We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Modern-day organisations often rely on strategic structures to streamline operations and ensure the successful delivery of projects. One such crucial entity is the Project Management Office (PMO). Despite its significance, PMO remains a mystery to many, often shrouded in ambiguity and misconceptions. Thus, it is crucial to learn What is PMO.
Additionally, there is a growing quest for enhanced project success rates. This drives organisations to rely more heavily on PMOs for effective Project Management. In this blog, we will explore What is a PMO?, its functions, responsibilities, structures and benefits it offers to Project Management Office. Read more to learn!
Table of contents
1) What is a PMO?
2) What is the Difference Between a PMO and a Project Manager?
3) Roles and Responsibilities of PMO
4) Benefits and Challenges of PMO
5) Types of PMO
6) What are Typical PMO Job Titles?
7) PMO Tools and Software
8) Conclusion
What is a PMO?
Project Management Office (PMO) is a group or department that provides guidance, support, and oversight to the Project Managers of a company or any team. A PMO can provide the support needed to make sure projects are done consistently to a high standard. The main goal of PMO is to ensure that all Project Management within the organisation is executed correctly.
They also focus on achieving goals in line with the requirements and objectives of the organisation. There are different varieties of PMOs at work, whose nature of role depends on the needs and environments of organisations.
What is the Difference Between a PMO and a Project Manager?
A PMO is an organisational structure that sets Project Management standards, methods and processes to ensure projects align with the strategic goals of an organisation. They oversee multiple projects, providing guidance, governance, and resources to ensure their success.
On the other hand, a Project Manager is an individual responsible for planning, executing, and closing a specific project, ensuring it meets its objectives, timelines, and budget. While the Project Management Office provides a framework and oversight, the Project Manager focuses on the day-to-day management of a single project within that framework.
The PMO facilitates communication across projects and stakeholders, offering a centralised view of project health, risks and opportunities for synergy. In contrast, the Project Manager handles Team Leadership, Problem-solving and Stakeholder Engagement for the project. Different Types of Project Managers may have varying responsibilities within these roles.
Roles and Responsibilities of a PMO
The Project Management Office plays a critical role in guiding and supporting Project Execution within an organisation. Its responsibilities start from setting Project Management standards to providing oversight and resources to project teams. Let’s discuss it in detail:
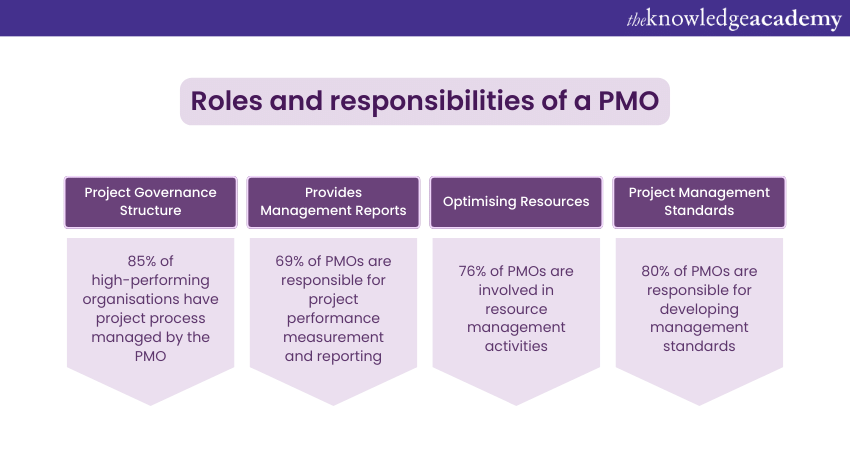
a) Establishes a Project Governance Structure
PMO develops a Project Governance structure that defines the roles, responsibilities, and decision-making capacities of the project stakeholders. They also ensure that the projects are prioritised and aligned with the short and long-term goals of the business. Additionally, they oversee that the project follows the organisational standards, processes, and methodologies.
b) Provides Management Reports
These professionals provide management reports that centralise information and deliver insights on the project status, progress, performance, risks, and issues. They communicate and collaborate with different stakeholders, such as the Project Managers, teams, sponsors, clients, and vendors to provide regular updates, feedback, and support.
c) Plan and Optimising Resources
PMO plan and optimise the allocation and utilisation of resources across the projects. They also monitor and measure the performance and value of each project and ensure timely delivery within the budget. They also manage the scope, schedule, quality, risks, and issues of each project.
d) Creates Project Management Standards
PMO creates and maintains Project Management standards, processes, and best practices. This ensures the quality, consistency, and alignment of the projects with the organisational goals and strategies.
