We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Two essential standards, ISO 27001 and ISO 27005, serve as beacons guiding organisations through the complex terrain of Risk assessment and mitigation. ISO 27001, with its comprehensive Information Security Management System (ISMS) framework, and ISO 27005, offering specialised Risk Management guidance, provide distinct avenues for safeguarding sensitive data and assets.
This blog unravels the critical distinctions between these standards, shedding light on their roles in fortifying an organisation's defences against modern-day threats. Risk Management in ISO 27001 and ISO 27005 mitigates uncertainty and achieves objectives with a systematic approach, ensuring effective control & direction. Let us steer the complex world of Risk Management in ISO 27001 and ISO 27005.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding ISO 27001
2) Delving into ISO 27005
3) Key differences between ISO 27001 and ISO 27005
4) Conclusion
Understanding ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is a transnational benchmark that outlines the requirements for installing, executing, sustaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). The primary purpose of ISO 27001 is to provide organisations with a systematic and structured approach to managing Information Security risks effectively. This standard is part of the broader ISO 27000 family, which includes related guidelines and frameworks for Information Security.
One of the critical components of ISO 27001 is its emphasis on Risk Management. In the context of this standard, Risk Management refers to the recurring cycle of recognising, evaluating, and treating Information Security risks to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets. Here is a breakdown of the Risk Management process as defined in ISO 27001:
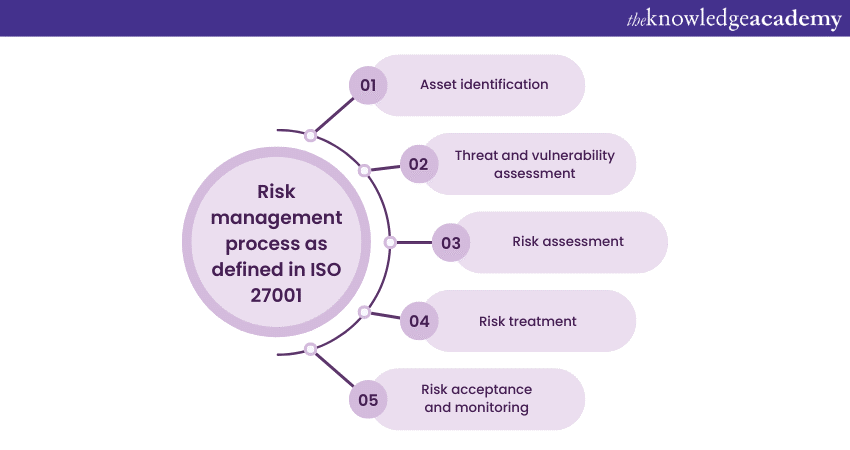
a) Asset identification: The first step in Risk Management involves identifying and cataloguing all information assets crucial to the organisation. This includes data, systems, hardware, software, personnel, and even physical assets that play a role in Information Security.
b) Threat and vulnerability assessment: ISO 27001 requires organisations to recognise possible threats and susceptibilities that could pose risks to these assets. Hazards can be internal or external, intentional or unintentional, and may include factors like cyberattacks, natural disasters, or human errors.
c) Risk assessment: After identifying threats and vulnerabilities, the organisation assesses the risks associated with each combination. This assessment considers the likelihood of an event and its potential impact on the organisation's information assets.
d) Risk treatment: ISO 27001 mandates that organisations develop a risk treatment plan. This plan outlines how each identified risk will be addressed. The options for risk treatment typically include risk mitigation (implementing controls to reduce risk), risk transfer (e.g., through insurance), risk avoidance (ceasing the activity that poses the chance), or risk acceptance (acknowledging and documenting the risk without additional action).
e) Risk acceptance and monitoring: In some cases, organisations may accept certain risks if they are within acceptable tolerance levels. However, this acceptance should be documented, and risks should be monitored to ensure they remain within proper bounds.
Delving into ISO 27005
ISO 27005, officially known as ISO/IEC 27005:2018, is a standard for Information Security Risk Management. ISO 27001 delivers a broad framework for establishing an Information Security Management System (ISMS). At the same time, ISO 27005 is a guideline that offers detailed principles and practices for effectively managing Information Security risks within an organisation.
ISO 27005 presents a systematic approach to information Security Risk Management, emphasising the importance of aligning Risk Management activities with the organisation's overall strategy and goals. Here is a more detailed breakdown of the Risk Management process as outlined in ISO 27005:
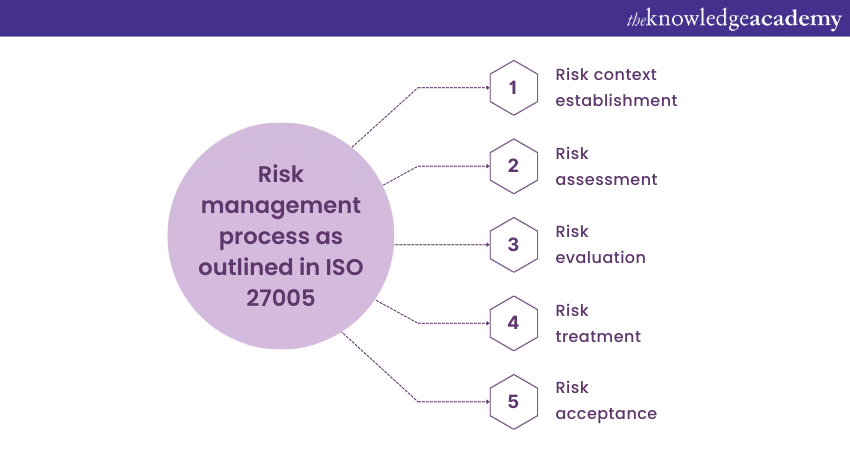
a) Risk context establishment: Before diving into risk assessment, ISO 27005 emphasises the importance of establishing the context for Risk Management. This involves defining the scope, objectives, criteria, and constraints guiding the Risk Management process. It ensures that Risk Management efforts are aligned with the organisation's strategic direction.
b) Risk assessment: Like ISO 27001, ISO 27005 advocates for identifying and assessing Information Security risks. This involves identifying the assets to be protected, understanding the threats and vulnerabilities, and estimating the potential impacts of different risks.
c) Risk evaluation: ISO 27005 places a significant focus on risk evaluation. Risks are evaluated based on predefined criteria, including the organisation's risk appetite, legal and regulatory requirements, and business objectives. This evaluation helps prioritize risks and determine their significance.
d) Risk treatment: Just as in ISO 27001, ISO 27005 emphasises the need for organisations to select and implement appropriate risk treatment options. These options may include risk mitigation (implementing controls to reduce risk), risk transfer (e.g., through insurance), risk avoidance (ceasing the activity that poses the chance), or risk acceptance (documenting and acknowledging the risk).
