We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Grasping the difference between Innovation vs Invention is vital today. Invention creates new products, processes, or ideas, while innovation improves or transforms existing ones. Both drive progress, with inventions laying the groundwork and innovations enhancing these foundations.
The impact of Innovation vs Invention is significant. Inventions expand human knowledge and capabilities, while innovations adapt these concepts to meet market needs. Understanding their interplay reveals their crucial roles in technological advancement and economic growth.
Table of Contents
1) What is an Invention
2) Characteristics of Invention
3) What is Innovation
4) Characteristics of Innovation
5) Innovation vs Invention
6) Innovation and Invention Examples That Shaped the Modern World
7) Conclusion
What is an Invention?
Invention is the act of creating a new product or introducing a process for the first time. The potential for innovation lies in the conception of an idea. The invention tackles a particular issue by incorporating technology, using its technical features to achieve a practical goal.
The ability to obtain a patent for an invention is based on its technical nature, requiring the use of scientific principles to achieve the intended result. Innovation is commonly described as a "lesson for practical application."
Characteristics of Invention
Inventions are important because they advance human knowledge and capabilities. They solve problems, improve existing solutions, or create new opportunities. Inventions can significantly impact various aspects of society, such as culture, economy, environment, health, education, and security.
Inventions possess unique traits that distinguish them as novel and creative solutions to existing problems. Here are some key characteristics of inventions:
a) Originality: An invention is entirely new, introducing a concept, product, or process that did not previously exist, setting it apart from existing ideas.
b) Novelty: Inventions provide a fresh perspective or solution to a problem, addressing needs in innovative ways.
c) Creativity and Ingenuity: Inventions stem from creative thinking and the resourceful application of existing scientific knowledge and ideas.
d) Problem-Solving: Inventors aim to tackle specific challenges or meet needs in society, industry, or daily life.
e) Resourcefulness: Inventors often work with limited resources, finding innovative ways to bring their vision to life.
f) Utility and Functionality: An invention must serve a purpose and offer tangible benefits or fulfill a need.
g) Potential for Impact: Successful inventions have the potential to make significant contributions to society, industries, or fields.
h) Legal Protection: Inventions can be protected through patents, granting exclusive rights to the inventor for a defined period.
What is Innovation?
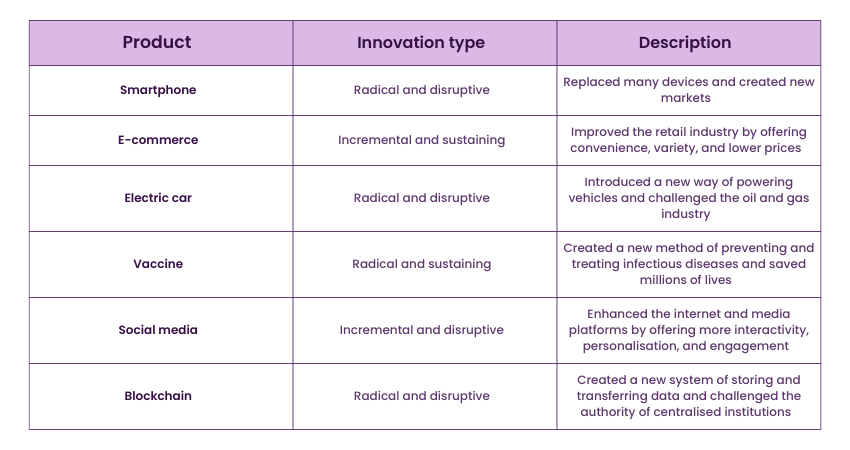
An Innovation means the implementation of a new or enhanced product, procedure, or concept that provides benefits to customers, users, or society. It is the outcome of inventive ideas, trial and error, or adjustment. An Innovation can either be incremental, enhancing an existing solution, or radical, establishing a new solution.
Innovation can either be disruptive, causing changes to the market or industry, or sustaining, ensuring the market or industry remains consistent. Innovations can be monetised, leading to financial gains or societal impact by tackling social or environmental challenges.
