We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

The role of a Penetration Tester has become very crucial in safeguarding sensitive information and fortifying Cybersecurity defences. As organisations grapple with the escalating threat of cyberattacks, the demand for skilled professionals who can ethically breach systems to uncover vulnerabilities is on the rise. So, if you want to become one, you need to know "How to Become a Penetration Tester?"
According to Indeed, the salary of a Penetration Tester is around £56,872/yr. Hence, to become a Penetration Tester, there are several pointers that you need to keep in mind. In this blog, you are going to learn in detail "How to Become a Penetration Tester?" the skills, educational background and exposure that you require. Read on ahead to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) Who is a Penetration Tester?
2) Requirements to become a Penetration Tester
3) What does a penetration tester do?
4) How much do penetration testers make?
5) Job roles and career pathways
6) Conclusion
Who is a Penetration Tester?
A Penetration Tester, commonly known as an Ethical Hacker, is a proficient Cybersecurity professional assigned to detect the vulnerabilities of computer systems, networks, and applications. Their core mission involves simulating potential cyberattacks, employing tactics akin to malicious hackers but with an ethical purpose. Through intentional probing for weaknesses, they unveil security flaws before malevolent actors can exploit them.
In Information Data Security, Penetration Testers, acting like private detectives, pre-emptively uncover vulnerabilities before criminal hackers capitalise on them. Job titles include Vulnerability Analysts, Information Security Analysts, Cloud Security Engineers, and Security Analysts. Engaged in an ongoing arms race with hackers, Penetration Testers utilise offensive defence, mirroring real attackers to identify and rectify vulnerabilities proactively in network devices, operating systems, and applications.
This strategic approach enhances information security by strengthening systems against potential cyber threats, fortifying resilience, and refining security controls. The perpetual dynamic between Ethical Hackers and malicious actors emphasises the continuous evolution of Cybersecurity measures.

Penetration Testers ensure organisations rectify vulnerabilities, bolster their defences, and safeguard sensitive data from potential breaches. These professionals possess a distinctive blend of technical understanding, strategic prowess, and ethical responsibility. Serving as digital guardians, they play a critical role in the Cybersecurity ecosystem, helping organisations stay ahead of cyber threats in an interconnected world.
Enhance your knowledge of Ethical hacking with our Ethical Hacking Training.
Requirements to become a Penetration Tester
In this section, you will learn "How to Become a Penetration Tester?" The following points will help you:
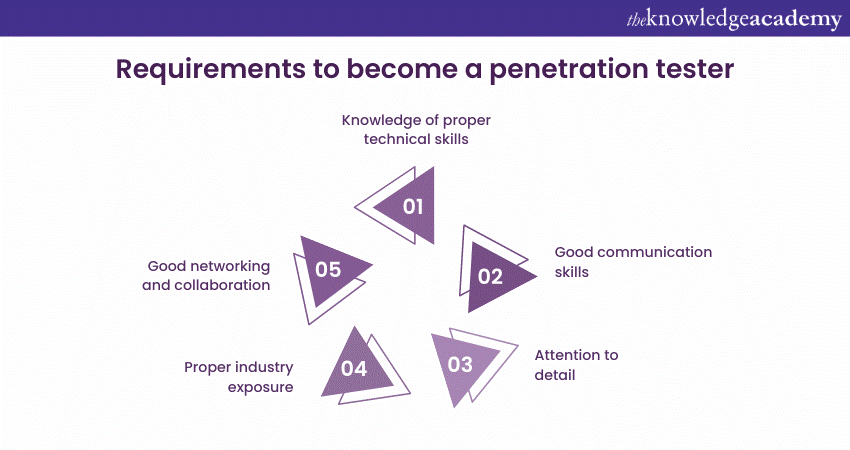
Skills required for a Penetration Tester
Becoming a proficient Penetration Tester requires a diverse skill set that spans technical expertise, problem-solving finesse, and ethical awareness. These skills form the basis for a successful Ethical Hacking and Cybersecurity.
