We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Every business dream of thriving on unwavering quality and trust. But is there a surefire blueprint to ensure that? International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 9001 provides an answer. As the world's most recognised Quality Management standard, it offers a framework for organisations to deliver consistent, high-quality products and services. In this blog, we’ll unpack the key ISO 9001 Requirements in a way that’s easy to grasp, ensuring you are ready to turn quality aspirations into reality. So read on and unlock the secrets of delivering excellence, one requirement at a time!
Table of Contents
1) What are the Requirements for ISO 9001?
2) Structure of ISO 9001
3) What are the Six Mandatory Procedures for ISO 9001?
4) Is ISO 9001 a Regulatory Requirement?
5) Does ISO 9001 Require a Quality Manual?
6) Conclusion
What are the Requirements for ISO 9001?
ISO 9001 focuses on documenting processes and procedures rather than prescribing how to implement them. This flexible approach allows organisations to tailor their Quality Management System (QMS) to fit their specific operations while maintaining compliance.
While not all ISO 9001 documents are mandatory, maintaining comprehensive records enhances QMS effectiveness. Below are the key documentation requirements and how to address them:
1) Scope of the QMS
Define the boundaries and applicability of your QMS, detailing the products, services, and operations it covers. Specify which departments, processes, and locations fall under its scope.
2) Quality Policy
Establish a commitment to quality, outlining your organisation's objectives and dedication to continuous improvement. This policy should align with regulatory requirements and customer expectations.
3) Quality Objectives and Plans
Set specific, measurable goals that support quality improvement. Outline actionable plans, assign responsibilities, and allocate resources to achieve these objectives effectively.
4) Control of External Providers
Develop a process to evaluate, select, and monitor suppliers to ensure they meet quality standards. Document performance assessments and re-evaluation criteria to maintain supplier reliability.
5) Maintenance and Calibration Records
Track maintenance and calibration of equipment used in monitoring and measuring processes. These records should confirm compliance with industry standards and include details of approved calibration labs.
6) Competence Records
Maintain training and competency records of employees to ensure they have the necessary skills for their roles. Document any additional training required for quality management.
7) Product/Service Requirements & Reviews
Keep records of product and service requirements, including updates, customer feedback, purchase orders, and tender requests to ensure quality expectations are consistently met.
8) Design and Development Records
Document design inputs, outputs, controls, and modifications. Ensure all changes are evaluated and recorded to verify compliance with defined requirements.
9) Evaluation of External Providers
Regularly assess supplier performance, keeping records of evaluation criteria, audit results, and ongoing monitoring to ensure quality consistency.
10) Product/Service Characteristics
Maintain documentation of product specifications and service conditions to support quality control processes and regulatory compliance.
11) Customer Property Records
Record how customer property is handled, stored, and maintained, ensuring any damages or issues are documented. This demonstrates responsibility and care for third-party assets.
12) Production/Service Changes
Document any unplanned changes in production or service delivery, including their impact, corrective actions taken, and necessary approvals.
13) Product/Service Conformity Evidence
Provide proof that products and services meet specifications. Keep records of responsible personnel who authorise their release.
14) Nonconformity Records
Track instances of nonconformance, corrective actions taken, and how compliance was restored to prevent recurrence.
15) Performance Monitoring
ISO 9001 emphasises continuous improvement. Document monitoring procedures, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), and assessment results to ensure process control.
Build a strong foundation in quality management – join our ISO 9001 Foundation Course now!
16) Internal Audits
Conduct and document regular internal audits to evaluate QMS effectiveness. Record findings, issues, and opportunities for improvement.
17) Management Reviews
Senior leadership should review the QMS periodically to ensure ongoing effectiveness. Maintain records of review meetings, audit results, quality objectives, and progress reports.
Structure of ISO 9001
The ISO 9001 Plastic Injection Moulding Standard requires that your organisation address the 10 ISO 9001 clauses, which are designed to drive continual improvement within your Quality Management System (QMS). These clauses, supported by Quality Management principles, enable your business to implement an effective QMS. Let's explore them in detail:
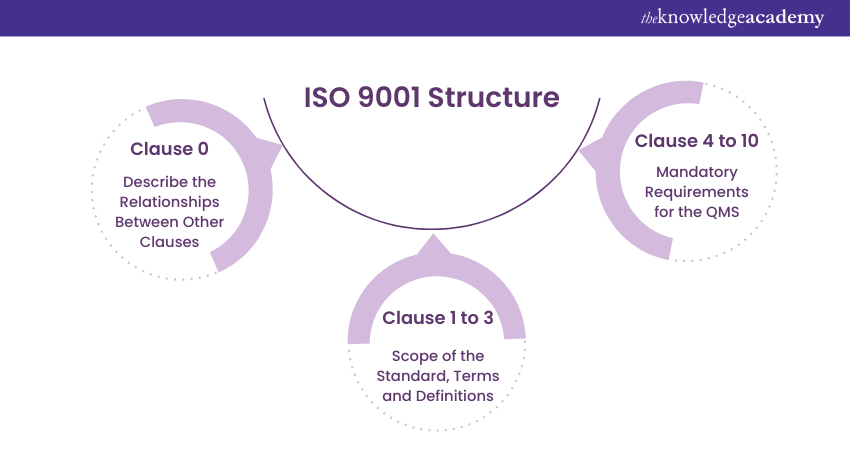
Clauses 0 – 3: Introduction, Scope, References, Terms and Definitions
Clauses numbered 0 to 3 of the ISO 9001 Standard offer foundational elements, setting the stage for the remaining ISO 9001 Requirements. While they are not mandatory for implementation, having a good grasp of them can help your organisation effectively use the standard. This is especially true when considering the differences between new, as understanding both can enhance your ability to leverage the standards to their full potential. Here’s a breakdown:
a) Introduction (Clause 0):
This clause delivers an overview of the Standard, its purpose, and the advantages of implementing a QMS. Additionally, it introduces key concepts, like the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, the process approach, and risk-based thinking.
b) Scope (Clause 1):
This clause outlines the scope of the ISO 9001 Standard by outlining what it covers and doesn’t cover.
c) References (Clause 2):
This section outlines any normative references. These are external documents that ISO 9001 refers to for additional information.
d) Terms and Definitions (Clause 3):
This clause highlights prominent terms used throughout the Standard to ensure clarity and consistent understanding.
Take the lead in quality assurance – become a certified expert with our ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Training.
Clause 4: Context of the Organisation
Clause 4 is where you set out your business's purpose and strategic direction regarding quality. It covers the following points:
a) Determining the internal and external factors as spotlighted by ISO 9001 Internal Audit that impact the quality of your services.
b) Identifying stakeholders in your business including suppliers, staff, and other interested parties.
c) Understanding customers and their needs.
Clause 5: Leadership and Commitment
This section on Leadership Requirements and Commitments explains the Requirements of top management. These include the following:
a) Fostering an organisation-wide customer focus
b) Creating and upholding a quality policy that sets direction and alignment
c) Identifying responsibilities and authorities across the QMS to offer clarification regarding who has the decision-making authority and what's expected of the functions operating within the system.
Do you wish to unlock your organisation's potential? Grab the chance with ISO 9001 Certification Courses - register now!
Clause 6: Planning for the QMS
An effective QMS operates on risk-based thinking, putting measures in place to address risks and opportunities. As an important part of the ISO 9001 Clauses, clause 6 requires companies to:
a) Document potential risks, including their chance of occurrence and severity.
b) Plan for prevention or reduction of undesired effects.
c) Integrate plans for enhancing desirable effects.

