We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Picture walking into your office only to discover that a critical server room has been compromised due to a small oversight in physical security. How would this affect your business operations? This scenario underscores the importance of ISO 27001’s Annex A.11. The International Standardization for Organization (ISO) 27001 highlights the necessity of physical and environmental security to safeguard your organisation’s assets from unauthorised access.
By adhering to the Annex A.11’s guidelines, you can guarantee that your organisation is compliant with ISO 27001 and robust against potential physical threats. IBM Security’s 2022 Cost of a Data Breach Report found that 19% of information security breaches were due to stolen or compromised credentials. Given such a circumstance, let’s explore this blog to see how it can help you create a secure and resilient operational space.
Table of Contents
1) What is Annex A 11?
2) Objectives of Annex A 11
3) ISO 27001 Physical and Environmental Security: An Overview
4) Purpose and Importance of Physical and Environmental Security
5) List of ISO 27001 Controls Under Physical and Environmental Security
6) Conclusion
What is Annex A 11?
ISO 27001 Annex A.11, titled “Physical and Environmental Security,” is a crucial component of the ISO/IEC 27001 standard, which focuses on Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). This annex outlines the necessary controls to protect an organisation’s physical and environmental security. It encompasses strategies to safeguard information and information processing facilities from unauthorised access, damage, and disruption.
By adhering to Annex A.11, organisations can ensure their physical infrastructure is robust and resilient, thereby safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining operational continuity. This is crucial for achieving the ISO 27001 Certification; and reflects a commitment to comprehensive security management. The key components of the Annex A11 controls are:
a) Theft and Loss of Information
b) Assets and Equipment Damage
c) Continuity of Operation
d) Natural Threats
e) Intentional or Unintentional Threat
Objectives of Annex A 11
Annex A 11 is a part of the ISO 27001 standard, which specifically addresses the control objectives and related controls for Physical and Environment Security. Annex A 11 is further divided into two control standards: A.11.1 Secure Areas and A.11.2 Equipment, each focused on different objectives.
Objective of A.11.1 Secure Areas
The primary objective of this control is to establish and maintain Secure Areas within an organisation. It restricts unauthorised physical access and monitor Secure Areas to detect and respond to any unauthorised access.
Objective of A.11.2 Equipment
The Annex A.11.2 objective is to secure and protect the information processing equipment and assets from theft, damage, and unauthorised access. This control helps to measures the use of equipment, maintenance and disposal of equipment to safeguard sensitive information.
ISO 27001 Physical and Environmental Security: An Overview
People with malicious intent can access data and information even with the best firewalls and network security measures if the physical security is weak. Based on this understanding, ISO 27001 key features goes beyond the technical controls and details a framework to protect the physical aspects of information security.
ISO 27001 Physical and Environment Security provides Information Security Management guidelines that require Physical and Environmental Security. ISO 27001 requirements aims to safeguard an organisation’s information assets by ensuring the physical conditions
Become an Information Security Management expert by registering for our ISO 27001 Courses now!
Purpose and Importance of Physical and Environmental Security
Protecting an organisation’s information assets from Physical and Environmental threats is necessary. Natural disasters, theft, and malicious attacks are all potential sources of these threats. As a result, organisations must implement appropriate security measures to protect and secure their IT assets.
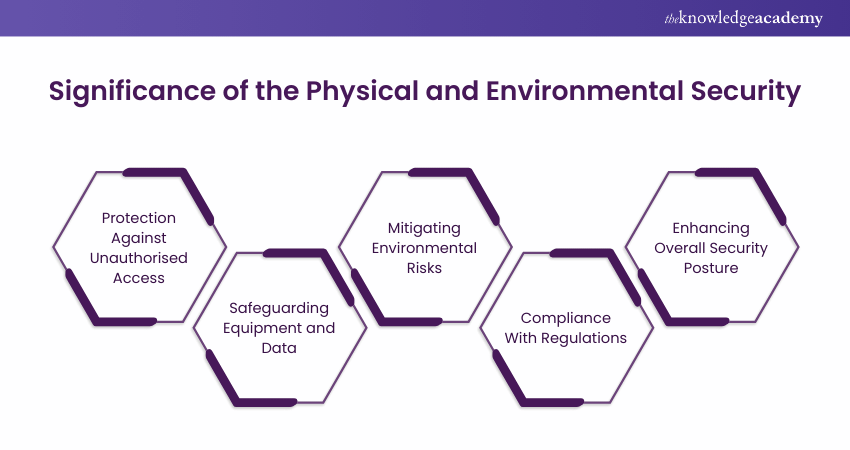
ISO 27001 Physical and Environmental Security aims to provide organisations with guidelines for protecting their information assets from Physical and Environmental threats. The ISO 27001 Controls detailed in Annex A.11 are designed to thwart unauthorised access to sensitive areas and equipment, as well as to alleviate the repercussions of environmental events that could potentially jeopardise the system's integrity, emphasising the significance of ISO 27001 controls.
List of ISO 27001 Controls Under Physical and Environmental Security
Annex A.11 is divided into two parts: Secure Area (A.11.1) and Equipment (A.11.2). These are two significant controls under which there are several other controls.
A.11.1 Secure Area details the guidelines to avoid unauthorised physical access to the organisation’s data storage or physical IT assets. A.11.2 Equipment details the guidelines to prevent asset loss, theft or damage that might interrupt business operations.