1) Technical skills: As Penetration Testers, you must possess a comprehensive range of technical skills and knowledge of penetration testing tools to identify vulnerabilities and simulate cyberattacks effectively. These skills include:
a) Networking know-how: A deep understanding of networking protocols, subnetting, and routing is essential for analysing and exploiting network vulnerabilities.
b) Programming proficiency: Proficiency in languages like Python, Java, C/C++, or scripting languages is invaluable for crafting custom tools and scripts that facilitate vulnerability assessment and exploitation.
c) Knowledge of operating systems: A solid grasp of operating systems, particularly Linux and Windows, is essential for assessing vulnerabilities across diverse platforms.
d) Web application expertise: Familiarity with web development languages like Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), and JavaScript. You should also be familiar with database systems because they are crucial for identifying web application security gaps.
e) Cybersecurity toolset: Proficiency in using tools like Nmap, Wireshark, Metasploit, and vulnerability scanners is crucial for conducting penetration tests and analysing results.
2) Soft skills: Beyond technical acumen, Penetration Testers must possess a range of soft skills to excel in their roles:
a) Problem-solving: The ability to analyse complex systems, uncover hidden vulnerabilities, and devise innovative attack scenarios requires strong problem-solving skills.
b) Attention to detail: Identifying subtle security flaws demands meticulous attention to detail, as small oversights can have significant consequences.
c) Communication: Effective communication skills are vital for articulating discoveries and recommendations clearly to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
d) Ethical mindset: Penetration Testers must possess a strong ethical foundation. You should also have an understanding of the importance of responsible hacking and respecting boundaries.
e) Adaptability: Adaptability is crucial for staying current with emerging threats and technologies.
f) Collaboration and teamwork: Penetration Testing often involves collaborating with diverse teams, including developers, IT professionals, and management. Working collaboratively and sharing insights contributes to more effective security outcomes.
g) Adaptability and resilience: Penetration Testers must adapt to new tools, attack vectors, and defence mechanisms while maintaining resilience in the face of evolving threats.
Unlock your potential as an Ethical Hacker with our Ethical Hacking Professional Course .
Educational background and training
To become a proficient Penetration Tester, you need to have both a relevant educational background and specialised training. While a formal degree isn't always a strict requirement, a solid academic foundation combined with targeted training helps you with the necessary knowledge and skills to excel in ethical hacking.
1) Computer Science or IT Degree:
If you have a degree in Computer Science, Information Technology (IT), or a related field, it provides a strong academic grounding for a career in Penetration Testing. These programs offer comprehensive coursework that covers programming, networking, operating systems, and Cybersecurity essentials. A Computer Science Degree enhances technical proficiency and offers a deep understanding of the systems and networks that Penetration Testers assess.
2) Cybersecurity certifications:
Complementing formal education with Cybersecurity certifications is a strategic step toward bolstering credibility and expertise:
a) Ethical Hacking Training: This certification focuses on Ethical Hacking techniques, tools, and methodologies. It covers areas such as network scanning, malware analysis, and social engineering.
b) CompTIA Security+: This certification provides a broader understanding of Cybersecurity principles, covering topics like network security, cryptography, and access control. It's an excellent starting point for those new to the field.
c) Online courses and workshops:
Numerous online platforms offer specialised courses and workshops dedicated to Penetration Testing. These courses provide hands-on training in various aspects of Ethical Hacking, ranging from Network Penetration Testing to web application security.
Gaining practical experience
Practical experience allows you to apply theoretical concepts, refine skills, and develop the problem-solving mindset required to navigate the complex landscape of Cybersecurity challenges.
1) Ethical Hacking labs and challenges: Online platforms have emerged as havens for Ethical hacking enthusiasts to practice their skills in simulated environments:
a) Hack The Box: This platform offers a range of virtual machines with varying levels of difficulty. You must exploit vulnerabilities, escalate privileges, and retrieve flags to progress. The platform provides an immersive experience, enabling testers to explore diverse attack vectors.
b) TryHackMe: With its user-friendly approach, TryHackMe offers guided paths for beginners and challenging rooms for more experienced testers. Each room provides a unique scenario and objectives, allowing you to apply techniques learned in a controlled setting.
c) OverTheWire: Focused on building fundamental skills, OverTheWire offers a series of progressively challenging wargames. These challenges teach essential concepts like Linux command-line usage, scripting, and network analysis.
