We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
The advances in software technology have been rapid over the past few decades. Such has been its pace that the Information Technology industry is slowly deploying software solutions to combat hardware problems. This trend is taking over the domain From AI-based text, voice and image generation to device drivers. This is where Network Function Virtualisation comes in as well.
Now, you might ask, “What is Network Function Virtualisation?”. Keep reading to learn more. This blog will delve into What is Network Function Virtualisation while exploring its working, benefits, drawbacks and applications.
Table of Contents:
1) What is Network Function Virtualisation?
2) Working of Network Functions Virtualisation
3) Network Functions Virtualisation architecture
4) Benefits of Network Function Virtualisation
5) Risks of Network Functions Virtualisation
6) Real-world applications of Network Function Virtualisation
7) Conclusion
What is Network Function Virtualisation?
Network Function Virtualisation is a revolutionary approach to designing, deploying, and managing networking services more agile and cost-effectively. In traditional network architectures, specific hardware devices, such as routers, firewalls, or load balancers, perform dedicated functions. NFV transforms this paradigm by virtualising these network functions, allowing them to run as software on general-purpose servers, often within a cloud environment.
The key idea behind NFV is to decouple network functions from proprietary hardware, enabling them to be implemented in software that can run on standard off-the-shelf servers. This shift from hardware-centric to software-centric network infrastructure brings several advantages. It enhances flexibility, scalability, and resource utilisation while reducing capital and operational expenditures.
In an NFV-enabled environment, virtualised network functions (VNFs) replace traditional, single-purpose appliances. These VNFs can be rapidly deployed, scaled, and moved across a network, providing dynamic and adaptable services. NFV leverages virtualisation and cloud computing technologies to create a more responsive and programmable network infrastructure.
Working of Network Functions Virtualisation
NFV revolutionises traditional networking by decoupling network functions, like firewalls or load balancers, from dedicated hardware and virtualising them. NFV employs standard servers to host these functions, optimising resource utilisation and scalability. It enables dynamic deployment, scaling, and chaining of network functions as needed.
Through software-based management, NFV enhances agility, reducing hardware dependencies and operational costs. This transformative approach streamlines network management accelerates service delivery and facilitates the integration of new technologies. NFV is integral to modernising network infrastructures, fostering flexibility and efficiency in adapting to evolving demands and innovations.
Unlock performance advantages with Virtualisation vs Containerisation for efficient IT solutions.
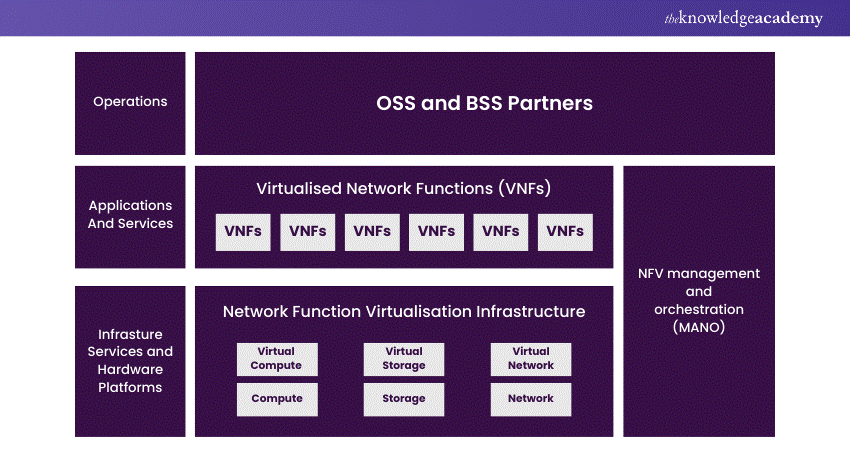
Network Functions Virtualisation architecture
Network Functions Virtualisation is a paradigm shift in networking where the conventional dedicated hardware components are replaced with software-based virtualised solutions. In a traditional network, devices like routers, switches, firewalls, etc., perform specific functions, but NFV introduces flexibility by leveraging software applications running on virtual machines.
a) Centralised Virtual Network Infrastructure: This foundational element utilises either a container management platform or a hypervisor. It abstracts computing, storage, and networking resources, providing a dynamic and scalable environment.
b) Applications: Software applications take the role of traditional hardware, delivering diverse network functionalities. These virtualised functions can include routing, load balancing, security, and more.
c) Framework (MANO): Management, Automation, and Network Orchestration (MANO) are crucial for efficiently managing the infrastructure. MANO streamlines operations, automates processes, and orchestrates network functions.
NFV enhances agility, scalability, and resource optimisation, making networks more adaptable to changing demands and reducing dependence on physical hardware components. The shift to NFV brings about cost-effectiveness, easier maintenance, and quicker deployment of network services.
Attain your understanding of route tables and network gateways by signing up for our Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Training now!
Benefits of Network Function Virtualisation
Network Function Virtualisation offers myriad benefits, transforming traditional networking by replacing dedicated hardware with software-based virtualised solutions. One key advantage is enhanced Flexibility and agility. NFV allows for dynamic scaling of network functions, enabling quick adaptation to changing demands without physical hardware changes. This flexibility accelerates service deployment and fosters innovation.
Another significant benefit is Cost efficiency. NFV eliminates the necessity for multiple specialised hardware components, reducing capital and operational expenditures. By leveraging standard IT infrastructure, NFV optimises resource utilisation and promotes a more cost-effective network architecture.