1) Secure Areas (Annex A11.1)
Annex A11.1 Secure Area control does not provide a one size fits all approach. To address different types of organisations and their specific risks and needs, the Annex A11.1 consists of six controls.
A.11.1.1 Physical Security Perimeter
This control discusses establishing a physical barrier to protect an asset from unauthorised access. The perimeter can be any physical barrier, like a fence or a wall. For ISO 27001 Physical Security to be effective, it needs to have the following elements:
a) A physical barrier
b) Intrusion detection system
c) Measures to control the access (gates, guards, ID)
d) Adequate lighting and surveillance cameras
A.11.1.2 Physical Entry Controls
This talks about restricting physical access to sensitive premises where only authorised personnel are allowed. This access restriction can be achieved with gates, fences, doors, etc. And can also be used in combination with measures like ID verification, locks, and guards.
A.11.1.3 Securing Offices, Rooms, and Facilities
This control states implementing robust and strict security measures in all the areas where assets are stored, processed, or utilised. The three most essential parts of this are:
a) Physical security (gates, locks, CCTV, etc.)
b) IT security (firewall, antivirus, etc.)
c) Environmental security (temperature, humidity, etc.)
A.11.1.4 Protecting Against External and Environmental Threats
According to this clause, critical assets should be protected against environmental and external threats from intruders, natural disasters, attackers, etc.
A.11.1.5 Working in a Secure Area
This control requires all working employees with access to critical information to be security-cleared and have the necessary security training. This control aims to prevent unauthorised access to any information, area, computer, or device.
A.11.1.6 Delivery and Loading Areas
Loading areas or where exchange (delivery) takes place is a crucial location that needs monitoring and securing. This control discusses securing such areas with adequate lighting, security cameras and posting guards.
Enhance your skills to safeguard your business data by registering for ISO 27001 Foundation Course!
2) Equipment (Annex A.11.2)
Under the Annex A.11.2 Equipment, there are nine controls to help organisation preventing and securing their risks and needs. These controls are as follows:
A.11.2.1 Equipment Siting and Protection
This control lays the guideline for site selection for equipment and the protection of existing equipment. When selecting a new site following things should be considered:
a) Physical threats like power outages, flooding, or any disaster
b) Risk of unauthorised access, theft, or interception
c) Risks to the safety of personnel from events like fire, explosion, electric shock, etc
d) Risk for pollution for other damage
A.11.2.2 Supporting Utilities
Organisations should only use those utilities that support effective management of information security. When selecting and implementing the supporting utilities, costs, impact on security, and benefits of ISO 27001 must be reviewed.
A.11.2.3 Cabling Security
Today, companies have become increasingly reliant on cabling systems to support their operations. However, since they are only a piece of hardware, the cabling infrastructure has security challenges. Organisations can use this standard to protect their cable infrastructure and develop an effective cabling security plan.
A.11.2.4 Equipment Maintenance
This control gives the organisation a guideline on equipment maintenance and ensures that all software and hardware are up to date.
A.11.2.5 Removal of Assets
When assets are at the end of their lifecycle, it is necessary to have a guideline in place to remove them from the system. This ISO 27001 framework ensures that information security is maintained while disposing of an equipment asset.
A.11.2.6 Security of Equipment and Assets off-premises
This control guides the organisation in securing the disposal of any equipment used to access, process or store crucial information. It also includes identifying equipment that needs to be reused or disposed of.
A.11.2.7 Secure Disposal or Reuse of Equipment
This control lays a guideline to develop security policies that deal with the handling of unattended user equipment. It ensures that equipment is physically secured or locked away safely to protect it from tampering.
A.11.2.8 Unattended User Equipment
This control lays a guideline to develop security policies that deal with the handling of unattended user equipment. It ensures that any such equipment is physically secured or locked away safely to protect it from potential tampering.
A.11.2.9 Clear Desk and Clear Screen Policy
This policy protects the organisation’s information accessed or used by employees at workstations. The following must be considered when laying clear desk and screen policy.
a) Level of protection required for the information
b) Workstation environment (cubicle, office, open area, etc.)
c) Implementing passwords, screensavers, etc.
Conclusion
By implementing these controls, organisations can reduce the risk of physical breaches and environmental events that might lead to financial losses or legal liability. Furthermore, ISO 27001 Compliance Annex A11: Physical and Environmental Security Policy shows the organisation’s commitment to best practices in information security.
Elevate your professional standing by signing up for our ISO 27001 Lead Implementer Course.
Frequently Asked Questions

The key components of a Physical and Environmental Security Policy include access control measures, surveillance systems, secure disposal of sensitive materials, protection against natural disasters, and controlled environmental factors like temperature and humidity. These steps ensure the safety of physical assets.

ISO 27001 aims to prevent physical security breaches such as unauthorised access to data centres, theft of equipment, tampering with security controls, and damage caused by environmental factors like fire or flooding.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 27001 Trainings, including the ISO 27001 Foundation Course, ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Course, and ISO 27001 Internal Auditor Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into ISO 22301 Clauses.
Our ISO & Compliance Blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO 27001 Standards, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Compliance skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 27001 Foundation
ISO 27001 Foundation
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 25th Aug 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