2) Personal projects and bug bounty programs: Engaging in personal projects and participating in bug bounty programs are ways to gain real-world experience while contributing to the security community:
a) Personal projects: Creating vulnerable applications, networks, or systems allows you to apply their knowledge in practical scenarios. By understanding how to exploit their creations, you can gain insights into potential vulnerabilities and defence strategies.
b) Bug bounty programs: Many organisations offer bug bounty programs, rewarding individuals for responsibly disclosing security vulnerabilities. Participating in these programs gives you the chance to test your skills on live applications, which are often used by millions of users.
3) Creating a portfolio: Documenting the results of practical experience through a well-curated portfolio is essential. A portfolio showcases hands-on projects, completed challenges, and successful bug bounty reports. It provides evidence of practical skills and demonstrates a commitment to continuous learning.
4) Networking and collaboration: Engaging with the cybersecurity community through forums, online communities, and conferences fosters collaboration, knowledge sharing, and exposure to various perspectives. Networking not only facilitates learning but also offers opportunities for mentorship and potential job referrals.
5) Challenges and growth: Practical experience is not without its challenges. Aspiring Penetration Testers like you may encounter frustration, failures, and moments of uncertainty. However, each challenge serves as a steppingstone to growth. The process of overcoming obstacles in practical scenarios enhances problem-solving skills, builds resilience, and cultivates the adaptability required in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity.
What does a Penetration Tester do?
Penetration Testers play a proactive and offensive role in Cybersecurity, conducting attacks on a company's digital systems to identify vulnerabilities. They use various hacking tools and techniques to uncover potential gaps that malicious hackers could exploit. Throughout this process, actions are meticulously documented, and a comprehensive report is generated detailing the methods employed and the success in breaching security protocols.
Some of their key tasks and responsibilities include the following:
a) Perform testing: Conduct tests on applications, network devices, and cloud infrastructures to assess their vulnerability.
b) Simulate social engineering attacks: Design and execute simulated social engineering attacks to evaluate an organisation's susceptibility.
c) Research and experiment: Explore different attack types through study and experimentation, staying abreast of emerging threats.
d) Develop testing methodologies: Create methodologies for Penetration Testing tailored to the organisation's needs.
e) Review code: Examine code for security vulnerabilities, identifying and addressing potential weaknesses.
f) Reverse engineer malware: Analyse and reverse engineer malware or spam to understand their workings and implications.
g) Document issues: Thoroughly document security and compliance issues encountered during testing.
h) Automation: Implement automation for standard testing techniques, enhancing efficiency in the testing process.
i) Report writing: Prepare both technical and executive reports outlining findings and recommendations.
j) Communication: Effectively communicate findings to technical staff and executive leadership, facilitating informed decision-making.
k) Security validation: Validate security improvements through additional testing, ensuring the effectiveness of implemented measures.
How much do Penetration Testers make?
While Penetration Testers are paid well generally, their actual pay scale is dependent on several factors such as job location, years of experience, skills acquired etc. Here is a succinct table illustrating their salaries in 7 major job markets:
|
Country |
Average salary per year |
|
USA |
$105,000 USD |
|
UK |
£72,727 GBP |
|
Canada |
$131,250 CAD |
|
UAE |
329,250 AED |
|
India |
3,649,350 INR |
|
Singapore |
$99,450 SGD |
|
Australia |
$144,000 AUD |
Source: Salary.com
Job roles and career pathways
Now that you know what it takes to become a Penetration Tester, let's look at some career opportunities:
Junior Penetration Tester
The role of a Junior Penetration Tester marks the entry point into the dynamic world of Ethical Hacking. This pivotal role is an apprenticeship of sorts, where aspiring ethical hackers gain hands-on experience, learn from seasoned professionals, and contribute to the vital task of securing digital landscapes.
a) In this role, individuals assist in conducting penetration tests, vulnerability assessments, and security audits. They learn to use Cybersecurity tools, analyse results, and contribute to reports that communicate findings and recommendations.
b) Junior testers refine their technical skills, from network scanning to identifying vulnerabilities in web applications. Each assessment offers a chance to develop proficiency in exploiting weaknesses, enhancing programming skills, and understanding various operating systems.
c) Working alongside experienced Penetration Testers provides invaluable mentorship. Junior Testers gain insights into strategic decision-making, client communication, and best practices in Ethical Hacking. This guidance helps shape their ethical hacking philosophy and professionalism.
d) A Junior Penetration Tester role serves as a foundation for future growth. The exposure to various systems, tools, and attack vectors lays the groundwork for advancing to more complex penetration tests and taking on greater responsibilities.
e) Junior Testers learn the ethical considerations integral to ethical hacking. They understand the importance of maintaining to legal boundaries, obtaining proper authorisation, and ensuring responsible disclosure of vulnerabilities.
