We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

With every move a business makes, risks follow like its shadow. This is where Risk Management comes in, overpowering the shadow by brightening business prospects. It’s the best way to spot potential hazards, plot safe routes, and stay ahead of unexpected waves. From data analysis and risk and reward analysis to building buffers and business experiments, the broad range of available Risk Management strategies helps entire industries turn challenges into successes.
This blog takes a deep dive into the key aspects of Risk Management, highlighting its importance, strategies, role of technology, and more. Read on, master these techniques and turn the biggest risks into long-term rewards.
Table of Contents
1) What is Risk Management?
2) Steps of Risk Management
3) Risk Management in Different Sectors
4) Risk Management Strategies
5) Risk Management Standards and Frameworks
6) Role of Technology in Risk Management
7) Benefits of Risk Management
8) Conclusion
What is Risk Management?
Risk Management is the systematic process of identifying, analysing, and responding to risks to achieve organisational objectives and minimise adverse effects. Here's how it can help your organisation:
a) It helps understand potential threats and risks for the organisation
b) It helps evaluate their likelihood and impact
c) It helps implement appropriate strategies to mitigate them
It is a comprehensive process involving several key elements to identify, evaluate, and control organizational risks effectively. These elements ensure a proactive and holistic approach to Risk Management in ISO 27001 and ISO 27005, enabling organizations to manage potential threats efficiently.

What is the Importance of Risk Management?
Risk Management is imperative in organisations due to the ever-changing market shifts. This gives rise to uncertainty and increases the likelihood of risks that can adversely affect an organisation such as financial losses, reputational damage, legal issues, and potential business failure. Below are some of the ways in which one can prevent this from happening.
a) Protect Resources: By identifying potential risks early on, you can safeguard your resources from threats.
b) Preserve Profits: By effectively managing your risks, you can protect your accumulated profits and avoid any unnecessary losses.
c) Create a Culture of Resilience: By managing risks efficiently, you can create a culture of resilience focusing on long-term success.
It enables organisations to make informed decisions, optimise opportunities, and navigate uncertainties successfully. Therefore, organisations must prioritise Risk Management as an integral part of their strategic decision-making process.
Want to master the skills to conduct effective change and project Risk Assessment? Sign up for our Risk Management for Change Training now!
Steps of Risk Management
The Risk Management process is systematic and proactive approach organisations undertake to identify, evaluate, control, and mitigate risks that could impact their objectives. It involves a series of steps that guide the effectively managing risks in the organisation. Its process includes the following stages:
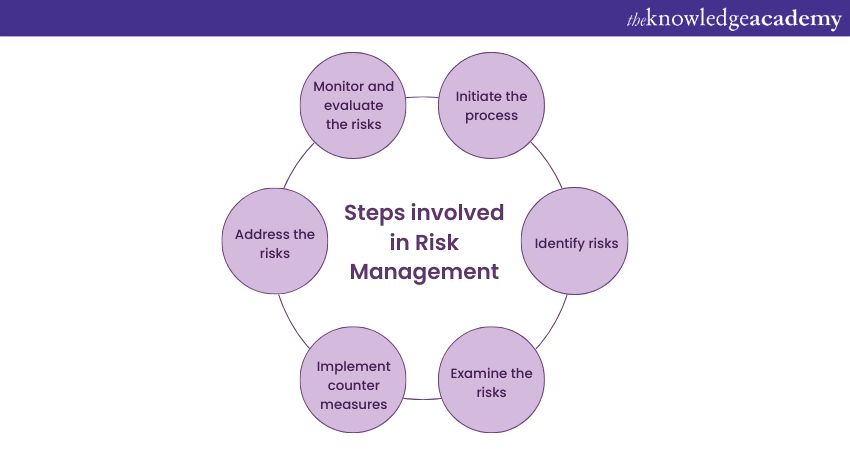
Establishing the Context
In this initial stage, organisations define the Risk Management process's objectives, scope, and criteria. They establish the context within which risks will be identified, evaluated, and managed. This involves considering internal and external factors influencing the organisation's risk landscape.
Risk Identification
The second stage involves identifying potential risks that may arise within the organisation. This includes the internal and external risks that could affect the achievement of objectives. The goal is to identify all relevant risks comprehensively, and here are the techniques to do that:
a) Brainstorming Sessions: By conducting brainstorming sessions and involving all the stakeholders, you can get different ideas for identifying the risks.
b) Data Analysis: You can harvest the power of data analysis to take logical decisions for detecting potential risks well in advance.
c) Expert Opinions: Ask for guidance from professionals and experts in the field for devising strategies to detect risks.
d) Historical Information: You can use historical data to identify patterns and trends to detect how and why various threats and risks arise.