Characteristics of Innovations
Innovation possesses distinct qualities that underscore its dynamic nature and its capacity to drive progress across various domains. Here are the key attributes:
a) Adaptability: Innovations are flexible, capable of adjusting to evolving circumstances, technologies, and markets, ensuring ongoing relevance.
b) Scalability: They can be expanded or scaled down to meet different needs and reach wider audiences.
c) Sustainability: Designed to endure, innovative solutions maintain their relevance over time, economically, socially, and environmentally.
d) Efficiency: Innovations aim to optimise processes, minimise waste, and maximise resource utilisation, leading to higher productivity.
e) User-Centricity: They focus on the needs and experiences of end-users, effectively addressing real-world challenges.
f) Risk-Taking and Experimentation: Innovation involves embracing risks and experimenting with new approaches, acknowledging that not every idea will succeed.
g) Collaboration and Diversity: Successful innovation thrives in environments that promote teamwork and value diverse perspectives, resulting in more creative solutions.
h) Continuous Improvement: Innovation is an ongoing process of refinement and enhancement, ensuring solutions remain competitive and effective.
i) Regulatory and Ethical Considerations: Innovative offerings must adhere to regulations and ethical standards to ensure safety, responsibility, and trust.
j) Market Awareness: Developed with an understanding of market demands, trends, and customer preferences, innovations ensure relevance and provide a competitive edge.
Empower your Leadership journey: Join our Leadership Skills Training today!
Innovation vs Invention
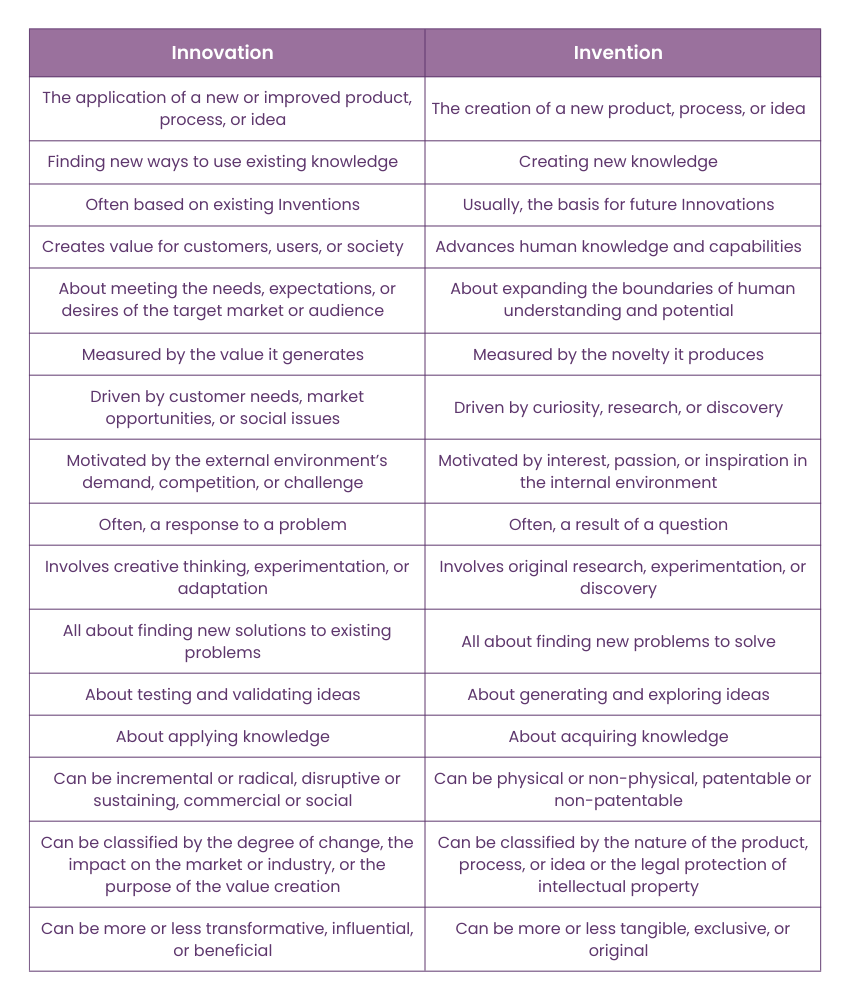
Innovation and Invention are essential for human progress but have different meanings and implications. Here are some of the main differences between them:
a) Definition and Basis:
Innovation: Application of a new or improved product, process, or idea. It involves finding new ways to use existing knowledge and is often based on existing inventions.
Invention: Creation of a new product, process, or idea. It generates new knowledge and often serves as the foundation for future innovations.
b) Value and Measurement:
Innovation: Creates value for customers, users, or society by meeting their needs, expectations, or desires. It is measured by the value it generates.
