat foods, using dedicated tools, and establishing good hygiene standards.
3) Improper Food Handling and Storage
Dangerous microorganisms thrive and multiply quickly once perishable products are left unchilled for long periods at room temperature. Incapacity of freezing or improper keeping can give rise to bacteria growth very fast. So, food poisoning is possible.
The appropriate temperature below 40°F (4°C) has to be used to refrigerate perishables and it is to be made sure that consumers eat them promptly or store them safely to stop the multiplication of bacteria.
Recognising and Preventing Biological Hazards
Biological Hazards like bacteria, Viruses, and Parasites can pose significant risks to Food Safety. Understanding these hazards and implementing preventive measures is crucial to safeguarding your health. The table below discusses some of the symptoms and prevention methods for the Biological Hazards:
|
Type of Biological Hazard |
Description and Symptoms |
Preventive Measures |
|
Bacteria |
a) Common in various foods b) It can cause symptoms like diarrhoea and vomiting. c) Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter are some common symptoms. |
a) Ensure proper cooking temperatures for meats. b) Practice thorough hand hygiene before and after food handling. c) To avoid cross-contamination, you can use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw food and food preparation. d) Promptly refrigerate perishable items. |
|
Viruses |
a) Viruses, even smaller than bacteria, can spread through contaminated food, water, or surfaces. b) Norovirus and hepatitis. |
a) Practice thorough handwashing with soap and water. b) Avoid consuming raw or undercooked foods, especially seafood and eggs. c) Keep food preparation area and utensils clean and sanitised. |
|
Parasites |
a) Parasites can contaminate food, particularly meat and seafood, leading to parasitic infections. b) Cryptosporidium and Giardia are common examples. |
a) Ensure proper cooking temperatures for meats and seafood. b) Use safe water sources for food preparation and consumption. c) Maintain proper hygiene during food handling and preparation. d) Educate yourself on safe food sources. |
Understanding and Mitigating Chemical Hazards
Chemical hazards are particularly important among the numerous factors related to Food Safety. These hazards involve substances that are potentially toxic and can contaminate food, posing a significant threat to health. Knowledge of such risks and preventive measures that prevent them by assuring Food Safety is of vital importance.
1) Food Additives and Preservatives
The use of food additives and preservatives, by which they can improve the product features, may be considered a harm when applied incorrectly. Acknowledging the boundaries and not going beyond them is the key aspect in it. Feel free to try less processed foods and scanning barcodes can help to decrease exposure.
2) Pesticide Residues
Pesticides used in agro-industrial processes inevitably end up on fruits. Careful washing and peeling of fruits and vegetables can decrease pesticide exposure. Choosing organic products can further reduce the risk of health damage related to pesticides.
3) Foodborne Toxins
Certain microbes generate toxins and cause contamination in food, which leads to foodborne diseases. Proper preservation and chilling of perishables, thorough cooking, and abstaining from consumption of rotten food can lessen the risks provoked by these toxins.
Here are Food Safety Questions and Answers You Should Go Through Before your Interview.
Physical Hazards: Identification and Prevention
Foreign objects mistakenly find their way into a food product, which represents one of the Physical Hazards in Food Safety and may pose risks to consumers. Identifying and, most importantly, preventing these Hazards is very important to keeping food quality intact.
1) Foreign Objects
Foreign substances such as glass, metal or plastic may emerge in food while processing, packaging, or handling. The effects of the pollution could be substantial, ranging from injuries and health consequences to legal accountabilities. The application of rigorous quality control standards and using only food-grade materials is essential. Additionally, performing periodic equipment inspections will significantly lower the chances of foreign object contamination.
2) Poor Facility Design
Inadequate facility design can create opportunities for Physical Hazards to contaminate food. Packaging improperly sealed and flawed equipment design can lead to Hazards. Therefore, designing facilities with Food Safety in mind and adhering to best practices is important. Training staff in correct handling procedures can also help minimise the risks associated with poor facility design.
3) Allergens and Cross-contact
Allergenic contaminants can lead to severe allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Cross-contact, where allergens are unintentionally transferred to allergen-free foods, is a concern. Some of the measures to prevent this include:
1) Maintaining separation between allergenic and non-allergenic foods during storage, preparation, and cooking.
2) Thoroughly clean utensils and equipment after handling allergenic ingredients.
3) Properly labelling allergenic foods and implementing dedicated spaces for allergen-free preparation to mitigate the risk of allergen-related reactions.
Elevate your Food Safety expertise with our Food Allergy Awareness Training!
How Can Digital Solutions Control Food Safety Hazards?
Proper identification, analysis, processing, and monitoring can significantly control Food Safety hazards. To achieve this, food business owners must implement a comprehensive Food Safety Management System (FSMS) within their operations.
FSMS is powered by artificial intelligence (AI), which simplifies the Food Safety process. Such a system can create a digital FSMS in an average of just 15 minutes. When utilising a digital FSMS, businesses can enjoy the following benefits:
1) Smart Notifications for Food Safety Tasks
An intuitive system can remind food handlers of upcoming Food Safety tasks. The smart notification system sends alerts whenever a task needs to be completed, ensuring that all tasks related to controlling food hazards are done on time. Daily notifications can be received through a smart Food Safety app.
2) Real-time Overview for Managers
Managers can save more time with a smart Food Safety System. A real-time dashboard provides an overview of the business's Food Safety status, showing which tasks are completed correctly and which need more attention. This feature can save managers up to 20% of their time by providing a clear overview of all branches and monitoring tasks to ensure consistent hazard control.
3) Customisable Monitoring Logs
The system generates digital monitoring tasks and checklists based on the business profile, helping the team accurately record all necessary parameters for controlling hazards. These monitoring logs and checklists can be customised to fit unique operations.
4) Step-by-step Instructions
Employees can learn how to accurately control food hazards with detailed, automatically generated instructions. Food safety managers can employ these instructions to train food handlers, ensuring tasks are completed accurately and effectively. Custom instructions can also be uploaded as images or videos.
5) Become More Sustainable with Digital Monitoring
Organisations can make their operations more sustainable by going digital. By leaving behind paper-based monitoring procedures, they can enhance workforce efficiency with a digital platform.
Switching to a digital FSMS can take the laborious process out of Food Safety management and ensure a higher standard of Food Safety control.
Digital solutions are revolutionising the way Food Safety issues are addressed, empowering businesses to better Food Safety practices.
a) Smart notifications: In the rush of food service, it is easy to miss important Food Safety tasks. Digital tools overcome this by implementing smart notification systems. These systems can send out automated alerts to staff's mobile devices or workstations, prompting them to check temperature, sanitise equipment, and conduct inventory reviews. Through such a meticulous approach, the fundamental operations are accomplished on time, thus reducing the risk of Food Safety problems.
b) Real-time overview: Managers and Food Safety Officers should be equipped with a holistic view of their business activities. Digital platforms offer real-time dashboards that present the essential Food Safety metrics and compliance statuses. The dashboards can display the live data from different stakeholders in the food supply chain which immediately inform the potential risks for rectification. This high degree of scrutiny is crucial for ensuring high Food Safety standards and prompt decision-making.
c) Customisable monitoring logs: Each food business and its monitoring requirements differ from one case to another. Digital Food Safety solutions provide individualised monitoring that can be customised to the needs of a particular business. These logs can be used to record different data such as cooking temperatures to cleaning schedules which can be updated as the business grows or laws and regulations are changed. Digital logs, due to their flexibility, provide businesses with the ability to always adhere to current Food Safety requirements.
d) Step-by-step Instructions: One of the challenges in Food Safety Management is the guarantee that every one of the staff members follows the procedures correctly. With digital solutions, a detailed plan of action can be developed that breaks down each of the tasks involved in the Food Safety plan. These tutorials might include pictures, videos, or other multimedia elements that make the process of comprehension and adherence easier. Through the standardisation of tasks, businesses are not only able to reduce human error but also maintain the same Food Safety standards.
Maintaining Food Safety at Home
The responsibility for guaranteeing Food Safety is not only that of food producers and restaurants. It covers our homes as well, where the correct treatment of food, storage and preparation processes remain key factors of our health. We are able to protect the health of our families and ourselves by practicing good habits. Let's check this section to maintain Food Safety at home.

