We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Production Management is a critical aspect of any manufacturing or service-oriented organisation. It involves planning, organising, and controlling the resources and processes involved in the creation of goods or services. Thus, it’s crucial to learning the Functions of Production Management process for maximising the benefits one can receive from it.
According to Statista the software market for Product Lifecycle Management made 16.42 billion GBP. This demonstrates the effect and popularity of the Product Mangement process across enterprises. If you too want to ensure optimal utilisation of resources, increase productivity and timely delivery of products, it’s time to understand the concept. Read this blog to discover the essential Functions of Production Management. Also, learn about forecasting, control, assurance and more.
Table of Contents
1) What is Production Management?
2) Basic functions of Production Management
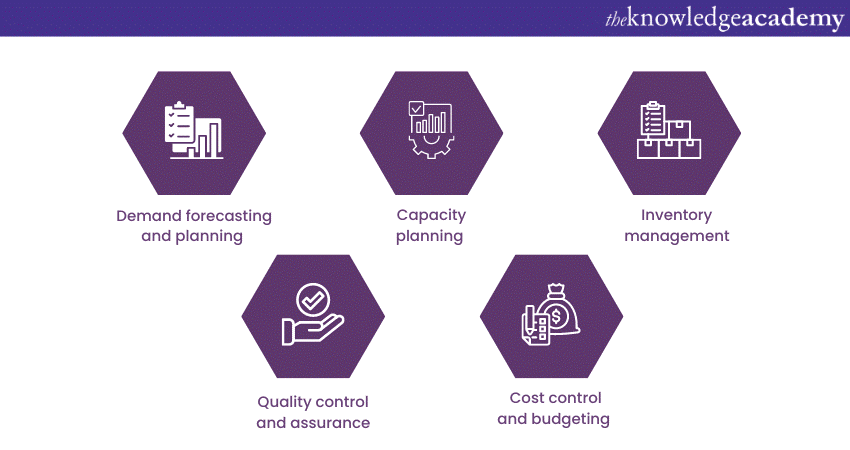
a) Demand forecasting and planning
b) Capacity planning
c) Inventory management
d) Quality control and assurance
e) Cost control and budgeting
3) Advanced functions of Production Management
4) Conclusion
What is Production Management?
Production Management is a dynamic and indispensable discipline that lies at the core of every manufacturing and service-oriented organisation. It serves as the backbone of the entire production process. It encompasses a comprehensive set of functions aimed at orchestrating and optimising various aspects of production. From conceptualising product ideas to delivering the finished goods or services to customers, Production Management is vital in ensuring seamless operations, efficiency, and profitability.
The modern business landscape demands swift adaptability to changing market dynamics and customer preferences. Production Management steps up to this challenge by providing a systematic and well-organised approach to production.
It helps organisations to remain agile and responsive in the face of uncertainty. Moreover, effectively managing resources and implementing continuous improvement initiatives allows Production Managers to lay the groundwork for a successful and sustainable business.
Wish to gain vital skills? Jumpstart your career with our course in Industry Training today!
Basic functions of Production Management
The basic functions of Production Management form the bedrock of manufacturing and operational processes. They provide a framework for translating raw materials into finished products in an organised and efficient manner. These functions are foundational, ensuring that the fundamental aspects of production are addressed systematically.
Basic functions ensure that core operations are streamlined, products meet initial standards, and resources are effectively utilised. Their centrality to production operations means that the overall system would falter without mastering these basic elements, affecting the quality of the end products. Some of these basic functions are as follows:
Demand forecasting and planning
Demand forecasting is a critical first step in Production Management. Analysing historical sales data and customer behaviour allows Production Managers to predict future product or service demand. Accurate demand forecasting allows businesses to plan their production schedules effectively, ensuring they can meet customer demands without overproducing or facing stockouts.
Forecasting helps Production Managers make informed decisions about resource allocation and capacity planning. With a clear understanding of expected demand, they can procure raw materials and secure production resources in advance, optimising inventory levels and reducing carrying costs. Moreover, demand forecasting aids in developing pricing strategies, promotional activities, and market expansion plans.
To improve forecasting accuracy, Production Managers can leverage advanced analytics and forecasting tools. Regularly reviewing and refining forecasting methods based on real-time market insights and customer feedback allows organisations to adapt to changing market conditions and instantly gain a competitive advantage.
Capacity planning
Planning capacity is the process of determining the production capacity required to meet the forecasted demand. This involves evaluating the capabilities of existing resources, such as machinery, labour, and technology. A thorough understanding of the organisation's production capacity is crucial to avoid overloading or underutilising resources.