Clause 7: Support and Resource Management
ISO 9001 Clause 7 states that your organisation offers adequate resources to operate an effective QMS. This includes providing resources for:
a) Robust infrastructure
b) Efficient working environments
c) Effective HR Management
Clause 8: Operational Planning and Control
Clause 8, or the operation section within ISO 9001:2015, describes a company's work developing and delivering goods or services to its customers. The ISO 9001 processes will set out:
a) The requirements and quality objectives of products or services.
b) The process guides, resources and documents employees need to successfully create products or services.
c) The monitoring, inspection or testing the company needs to ensure top quality of products and services.
d) The rules governing the development and storage of records.
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
This section outlines the ISO Quality Standards for measuring customer satisfaction, internal audit, monitoring, analysis, and process performance as outlined in this section, align with the ISO 9001 Audit Checklist. The prerequisites for the management review, such as the inputs and outputs, are also mentioned.

Clause 10: Improvement Actions
The final ISO 9001 Clause focuses on the importance of continual improvement within a business. Clause 10 states that measures must be put in place to:
a) Improve products and services for the growth of the business.
b) Better match customer needs and improve customer satisfaction.
c) Identify instances of processes not achieving the goals and update them accordingly.
Want to become an expert in Internal Auditing? Join ISO 9001 Internal Auditor Training now!
What are the Six Mandatory Procedures for ISO 9001?
The six mandatory procedures for ISO 9001 are:
1) Control of Documents
2) Control of Records
3) Internal Audit
4) Control of Non-Conforming Products
5) Corrective Action
6) Preventive Action
Discover the essential guidelines to elevate your company's quality! Download the ISO 9001 PDF and begin your journey toward excellence today.
Is ISO 9001 a Regulatory Requirement?
No, ISO 9001 is not a regulatory requirement. It is a voluntary international standard for Quality Management Systems (QMS). However, some industries or contracts may require ISO 9001 certification as a condition for doing business, ensuring compliance with quality and customer satisfaction standards.
Does ISO 9001 Require a Quality Manual?
No, ISO 9001:2015 does not mandate a quality manual. Unlike previous versions, it allows organisations to document their QMS in a way that best suits their operations. However, businesses often maintain a quality manual as a best practice to provide structure and clarity in their processes.
Conclusion
In essence, achieving ISO 9001 Requirements isn’t just a compliance exercise; it’s a commitment to delivering quality at every level. It streamlines processes, builds customer trust, and sets businesses apart in a competitive market. When quality becomes a habit, success follows naturally.
Lead the way in quality excellence – Get Our ISO 9001 Lead Implementer Certification and make a lasting impact!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Seven Principles of Quality Management?

The seven principles of quality management in ISO 9001 are: Customer Focus, Leadership, Engagement of People, Process Approach, Improvement, Evidence-Based Decision Making, and Relationship Management. These principles help organisations enhance efficiency and ensure continuous improvement in quality performance.
Who Needs to Comply With ISO 9001?

ISO 9001 applies to any organisation—regardless of size or industry—that wants to improve quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. While compliance is voluntary, businesses in regulated sectors, government contracts, or competitive industries often seek certification to meet stakeholder expectations and industry requirements.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 9001 Certification Courses, including the ISO 9001 Foundation Course, ISO 9001 Lead Auditor Course, and ISO 9001 Internal Auditor Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is ISO.
Our ISO & Compliance Blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO 9001 Requirements, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your ISO 9001 knowledge base, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 9001 Foundation course
ISO 9001 Foundation course
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