Proper cooking techniques
When preparing food at the desired temperature, it is crucial to keep the microorganisms and disease-causing bacteria being annihilated. Alongside that, a thermometer becomes the main companion to the cook. It is essential for achieving a safe temperature for different meats, chicken, and seafood.
We will use the ground meat as our primary example – the internal temperature must reach 160°F (71°C). The chicken and turkey, on the other hand, should be cooked to a temperature of 165°F (74°C). There should be strict control on the reheating of leftover foods. They need to be heated to a temperature of 165°F (74°C) to ensure that bacteria do not survive.
Safe Food Storage
The food has to be stored well to avoid the growth of bacteria and taste destruction. Refrigerate immediately with no perishable food, and its internal temperature is about 40 4 °F (4 °C).
Never mix cooked and raw meat to prevent cross-contamination. Place raw meats on a lower shelf where any drop would be prevented.
Hygienic Food Preparation
A clean and controlled food preparation environment is the first line of defence against potential Hazards in our meals. Good hygiene during food preparation is crucial for Food Safety. Practising good hygiene during food preparation is crucial for Food Safety. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before and after handling food. After each use, clean cutting boards, utensils, and surfaces with hot, soapy water.
Always prefer using separate cutting boards for raw meats, fruits, and vegetables to prevent cross-contamination. This will help eliminate the risk of cross-contamination and eventually help build a safer culinary environment.
Avoid Cross-contamination
Cross contamination happens when bacteria that cause harm gets moved from one surface or food to the other. To avoid this, do not mix raw meats, poultry, seafood, and juices with salad or other dishes. Marinating meats such as chicken, fish, and beef should be done in the refrigerator. Any leftover marinade that has come into contact with raw meat should be discarded.
Empower your Food Safety skills - register for our Food Safety Training!
Conclusion
Understanding and acknowledging the Food Safety Hazards is crucial to ensure your well-being and surroundings. By identifying, preventing, and managing these Hazards, individuals can contribute to safer food practices, protect consumer health, and ensure the integrity of the food industry.
Learn and prioritise your Food and safety standards by registering for our Food Hygiene and Safety Training!
Frequently Asked Questions

Businesses can minimise Food Safety Hazards by implementing a comprehensive Food Safety Management System (FSMS), conducting regular staff training, adhering to strict hygiene practices, ensuring proper equipment maintenance, and performing routine inspections to detect and address potential risks promptly.

Yes, specific regulations such as the FDA's Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) in the U.S. and the European Union's General Food Law Regulation mandate strict Food Safety protocols. These include hazard analysis, preventive controls, regular inspections, and compliance with hygiene standards to ensure the effective control of Food Safety Hazards.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Food Hygiene and Safety Courses, including Food Safety and Hygiene Course, Food Hygiene and Safety in Manufacturing Training, and Food Allergy Awareness Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Food Safety methodologies.
Our Health & Safety Blogs cover a range of topics related to Food and Safety, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Food Safety skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Food Safety and Hygiene Course
Food Safety and Hygiene Course
Fri 3rd Jan 2025
Fri 7th Mar 2025
Fri 2nd May 2025
Fri 4th Jul 2025
Fri 5th Sep 2025
Fri 7th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