Effective capacity planning allows Production Managers to identify potential bottlenecks and allocate resources efficiently. Optimising production capacity lets organisations respond promptly to changes in demand and enhance customer satisfaction. It also helps in identifying areas where investments in new equipment or technology might be necessary to support future growth.
A crucial aspect of capacity planning is workforce management. Production Managers need to ensure that they have a skilled and well-trained workforce to handle production demands. This process involves training and development opportunities for existing employees or hiring additional personnel during peak production periods.
Inventory management
Inventory management involves overseeing the acquisition, storage, and distribution of raw materials and finished goods. Production Managers must strike a delicate balance between maintaining optimal inventory levels and avoiding excess carrying costs.
Effective inventory management starts with accurately forecasting demand. Aligning production with demand forecasts can reduce excess inventory and the risk of obsolescence. This frees up capital for other critical investments and reduces inventory holding costs. Just-in-time (JIT) inventory management is a popular approach for keeping inventory levels low while ensuring the timely arrival of materials. Adopting JIT principles in organisations can minimise inventory carrying costs and improve overall production efficiency.
Another aspect of inventory management is safety stock management. Production Managers need to maintain a buffer of safety stock to address unexpected demand fluctuations or supply chain disruptions. Establishing appropriate safety stock levels can help organisations can mitigate the risk of stockouts and maintain a reliable supply to customers.
Quality control and assurance
Maintaining high product quality is crucial for customer satisfaction and brand reputation. Quality control involves implementing product monitoring and inspection at various stages of production. This ensures that products meet the defined quality standards and any defects are identified and rectified promptly.
Production Managers must establish quality assurance programs that encompass training employees on quality standards, conducting regular audits, and addressing any deviations from established procedures. Fostering a culture of quality consciousness allows organisations to reduce rework and enhance their competitive advantage.
Continuous improvement is central to quality control and assurance. Production Managers must analyse data from quality control processes to identify recurring issues and implement corrective actions. Collaborating with design and engineering teams can also lead to product improvements that enhance overall quality and customer satisfaction.
Establish better communication skills with our Facilitation Skills Training today!
Cost control and budgeting
Cost control and budgeting are integral to effective Production Management. Production Managers must closely monitor production costs and implement cost-saving measures without compromising product quality or customer satisfaction. Analysing production processes and identifying cost-saving opportunities allows Production Managers to optimise resource utilisation and minimise waste.
Budgeting plays a crucial role in allocating resources and planning production activities. Creating comprehensive budgets for projects allows Production Managers to ensure that projects remain financially viable and align with the organisation's strategic goals. Implementing lean manufacturing principles can help streamline production workflows and reduce unnecessary costs.
Tracking and analysing production costs against budgeted amounts enable Production Managers to make informed decisions and identify areas where cost-saving measures can be implemented. Regular financial reviews help in maintaining cost discipline and enhancing overall profitability.
Interested in learning about the managerial process? Try our Product Management Training today!
Advanced functions of Production Management
Advanced functions of Production Management delve into the intricate and sophisticated aspects of manufacturing and operational processes. These functions expand beyond the foundational basics, focusing on optimising and refining the production ecosystem. They tackle the complexities that arise as organisations grow, markets evolve, and technologies advance.
While basic functions lay the groundwork for standardised operations, advanced functions ensure adaptability and continuous enhancement in the production lifecycle. Their strategic nature ensures that businesses not only maintain their current standing but also innovate and stay ahead of emerging challenges and opportunities. Mastery of these advanced elements is crucial for sustained competitiveness and long-term success. Some of these advanced functions are as follows:
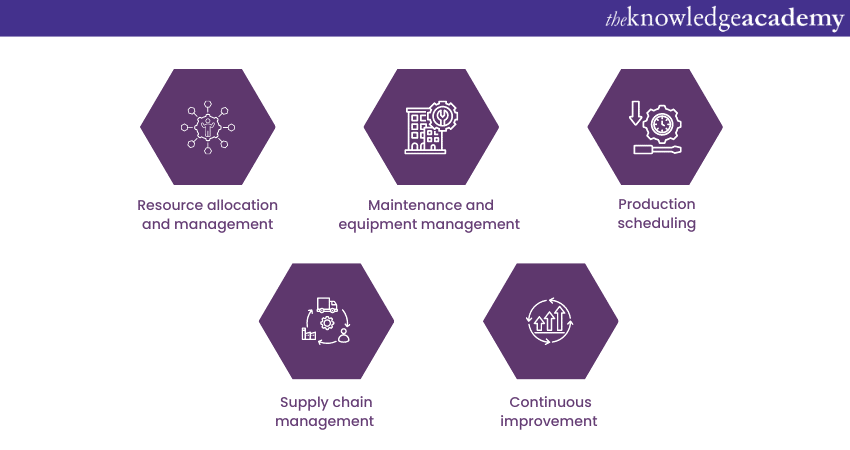
Resource allocation and management
Resource allocation is about assigning the right resources to specific production tasks to achieve optimal efficiency. This includes labour, raw materials, equipment, and financial resources. Production Managers must balance resource allocation to avoid wastage, reduce production delays, and maintain a smooth workflow.