Want to safeguard your business? Learn about the Types of Risk Management and how to protect your assets today!
Risk Assessment
Once risks are detected, the next step is to examine their likelihood of occurrence and potential impact on the organisation. Risk assessment involves evaluating the severity of consequences and the probability of risks materialising. This helps prioritise risks based on significance, allowing organisations to allocate resources effectively.

Risk Control Measures
After assessing risks, organisations develop and implement strategies to control and manage them. Risk control measures aim to reduce the likelihood or impact of identified risks. This may involve implementing policies, procedures, and controls to mitigate risks. The aim is to choose the most suitable risk treatment options, such as risk avoidance, reduction, transfer, or acceptance, with the help of Risk Management Softwares to streamline and enhance the decision-making process.
Risk Action and Management
This stage involves taking concrete actions to address identified risks and actively manage them throughout the organisation. It also involves monitoring and reviewing risk mitigation measures to ensure their ongoing effectiveness. Here's how it can help your organisation:
a) Roles and Responsibilities: It helps establish clear roles and responsibilities for everyone involved in the organisation.
b) Define Processes: It helps create and define Risk Management processes and how to implement them.
c) Stakeholder Involvement: It helps ensure effective communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
Risk Monitoring and Review
Continuous monitoring and review are essential for effective Risk Management. Organisations regularly assess the effectiveness of such strategies, monitor changes in the risk landscape, and identify emerging risks. This allows them to adapt their approach as needed, ensuring it remains relevant and effective.
The Risk Management process is cyclical and iterative, where each stage informs and influences the others. It requires ongoing commitment, involvement, and engagement from all levels of the organisation. By following a systematic process, organisations can proactively identify, evaluate, and mitigate risks, protecting their resources and enhancing their overall resilience, which can be highlighted in your Risk Management Resume for potential employers.
Enhance your Risk Management skills with MoR® 4 Practitioner Risk Management Certification and take the next step in your career – Signup now!
Risk Management in Different Sectors
While Risk Management is universally applicable, its strategies vary depending on the nature of the industry. Let's explore how Risk Management operates across the following sectors:
1) Construction: The construction industry faces many risks, from cost overruns and project delays to safety hazards and environmental concerns. Risk Management is this sector encompasses:
a) Detailed project planning
c) Rigorous safety protocols
d) Insurance coverage
Emerging technologies like Building Information Modelling (BIM)can also be leveraged to mitigate potential issues before they escalate.
2) Logistics: Risk Management in the logistics industry deals with potential disruptions in the supply chain. These include:
a) Mismanaged inventories
b) Transportation delays
c) Supplier failures
d) Compliance issues
Adopting forecasting tools, real-time tracking and analytics can help manage these risks.
3) Manufacturing: In the manufacturing sector, risks include supply chain disruptions, equipment failure, quality control issues and safety incidents. The Risk Management strategies include:
a) Diversified supplier networks to mitigate supply chain risks
b) Preventive maintenance programs to minimise equipment downtime
c) Stringent quality control measures
d) Rigorous safety training
4) Oil & Energy: The oil and energy sector have to contend with a unique set of risks including:
a) Regulatory compliance
b) Environmental risks
c) Market volatility
d) Safety hazards
To manage these risks, firms in this industry adopt sophisticated market prediction tools, environmental management systems, regular compliance audits and safety protocols. Additionally, investments in renewable energy sources help avoid risks related to fossil fuel dependency.
5) Food Production: Food production risks range from food safety and quality concerns to regulatory compliance and supply chain disruptions. To manage these risks, the industry must implement:
a) Traceability systems to track food from farm to fork
b) Food safety and quality assurance programs
c) Compliance with food safety regulations such as the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA)
Access the ISO 31000 Risk Management PDF for Free! Learn the best practices for risk management with this detailed PDF.
Risk Management Strategies
Numerous Risk Management strategies are applied across diverse sectors. Let's explore 10 of them:
1) Business Experiments: These involve running ‘what-if’ scenarios to evaluate different outcomes of potential threats or opportunities. IT, marketing and financial teams are well-versed in conducting business experiments.
2) Theory Validation: These strategies use group surveys and questionnaires to gain feedback based on experience. If a new product or service is developed or enhancements are made, it makes sense to get direct, timely, and relevant feedback from end users.
3) Minimum Viable Product Development: An effective Risk Management strategy must consider building products using core modules and features that are relevant and useful for the majority of their customers—this is called a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). It helps to keep projects within scope and helps companies get to market faster.
4) Isolating Identified Risks: IT teams are used to internal and external help in detecting security gaps or flawed processes. In doing so, they remain proactive in identifying security risks ahead of an event.
