We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Be it for protecting children, vulnerable adults, or sensitive information, the Importance of Safeguarding cannot be overstated. But have you ever wondered what steps are necessary to ensure everyone’s safety? Or how safeguarding impacts your daily lives? This comprehensive blog will delve into its significance, highlighting key practices and principles that everyone should be aware of.
From comprehending the basics to implementing effective strategies, this blog will provide you with the knowledge to make a difference. Let’s dive in and uncover the vital Importance of Safeguarding our communities.
Table of Contents
1) What is Safeguarding?
2) The Importance of Safeguarding
3) Principles of Safeguarding
4) Different Types of Abuse and Neglect
5) Distinguishing Safeguarding for Adults and Children
6) What is a Safeguarding Policy?
7) Conclusion
What is Safeguarding?
Safeguarding involves measures to protect the well-being, safety, and rights of vulnerable individuals, including at-risk children, young people, and adults. It aims to prevent abuse, neglect, harm, and exploitation through proactive strategies, support, and safe environments. Central to safeguarding is recognising individual rights and dignity, promoting openness and transparency, and encouraging community and organisational participation. It goes beyond protection, fostering trust and resilience to ensure everyone can live free from abuse or harm.
The Importance of Safeguarding
Safeguarding is crucial in ensuring the well-being and safety of vulnerable individuals, including at-risk children, young people, and adults. By recognising and addressing potential risks, safeguarding creates environments where individuals can thrive without fear. Here are some key reasons why safeguarding is important:
a) Protects Vulnerable Individuals: Ensures the safety and well-being of at-risk children, young people, and adults.
b) Prevents Abuse and Neglect: Implements proactive strategies to stop harm before it occurs.
c) Promotes Individual Rights: Upholds the dignity and rights of every person, regardless of age or vulnerability.
d) Fosters Safe Environments: Creates spaces where individuals can thrive without fear of abuse or harm.
e) Encourages Community Participation: Involves the community and organisations in safeguarding efforts.
f) Builds Trust and Resilience: Nurtures a culture of openness, transparency, and trust, helping individuals build resilience.
g) Supports Overall Well-being: Goes beyond protection to ensure a holistic approach to the well-being of vulnerable individuals.
Principles of Safeguarding
The Principles of Safeguarding form the foundation for creating a protective environment for vulnerable individuals. These principles emphasise the commitment to ensuring the safety, well-being, and rights of at-risk children and adults. Key aspects include:
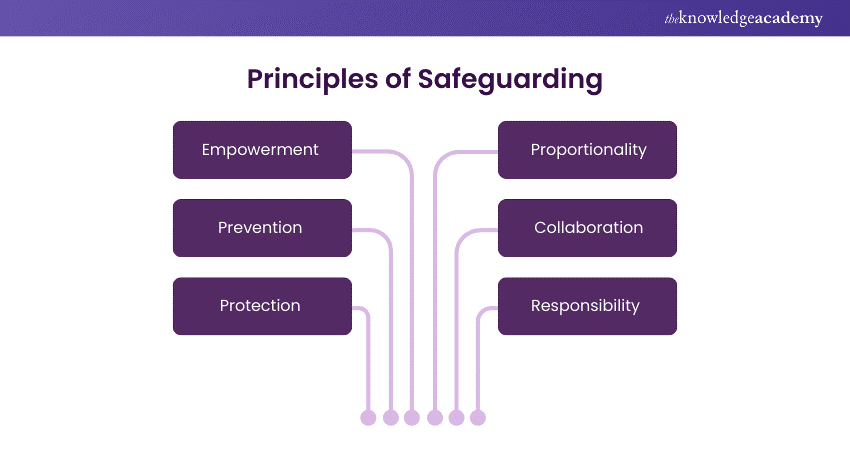
These principles guide professionals and organisations in preventing abuse, recognising signs of vulnerability, and responding effectively. By adhering to these principles, Safeguarding becomes a holistic and proactive endeavour, fostering a culture prioritising the protection and dignity of those at risk of harm or exploitation.
Enhance your safeguarding expertise with our comprehensive Safeguarding Officer Training — safeguarding the vulnerable, one step at a time.
Different Types of Abuse and Neglect
Comprehending the various forms of abuse and neglect is crucial for effective safeguarding. Here are some key types of abuse and neglect:
a) Physical Abuse: Inflicting physical harm or injury through actions like hitting, shaking, or burning.
b) Emotional Abuse: Causing psychological harm through verbal abuse, threats, humiliation, or isolation.
c) Sexual Abuse: Involving a person in sexual activities without their consent, including exploitation and harassment.
d) Neglect: Failing to provide necessary care, supervision, or protection, resulting in harm or risk of harm.
e) Financial Abuse: Exploiting or misusing a person’s financial resources without their consent.
f) Institutional Abuse: Poor care practices within an institution, leading to neglect or abuse of individuals.
g) Self-neglect: When an individual fails to care for their own basic needs, leading to harm or risk of harm.