Scalability is a core advantage. NFV enables seamless scaling of network resources based on demand, ensuring efficient utilisation of resources during peak times and cost savings during lower demand periods. This scalability contributes to improved overall network performance.
Moreover, NFV enhances Service innovation. The shift from hardware-centric to software-centric solutions allows for easier integration of new services and functionalities. This fosters a more dynamic and innovative networking environment, enabling providers to roll out services more rapidly.
NFV also contributes to Increased network efficiency by streamlining operations and automating various processes. Automation reduces manual intervention, minimising the risk of errors and optimising the use of resources.
Evaluate networks to set up your IoT ecosystem by signing up for our Internet of Things (IoT) Systems and Applications Training now!
Risks of Network Functions Virtualisation
Network Functions Virtualisation introduces transformative benefits to networking but is not without its set of challenges and risks. Understanding these risks is crucial for organisations adopting NFV to make informed decisions and implement effective risk mitigation strategies.
a) Security concerns: NFV relies heavily on software, making it susceptible to cybersecurity threats. Virtualised network functions (VNFs) could be vulnerable to attacks, and the shared nature of virtualised environments introduces potential risks of unauthorised access and data breaches.
b) Performance issues: While NFV enhances flexibility, performance degradation is risky, especially if not implemented correctly. Virtualised functions may not always match the performance levels of dedicated hardware, impacting critical networking operations.
c) Interoperability challenges: Integrating diverse NFV components from different vendors may lead to interoperability issues. Ensuring seamless communication and coordination between various virtualised elements can be complex.
d) Scalability: NFV's promise of scalability could become a challenge if the infrastructure is not designed to handle sudden spikes in demand. Inefficient scaling mechanisms may result in degraded service quality during peak loads.
e) Reliability and availability: Reliability concerns arise as the dependence on software increases. Failures in virtualised components or the underlying infrastructure can lead to service disruptions, impacting availability.
f) Complexity in management: The dynamic nature of NFV introduces complexities in management and orchestration. Organisations may face challenges in effectively controlling and monitoring the virtualised network functions.
g) Migration challenges: Transitioning from traditional networking to NFV requires careful planning. Migrating existing services and functions to a virtualised environment can be challenging, leading to potential disruptions during the migration process.
Real-world applications of Network Function Virtualisation
NFV has found extensive applications across various industries, transforming how networks are designed, deployed, and managed. The real-world applications of NFV contribute to enhanced efficiency, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness in network operations.
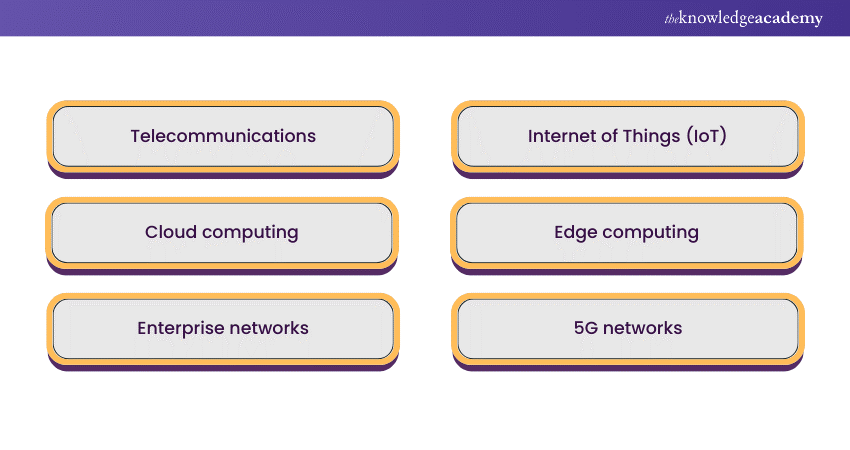
a) Telecommunications: NFV is widely adopted to virtualise functions like session border controllers, firewalls, and load balancers. This enables telecom operators to scale their networks more efficiently, introduce new services rapidly, and reduce the reliance on specialised hardware.
b) Cloud computing: NFV plays a crucial role in cloud computing environments, allowing the dynamic deployment and scaling of network functions based on demand. This flexibility is essential for delivering reliable and scalable cloud services.
c) Enterprise networks: Businesses leverage NFV to optimise their network infrastructure. Virtualising functions like WAN optimisation, intrusion detection, and network security give enterprises the agility to adapt to changing business requirements.
d) Internet of Things (IoT): NFV supports IoT deployments by efficiently managing the networking requirements of connected devices. It enables the creation of scalable and adaptable networks capable of handling the diverse communication needs of IoT devices.
e) Edge computing: NFV is instrumental in edge computing scenarios, where network functions are deployed closer to end-users or devices. This reduces latency and enhances the overall performance of applications that require low-latency interactions.
f) 5G networks: NFV is integral to implementing 5G networks, allowing for the virtualisation of core network functions. This accelerates the deployment of 5G services and facilitates the efficient management of network resources.
Learn to install, create and operate your virtual machine with Hyper-V by signing up for our Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies Course now!
Conclusion
Hopefully, this blog helped you understand Network Function Virtualisation and its role in the modern Information Technology Industry. From Telecommunications to Edge Computing, this technology has found its foothold across domains and gaining a deeper understanding of it will help you grow professionally.
Embark on a tech-forward journey with our Advanced Technologies Courses today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies
Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