e) Risk acceptance: ISO 27005 recognises that not all risks can or should be eliminated or reduced to zero. Some wagers may be deemed acceptable based on the organisation's risk appetite and evaluation criteria. However, even accepted risks should be documented and monitored to remain within proper bounds.
Ready to establish a strong foundation in Information Security Risk Management? Join our ISO 27005 Foundation Training!
Key differences between ISO 27001 and ISO 27005
Risk Management in ISO 27001 and ISO 27005 is crucial, but these two standards differ significantly in how they approach and integrate Risk Management within their frameworks.
ISO 27001 is a comprehensive framework for establishing an Information Security Management System (ISMS). While Risk Management is an essential component of ISO 27001, it is just one part of a broader framework that covers various aspects of Information Security Management. ISO 27001 provides a structured approach to managing Information Security risks within the context of the ISMS.
ISO 27005, on the other hand, is a specialised guideline solely focused on Information Security Risk Management. Unlike ISO 27001, it is not a complete management system standard but a detailed guideline that provides principles and practices for risk assessment, treatment, and monitoring. ISO 27005 offers organisations a more granular and specific approach to managing risks.
ISO 27001's primary focus is establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an ISMS. The ISMS framework covers various Information Security aspects, including policies, procedures, controls, incident management, and compliance. Risk Management in ISO 27001 is just one element of ensuring the security of information assets within this broader context.
ISO 27005's core purpose is to provide detailed Information Security Risk Management guidance. It concentrates on the processes and methodologies required to effectively identify, assess, and treat risks. ISO 27005's primary goal is to help organisations enhance their Risk Management practices by offering a more specialised and in-depth perspective.
ISO 27001 delivers a framework for organisations to implement a fully integrated ISMS. Risk Management is integral to the overall ISMS, alongside other components like security policies, controls, and incident response. Organisations seeking ISO 27001 Certification must implement and demonstrate adherence to the entire framework.
ISO 27005 can be used as a supplementary guideline within the framework of ISO 27001 to enhance an organisation's Risk Management practices. However, ISO 27005 can also be employed independently, allowing organisations to focus specifically on improving their Risk Management without adopting the entire ISMS framework. This flexibility makes it suitable for organisations with varying needs.
Conclusion
As we conclude our investigation into Risk Management in ISO 27001 and ISO 27005, it is evident that both standards are invaluable resources for fortifying Information Security. ISO 27001, with its holistic ISMS framework, ensures a comprehensive approach to Information Security, ideal for organisations seeking certification. In contrast, ISO 27005's specialised guidance offers a more granular focus on Risk Management, allowing flexibility and customisation.
Frequently Asked Questions

a) Establish the context and scope of the ISMS
b) Identify the information assets and their owners
c) Identify the threats and vulnerabilities that could affect the assets
d) Analyse and evaluate the risks using ISO 27005 methods
e) Select and implement appropriate controls from ISO 27001 Annex A
f) Monitor and review the effectiveness of the controls and the ISMS
g) Continually improve the ISMS based on feedback and changes

The best way for organisations to combine the strengths of ISO 27001 and ISO 27005 is to use ISO 27005 as a detailed guideline for conducting Risk assessment, treatment, and monitoring and to use ISO 27001 as a comprehensive framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an ISMS. By doing so, organisations can benefit from the following advantages:
a) Aligning their Information Security objectives with their business goals and strategies
b) Enhancing their reputation and trust among stakeholders and customers
c) Reducing the likelihood and impact of Information Security incidents and breaches
d) Complying with legal and regulatory requirements and industry best practices
e) Improving their performance and efficiency in managing Information Security risks

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 27005 Courses, including ISO 27005 Foundation, Lead Auditor and Internal Auditor. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Risk Management methodologies.
Our IT Security and Data Protection blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO 27005, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Security and Data Protection skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming ISO & Compliance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 27005 Foundation
ISO 27005 Foundation
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