Effective resource management also involves monitoring resource utilisation and performance. Tracking resource usage allows Production Managers to identify areas where improvements can be made, such as reducing material waste or optimising machine downtime. Regularly analysing resource data helps organisations make informed decisions and improve overall productivity.
Resource management extends beyond the production floor. Production Managers must also coordinate with procurement teams to ensure timely and cost-effective sourcing of raw materials. They collaborate with finance departments to manage budgets and allocate funds appropriately for production-related expenses.
Maintenance and equipment management
Proper maintenance and equipment management are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliable performance of machinery and equipment. Production Managers must establish a preventive maintenance program to schedule routine maintenance tasks and inspections.
Implementing preventive maintenance allows Production Managers to reduce the risk of unexpected breakdowns, production delays, and costly repairs. Well-maintained equipment also operates more efficiently, leading to higher productivity and lower energy consumption.
Equipment management involves tracking the performance and maintenance history of machinery. This data helps in identifying equipment that requires replacement, ensuring that production adheres to quality standards. Production Managers must prioritise employee training in equipment operation and maintenance. Skilled and knowledgeable employees can detect potential issues early on, contributing to smoother operations and equipment effectiveness.
Production scheduling
Production scheduling can be considered a detailed plan creation process, which is later for executing production tasks in a systematic and time-efficient manner. It involves determining the sequence of operations, allocating resources, and setting realistic timelines for each production activity. Effective production scheduling optimises production flow and reduces production cycle times. This enables organisations to meet customer demand with shorter lead times, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Production Managers use various scheduling techniques, such as Gantt charts, Critical Path Method (CPM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. These tools help them visualise and manage production schedules effectively. These tools help in identifying potential bottlenecks and secure resource allocation to meet production deadlines.
Production scheduling should also consider factors like machine maintenance and setup times. Carefully planning maintenance activities and reducing setup times will help Production Managers maximise machine availability and overall production efficiency.
Supply chain management
Production Management is closely intertwined with supply chain management. Production Managers need to maintain effective communication and collaboration with suppliers and logistics partners to ensure a smooth flow of materials and timely delivery of finished goods.
Strong supplier relationships can lead to favourable terms, reliable material deliveries, and reduced procurement lead times. Production Managers must regularly assess supplier performance and identify future risks in the supply chain to mitigate disruptions.
Additionally, implementing just-in-time (JIT) or vendor-managed inventory (VMI) arrangements with suppliers can reduce inventory carrying costs and optimise material flows. Collaborating with suppliers to streamline supply chain processes can lead to greater efficiency and improved overall supply chain performance.
Production Managers must also monitor the entire supply chain for potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Identifying these weak points allows for corrective actions and an option to explore alternative supply chain strategies to enhance resilience and responsiveness.
Want to learn the distribution process? Try our Supply Chain Management Training today!
Continuous improvement
Continuous improvement is a fundamental aspect of successful Production Management. Production Managers must foster a culture of innovation and learning within the organisation to encourage employees to contribute improvement ideas actively. Lean manufacturing and Six Sigma methodologies are commonly used to drive continuous improvement in production processes.
Regular performance reviews and data analysis help Production Managers identify improvement areas. Encouraging employee involvement in improvement initiatives through suggestion programs or Kaizen events can boost employee engagement. Benchmarking against industry leaders or best practices can also inspire Production Managers to strive for excellence and identify areas where the organisation can achieve a competitive advantage.
Conclusion
This blog on various Functions of Production Management underscores the symbiotic relationship between foundational basics and advanced nuances in Production Management. Together, they form a cohesive strategy, ensuring businesses remain stable yet agile. For any enterprise aiming to thrive, mastering both these functions is not just advisable but imperative, paving the way for sustainable success in the dynamic world of production.
Interested in learning about the management of facilities? Try our Facilities Management Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Product Management Training
Product Management Training
Fri 27th Dec 2024
Fri 21st Feb 2025
Fri 25th Apr 2025
Fri 20th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 31st Oct 2025
Fri 19th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