They provide training and knowledge sharing across the teams on Project Management tools, techniques, and methodologies. A PMO also implements and sustains effective Change Management Best Practices that involve engaging, communicating, and training the project stakeholders.
Master the art of efficient planning and execution with our Project Management Training. Gain skills to lead projects successfully—Sign up now to excel!
Benefits and Challenges of PMO
Project Management Office can have different types, functions, and challenges depending on the needs and context of the organisation. Let's look at the benefits and challenges that PMOs can leverage and go through:
Benefits of PMO
Some of the benefits of having a PMO are as follows:
a) Standardisation: A PMO can unify an organisation's project approach by standardising its methods and Project Management Processes. It ensures the quality, consistency, and alignment of projects with the organisational goals and strategies.
b) Reduced Costs: A PMO controls the expenses through resource allocation and optimisation. The implementation of the latest standards and tools improves the efficiency and productivity of the project teams and reduces waste and errors.
c) Improved Risk Management: A PMO can assist in the determination, analysis, and minimisation of risks and issues that may arise during the project lifecycle. They not only offer contingency plans but also offer solutions in case of unexpected events or changes.
d) Enhanced Communication and Coordination: A PMO can facilitate the sharing of information and feedback among the key players in the project, such as the Project Managers, teams, sponsors, customers, and vendors. It ensures that everyone clearly understands the objectives, project scope, deliverables, and expectations.
e) Increased Customer Satisfaction: A PMO can help to meet or exceed the customer's requirements through the delivery of quality products or services within the allotted period and budget. It builds a positive relationship with the customer by providing regular updates, reports, and support.
Challenges in PMO
Some of the challenges of implementing or running a PMO are:

a) Rigid Corporate Culture and Resistance to Change: A PMO may face difficulties gaining acceptance and support from the organisation's senior management or other departments. Some stakeholders may perceive the PMO as threatening their autonomy or authority or as an unnecessary bureaucracy that adds complexity and overhead.
b) Lack of Experienced PMO Leadership and Experienced Project Managers: A PMO may struggle to find or retain qualified Project Managers and leaders with Project Management Skills, knowledge, and experience to manage complex and diverse projects. They may also face challenges in developing or maintaining a consistent vision, strategy, and direction for the project portfolio.
c) Lack of Appropriate Change Management Strategy: A PMO may fail to implement or sustain effective Change Management practices that involve engaging, communicating, and training the project stakeholders. They may also neglect to monitor and measure the impact and value of the changes created by the projects.
Types of PMO
There are different types of PMOs that vary in their degree of control, influence, and support over the projects and the organisation. Here are some of the common types of PMOs and their characteristics:
Directive PMO
A directive PMO represents the apex of Project Management control within an organisation. They establish Project Management standards and guidelines and also actively manage and execute projects with Project Managers directly reporting to them. This close involvement ensures strict adherence to methodologies and alignment with strategic objectives.
Additionally, Directive PMOs bridge the gap between an organisation's strategic vision and projects execution. They enable effective project Portfolio Management and empower the organisation to pursue initiatives that deliver maximum value and impact. These professionals bring structure and control to Project Management that are particularly suited for organisations prioritising strategic alignment, and centralised project oversight.
Controlling PMO
A Controlling PMO takes a more assertive stance in Project Management, establishing and enforcing standards, processes, and methodologies. It ensures adherence to established guidelines and practices, monitoring project progress, managing portfolios and aligning projects with organisational objectives. With authority over Project Resource Management allocation and project prioritisation based on strategic importance, they make critical decisions regarding project execution.
Controlling PMOs emphasise compliance with standards for consistent practices. While improving Project Governance and alignment this approach may feel restrictive to some team. Controlling PMOs are particularly valuable in organisations where standardisation and alignment with strategic objectives are top priorities.
Supportive PMO
A Supportive PMO serves as a valuable resource hub offering guidance, tools and best practices to Project Managers and teams. They provide consultative support in implementing effective Project Management Methodologies, encourage knowledge sharing, and offer training programs. Supportive PMOs do not directly control the project. Instead, they empower Project Managers with the tools and knowledge.This approach fosters flexibility and adaptability, allowing project teams to tailor their Project Management approaches to specific project needs. By promoting continuous improvement, Supportive PMOs contribute to enhanced Project Management practices and improve project outcomes.