5) Building in Buffers: Project managers recognise the need to make a buffer, whether it's a technology or audit project. Buffers reduce risks by ensuring initiatives stay within the intended scope. Depending on the project, buffers may be time-based, financial, or resource-based.
6) Data Analysis: Data gathering and analysis are critical in managing risks. For example, qualitative risk analysis can help detect potential project risks.
7) Risk-reward Analysis: Conducting a risks and reward analysis help companies and project teams gauge the benefits and drawbacks of an initiative before investing time, resources, or money. It provides insight into the cost of lost opportunities.
8) Lessons Learned: With every initiative a company accomplishes or abandons, lessons will inevitably be learned. These lessons can significantly reduce risks in future projects or undertakings.
9) Contingency Planning: Companies must have multiple plans or options based on diverse scenarios. Contingency planning is about anticipating things that may go wrong and planning alternate solutions for unforeseen circumstances.
10) Leveraging Best Practices: Best practices are tried-and-tested ways of doing things. While best practices differ from project to project or industry to industry, they ensure companies don’t have to recreate the wheel.
Boost Your Interview Confidence – Check Out the Best Risk Management Interview Questions!
Risk Management Standards and Frameworks
Risk Management standards and frameworks provide organisations with guidance and best practices to implement such processes effectively. These standards and frameworks offer structured approaches to identify, evaluate, control, and mitigate risks.
They provide a common framework and set of principles that organisations can adopt to enhance their Risk Management practices. The following are some of its prominent standards and frameworks:
ISO 31000:2018
ISO 31000 is an international standard used for the management of risks. It provides techniques, a framework, and a process for managing risks effectively. The standard emphasises integrating Risk Management into an organisation's governance and decision-making processes. ISO 31000 promotes a systematic approach to managing risks and helps organisations create a risk-aware culture.
COSO ERM Framework
The Committee of Sponsoring Organisations of the Treadway Commission Enterprise Risk Management (COSO ERM) Framework is widely recognised and used globally. It offers a comprehensive framework for managing risks across the organisation. The framework emphasises integrating the process of managing risks with strategy-setting and Performance Management processes, promoting a holistic approach.
PMI's PMBOK Guide
The Project Management Institute's (PMI) Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) Guide includes a section on Risk Management. It provides project managers with a structured approach to identify, analyse, and respond to risks specific to project environments. The PMBOK Guide outlines processes, tools, and techniques for effectively managing project’s risks.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework is designed to help organisations manage cybersecurity risks. It provides a framework for analysing and improving an organisation's cybersecurity posture. The framework focuses on identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity risks and incidents.
IEC 31010 Risk Assessment Techniques
IEC 31010 is a standard that guides various risk assessment techniques. It offers a range of methods and tools to assess risks, including quantitative and qualitative approaches. The standard helps organisations select appropriate risk assessment techniques based on their specific needs and objectives.
These standards and frameworks serve as valuable resources for organisations seeking to enhance their Risk Management capabilities. By adopting and implementing these frameworks, organisations can establish consistent practices for managing risks, improve decision-making processes, and strengthen their overall culture of managing risks.
Take your Risk Management expertise to the next level with our Certified Risk Management Professional CRMP Course – Signup today!
Role of Technology in Risk Mangement
Technology has revolutionised Risk Management by enabling organisations to perform:
1) Data-driven Risk Assessments
2) Real-time Risk Monitoring
3) Enhanced Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
4) Cybersecurity and Data Protection
5) Collaboration and Communication
6) Automation and Process Efficiency
To unlock the full potential of technology in Risk Management, organisations can:
1) Adopt integrated Risk Management platforms that centralise risk data, enable risk assessments, and provide real-time risk monitoring capabilities.
2) Utilise advanced analytics techniques, such as predictive analytics and machine learning, to uncover hidden patterns, predict future risks, and support decision-making. AI-powered Risk Management systems can automate risk assessments and provide intelligent insights.
3) Invest in strong cybersecurity solutions to protect against cyber threats and ensure data privacy.
4) Use data visualisation tools to present risk information intuitively. Dashboards and reporting tools allow stakeholders to understand the risks, monitor risk indicators, and make data-driven decisions.
5) Implement automated monitoring systems.
Looking into a career as a Regulatory Analyst? Learn all about the Regulatory Analyst Salary and the skills that can boost your earnings.