Senior Penetration Tester
A Senior Penetration Tester occupies a pivotal position in Ethical Hacking. This role has a lot of experience and expertise that contributes to the resilience of digital ecosystems. With a refined skillset and a profound understanding of Cybersecurity nuances, Senior Testers undertake intricate assessments, offer strategic insights, and mentor junior team members.
a) Senior Penetration Testers step into leadership roles, guiding the direction of assessments, coordinating teams, and providing high-level strategic recommendations. Their experience allows them to identify potential blind spots, prioritise vulnerabilities, and tailor assessments to meet specific organisational needs.
b) Senior Testers engage in complex assessments that require a deeper understanding of systems, applications, and network environments. They craft multifaceted attack scenarios, uncover subtle vulnerabilities, and simulate advanced cyber threats to evaluate an organisation's preparedness.
c) Sharing insights with Junior Testers and less-experienced colleagues is a hallmark of seniority. By mentoring, they contribute to the growth of the ethical hacking community, ensuring the next generation is well-equipped to safeguard digital landscapes.
d) Beyond executing assessments, senior testers often serve as advisors to organisations. They help formulate comprehensive Cybersecurity strategies, guide risk management decisions, and assist in creating resilient defence mechanisms.
e) Senior Penetration Testers stay updated with emerging threats, attack techniques, and defence strategies, positioning themselves as industry thought leaders.
Penetration Testing Consultant
A Penetration Testing Consultant represents the pinnacle of Ethical Hacking expertise, combining years of experience with the ability to provide strategic guidance to organisations seeking to enhance their Cybersecurity posture. As a trusted advisor, the consultant offers specialised insights, tailored solutions, and visionary leadership to safeguard digital assets against evolving threats.
a) Penetration Testing Consultants offer strategic counsel that extends beyond assessments. They collaborate closely with organisations to develop comprehensive Cybersecurity strategies, aligning technical assessments with broader business goals.
b) Consultants tailor their approach to each organisation's unique needs. They design customised assessments that address specific vulnerabilities and recommend targeted solutions to mitigate risks effectively.
c) Effective communication is key for Consultants. They translate complex technical insights into actionable recommendations that resonate with stakeholders, from technical teams to C-suite executives.
d) Consultants stay at the forefront of the Cybersecurity landscape, continuously learning about emerging threats, attack methodologies, and cutting-edge defence strategies. Their insights influence industry trends and practices.
e) Organisations with intricate IT infrastructures benefit from consultants who can navigate complexities while conducting assessments. Consultants unravel intricate networks, intricate systems, and diverse applications to uncover vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
In this intricate world of Ethical Hacking, you came to know How to Become a Penetration Tester. From foundational education and practical experience to strategic growth, you are now equipped to safeguard digital realms, armed with expertise, ethics, and a commitment to Cybersecurity
excellence.Elevate your Cybersecurity skills with our Mastering Metasploit Framework Course.
Frequently Asked Questions

To be a Penetration Tester, a bachelor's degree in Cybersecurity or related field is beneficial. Certifications like Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP), and experience in networking, programming, and security tools are crucial. Strong analytical skills and Ethical Hacking knowledge are essential qualifications.

To become a Penetration Tester, acquire a strong foundation in networking, programming, and cybersecurity. Gain hands-on experience with hacking tools and techniques. Pursue relevant certifications like CEH or OSCP. Engage in real-world scenarios through labs, and Ethical Hacking courses. Stay updated on the latest security trends and continuously enhance your skills.

Becoming a Penetration Tester typically takes 2-4 years. This involves obtaining a relevant bachelor's degree or equivalent certifications, gaining hands-on experience in Cybersecurity, and continually updating skills. Factors such as prior knowledge and the complexity of expertise desired can influence the timeframe.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Automation & Penetration Testing Courses, including Tools and Techniques for Penetrating Testing, Fundamentals of Test Automation etc. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Cyber Security Skills.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to the Fundamentals of Test Automation, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Fundamentals of Test Automation
Fundamentals of Test Automation
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 3rd Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