Boost your career with the skills you’ll gain from our Microsoft Project Training – Register today!
What are Typical PMO Job Titles?
A Project Management office (PMO) encompasses various job titles, typically staffed by experienced Project Management professionals, many holding the PMI Project Management Professional certification. Staff should have budgeting, scheduling, planning, and organisational experience. Key positions include:
a) PMO Manager: The leader of the PMO, responsible for overseeing operations and ensuring team members follow established methodologies, procedures, and timelines.
b) Project Manager: Works closely with the PMO manager to address constraints on individual projects. They coordinate the PMO team to meet project requirements and deadlines.
c) Project Coordinator: Supports the project manager by tracking progress and ensuring projects stay on schedule. They also organise meetings and report project statuses to stakeholders.
d) Project Portfolio Manager (PPM): Handles large project portfolios. Even after project completion, they evaluate its business value and assess its ongoing impact.
e) Project Analyst: Analyses data related to project progress and market trends to provide insights for decision-making to the project and PMO managers.
f) PMO Process Specialist: Ensures compliance with all relevant policies and procedures, helping the manager maintain adherence to established guidelines.
g) Project Assistants: Handle routine administrative tasks and assist other team members. Larger PMOs may employ multiple assistants to support their projects effectively.
These roles ensure the PMO functions efficiently, meeting organisational goals and objectives.
Enhance job prospects and increase your earning potential with our PMP® Training – Sign up now!
PMO Tools and Software
PMO tools and software are essential for effective Project Management. They offer functionalities that support the planning, execution, monitoring, and reporting of projects. Some of the tools and Project Management Software include:
a) Project Scheduling and Planning Tools: These tools are fundamental for creating Project Management Timelines, scheduling tasks, and allocating resources. Examples include Microsoft Project, Asana, and Trello. Asana and Jira are particularly effective for enhancing team collaboration and streamlining workflows.
b) Collaboration and Communication Tools: Essential for team communication and collaboration on projects. Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom facilitate real-time communication and file sharing.
c) Resource Management Tools: These helps track and manage the allocation of resources across projects. Tools like Smartsheet and Resource Guru are popular choices.
d) Portfolio Management Tools: These are useful for overseeing a portfolio of projects to ensure alignment with organisational goals. Examples include Clarity PPM and Planview.
e) Risk Management and Analysis Tools: These assist in identifying, analysing, and mitigating project risks. Tools like RiskyProject and nTask are used in this area.
f) Financial Management Tools: Important for budgeting, forecasting, and tracking project expenses. Oracle NetSuite and QuickBooks offer solutions for Financial Management.
g) Reporting and Dashboards: Tools that provide visualisations and reports on project performance. Power BI and Tableau are examples of tools that can generate insightful dashboards.
Is PMO Higher Than Project Manager?
The Project Management Office (PMO) is not a role but a department overseeing project standards and practices. A PMO manager typically ranks higher as they oversee multiple projects and project managers. However, hierarchy depends on the organisation's structure and reporting lines.
What is PMO vs PM Roles?
The PMO sets Project Management standards, provides tools, and ensures processes are followed across projects. A Project Manager, on the other hand, is responsible for planning, executing, and delivering individual projects. The PMO supports project managers to ensure alignment with
Conclusion
Understanding "What is a PMO?" along with its key roles and responsibilities, underscores its significance for organisations aiming to elevate their Project Management results and competencies. PMOs are instrumental in fostering standardisation, reducing costs and improving Risk Management. Additionally, they enhanced communication and coordination, leading to greater customer satisfaction.
Equip yourself with the tools to identify and mitigate potential project risks with our Project Management Courses – join today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does a Good PMO Look Like?

A good PMO ensures project alignment with organisational goals, provides clear processes, and supports teams with tools and expertise. It promotes collaboration, tracks project performance, and mitigates risks. A well-structured PMO drives efficiency, transparency, and consistent delivery of successful projects.
What is an Example of a PMO Strategy?

An example of a PMO strategy is implementing a centralised project dashboard to monitor progress, allocate resources, and identify risks. This strategy focuses on standardising project workflows, ensuring alignment with business objectives, and enabling data-driven decision-making across all projects.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers Project Management Courses including Jira Masterclass, Software Estimation Training, and Smartsheet training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Top 13 Project Management Trends.
Our Project Management Blogs covers a range of topics related to Project Management Businesses, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Project Management Course
Introduction to Project Management Course
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