Invention: Advances human knowledge and capabilities by expanding the boundaries of understanding and potential. It is measured by the novelty it produces.
c) Drivers and Motivation:
Innovation: Driven by customer needs, market opportunities, or social issues. Motivated by external demands, competition, or challenges, and often a response to a problem.
Invention: Driven by curiosity, research, or discovery. Motivated by internal interest, passion, or inspiration, and often a result of a question.
d) Process and Approach:
Innovation: Involves creative thinking, experimentation, or adaptation. Focuses on finding new solutions to existing problems, testing and validating ideas, and applying knowledge.
Invention: Involves original research, experimentation, or discovery. Focuses on finding new problems to solve, generating and exploring ideas, and acquiring knowledge.
e) Types and Classification:
Innovation: Can be incremental or radical, disruptive or sustaining, commercial or social. Classified by the degree of change, market or industry impact, or value creation purpose, these different approaches represent various types of Innovation. It can be more or less transformative, influential, or beneficial.
Invention: Can be physical or non-physical, patentable or non-patentable. Classified by the nature of the product, process, or idea, or intellectual property protection. It can be more or less tangible, exclusive, or original.
Transform ideas into impact: Join our Managing Innovation Training now!
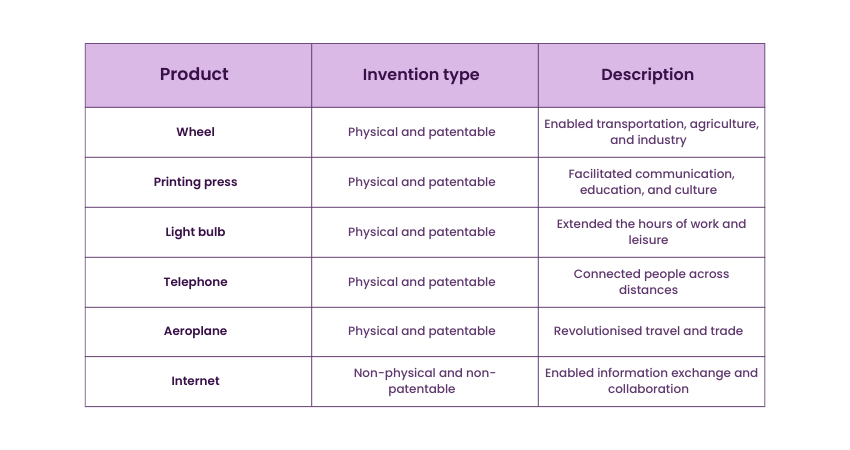
Innovation and Invention Examples that Shaped the Modern World
1) Microprocessor
a) Invention: The microprocessor, developed by Intel’s Ted Hoff and Federico Faggin, is a small electronic device that acts as the brain of a computer.
b) Innovation: The innovation lies in the continuous development and evolution of microprocessors, which have enabled the creation of numerous electronic devices, advancements in computing power, and the foundation of the digital age.
2) Light Bulb
a) Invention: Thomas Edison’s creation of a practical and commercially viable electric light bulb revolutionised indoor lighting.
b) Innovation: The innovation emerged through the widespread adoption and application of light bulbs, leading to the electrification of cities, the establishment of lighting industries, and advancements in lighting technology.
Conclusion
Innovation and Invention are frequently used interchangeably, but they carry distinct interpretations and consequences. Business Model Innovation is a form of innovation that focuses on redefining how a business creates, delivers, and captures value. Innovation is the implementation of a novel or enhanced product, procedure, or concept that provides benefits for consumers, individuals, or the community. Innovation involves developing a novel product, procedure, or concept that has not been previously created.
Lead with Confidence: Discover Our Leadership Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Innovation always better than Invention?

Innovation and Invention are both important and valuable, but they have different purposes and outcomes. Innovation is better when the goal is to create value for customers, users, or society, while Invention is better when the goal is to advance human knowledge and capabilities. Innovation and Invention can also complement each other, as Inventions can inspire Innovations and enable Inventions.
How can I become more innovative or inventive

This question has no definitive answer, as Innovation and Invention depend on various factors, such as personality, skills, motivation, environment, and resources. Be curious and open-minded and seek new knowledge and experiences and Identify problems, needs, or opportunities and generate ideas or solutions.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Leadership Training, including Social Innovation Courses, Innovation courses, etc. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights about Innovation in the Innovation Course.
Dive into our Business skills blogs, a trove of resources covering Leadership training. Whether you are a beginner or aiming to enhance your Leadership Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and insightful blogs are your go-to source.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Managing Innovation
Managing Innovation
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