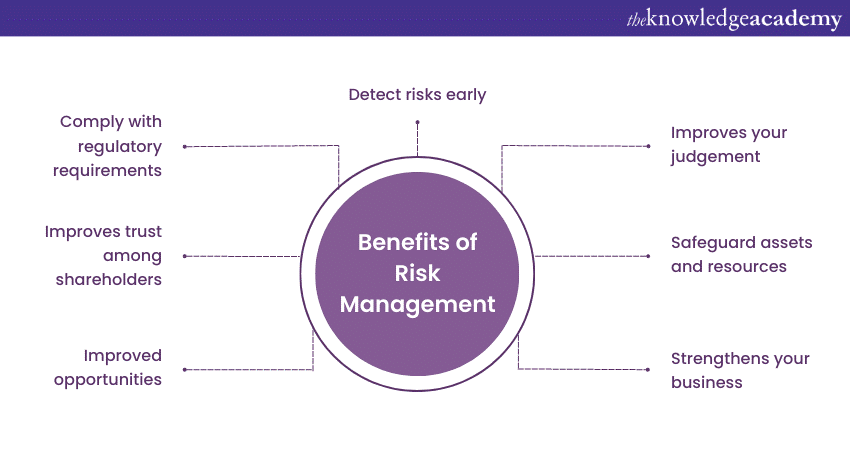
Benefits of Risk Management
Risk Management plays a pivotal role in safeguarding the success and sustainability of organisations across various sectors. By implementing such practices effectively, businesses can enjoy several key benefits. Some of its significant advantages include:
Proactive Risk Identification
Risk Management enables organisations to identify potential risks before they escalate into major issues. By systematically assessing and analysing risks, businesses can anticipate challenges and take proactive measures to mitigate them. Here's how it can help your organisation:
a) Helps prevent and minimise the impact of risks
b) Reduces potential losses
c) Prevents disruptions
Improved Decision making
Risk Management provides organisations with valuable insights to make informed decisions. It allows decision-makers to consider potential risks and their associated consequences when evaluating options. By factoring in risks, organisations can make better decisions that align with their objectives, leading to improved outcomes and reduced uncertainty.
Protection of Resources and Assets
Effective Risk Management helps protect an organisation's valuable resources and assets. By identifying and addressing potential risks, businesses can prevent financial losses, damage to physical assets, or reputational harm. Strategies like insurance coverage and robust security measures can safeguard resources and ensure business continuity.
Enhanced Business Resilience
Risk Management fosters business resilience by equipping organisations with the capability to withstand and recover from adverse events. This resilience allows organisations to adapt, recover, and continue operations, even in challenging circumstances. Here's how preparing for potential risks can help your businesses:
a) Develops contingency plans
b) Establishes response mechanisms
c) Helps allocate resources efficiently during times of crisis
Optimised Opportunities
Risk Management focuses on mitigating threats and enables organisations to seize opportunities. Businesses can make calculated decisions to pursue opportunities with favourable risk-reward ratios by evaluating risks and potential rewards. Its practices can help organisations capitalise on emerging trends, innovate, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Stakeholder Confidence
Implementing robust Risk Management practices instils confidence in stakeholders, including investors, customers, and partners. Demonstrating a proactive approach to managing risks demonstrates commitment towards responsible and sustainable business practices. This enhances trust, credibility, and long-term relationships with stakeholders, contributing to the overall success and reputation of the organisation.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements related to Risk Management. Effectively implementing the practices of managing risks ensures compliance with legal and regulatory obligations. Meeting these standards can prevent your organisation from the following consequences such as:
a) Penalties: Following regulations help your organisation avoid penalties from regulatory bodies.
b) Litigation: Lawsuits are no fun, and following guidelines and standards can save you from potential lawsuits.
c) Reputational Damage: By complying with regulation, you can protect your reputation that took years to build.
In summary, Risk Management offers numerous benefits to organisations, and it is crucial for navigating challenges in these turbulent times. By embracing it as an integral part of their operations, businesses can, with the support of a Risk Manager Job Description, navigate uncertainties, seize opportunities, and achieve sustainable growth.
Discover effective Risk Management strategies with MoR® Management of Risk courses and enhance your risk management skills – Signup now!
Conclusion
In summary, understanding Risk Management and exploring a Risk Management Case Study offers numerous benefits to organisations, making it crucial for navigating challenges due to the volatile nature of the business landscape. By embracing Risk Management as an integral part of their operations, businesses can navigate uncertainties, seize opportunities, and achieve sustainable growth.
Lay a strong foundation for your Risk Management skills and knowledgebase with our Management of Risk (MoR®) Foundation V3 Course – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Four C's of Risk Management?

The four Cs of Risk Management are culture, competence, control, and communication.
What are the Four Pillars of Risk?

The four pillars of Risk Management are supervision, monitoring & control, interventions and treatment, and victim safety planning.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various MoR® Management of Risk Courses including the MoR® 4 Practitioner Risk Management Certification and the Certified Risk Management Professional (CRMP) Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Risk Management Process.
Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to Risk Management, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Risk Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 MoR® 4 Practitioner Risk Management Certification
MoR® 4 Practitioner Risk Management Certification
Mon 19th May 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