Discriminatory Abuse: Harassment or unfair treatment based on characteristics such as race, gender, disability, or age.
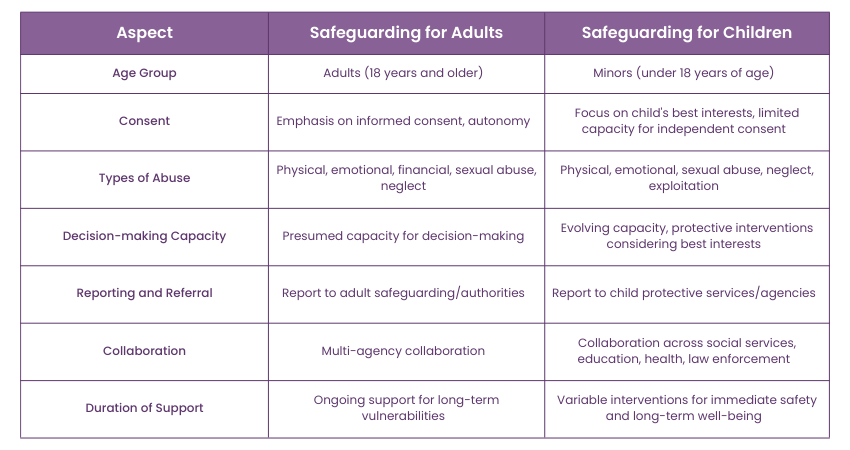
Distinguishing Safeguarding for Adults and Children
Safeguarding practices differ significantly between adults and children due to their distinct needs and vulnerabilities. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effectively implementing safeguarding measures tailored to the specific needs of both groups:
What is a Safeguarding Policy?
A Safeguarding policy is a comprehensive document that outlines an organisation's commitment, procedures, and responsibilities in ensuring the well-being and safety of vulnerable individuals, including children, young people, and adults at risk. This policy is a proactive framework to prevent and respond to potential risks, abuse, or harm within the organisation's activities or environments.
The key elements of a Safeguarding policy typically include:
a) Statement of Commitment: Articulates the organisation's dedication to fostering a secure environment for all involved individuals.
b) Definition of Terms: Defines key terms related to Safeguarding and ensuring a shared understanding among staff, volunteers, and stakeholders.
c) Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly outlines the roles and responsibilities of staff, volunteers, and other stakeholders in Safeguarding individuals. This includes the appointment of a designated Safeguarding officer or team.
d) Reporting Procedures: Establishes a clear and confidential reporting mechanism for concerns or incidents of abuse or harm, ensuring that information is appropriately handled and escalated when necessary.
e) Preventive Measures: Outlines preventive measures and best practices to minimise the risk of abuse, such as staff training, background checks, and risk assessments.
f) Response and Support: Details the procedures for responding to concerns or incidents, including supporting victims and reporting to relevant authorities.
g) Review and Monitoring: Specifies the regular review and updating of the Safeguarding policy to align with legal requirements, best practices, and organisational changes.
Empower your employees with the essential safety skills – sign up for our Health and Safety In The Workplace Training now!
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Importance of Safeguarding cannot be overstated; since it’s a commitment to protecting our most vulnerable state. By understanding its significance and implementing robust measures, you can create safer environments for everyone. Let’s champion safeguarding and make a difference, one step at a time.
Transform lives and elevate your career with our comprehensive Life Coach Training – join us now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Everyone interacting with vulnerable individuals, including professionals in education, healthcare, social services, and community work, must be aware of safeguarding practices. This includes teachers, care workers, volunteers, and managers, ensuring they can recognise signs of harm, follow protocols, and promote a safe environment.

The legal framework on safeguarding in the UK involves the Children Act 1989, the Care Act 2014, and the Safeguarding Vulnerable Groups Act 2006. These laws define responsibilities, establish guidelines, and ensure organisations implement protective measures to prevent abuse and neglect of children and vulnerable adults.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Healthy Lifestyles Trainings, including the Life Coach Training, Meditation Course, and Yoga Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Psychological Safety in the Workplace.
Our Health & Safety Blogs cover a range of topics related to Safeguarding, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Health and Safety knowledge, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Safeguarding Officer Training
Safeguarding Officer Training
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


