We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Do you wish to drive organisational success with your problem-solving and quality improvement skills? Do you want to showcase your capability to understand issues during interviews deeply? If yes, then consider preparing with Root Cause Analysis Interview Questions.
Today, more than 3000 jobs are opened across various industries for Root Cause Analysis (RCA) experts, according to Glassdoor. With such high demand across domains, the competition among prospective RCA job seekers has also increased.
If you want to cut through this high competition, it’s time to get prepared for the interviews. Read this blog to prepare yourself with Root Cause Analysis Interview Questions and answers to gain the confidence needed to succeed in the interview room.
Table of Contents
1) Top 18 Interview Questions for Root Cause Analysis
a) What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
b) Why is RCA important in problem-solving?
c) What are the steps involved in Root Cause Analysis?
d) How would you define a "root cause"?
e) Can you explain the difference between direct causes and root causes?
f) What are some common tools and techniques used in Root Cause Analysis?
g) What role does data analysis play in RCA?
h) Can you explain the 5-Whys technique in detail?
i) Explain the main types of root causes.
2) Conclusion
Top 18 Interview Questions for Root Cause Analysis
Are you a working professional looking to improve your RCA skills or a recently graduated candidate aiming to excel in RCA-related interviews? If yes, these Root Cause Analysis Interview Questions and Answers can become your helping hand in cracking the interviews. So, let’s have a detailed look at them:
1) What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
Root Cause Analysis is a structured process used to identify the underlying reasons behind problems, failures, or incidents. It goes beyond addressing the immediate symptoms and aims to find the fundamental cause that, if addressed, can prevent the problem from recurring in the future.
2) Why is RCA important in problem-solving?
RCA is important in problem-solving because it:
a) Identifies the underlying reasons behind problems or failures
b) This prevents issues from recurring in the future
c) Enhances efficiency and productivity
d) Improves decision-making and problem-solving skills
e) Drives continuous improvement and innovation
f) Helps allocate resources effectively
g) Reduces costs and saves time
h) Enhances product quality and customer satisfaction
i) Enables an effective risk management
3) What are the steps involved in Root Cause Analysis?
The steps involved in Root Cause Analysis typically include:
a) Problem identification and description
b) Gathering relevant data and information
c) Identifying possible causes using techniques such as the "5 Whys" or Fishbone Diagrams
d) Analysing the data to determine the root cause
e) Developing and implementing corrective actions
f) Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the implemented solutions
4) How would you define a "root cause"?
A Root Cause is an underlying reason or factor that, if addressed or eliminated, will prevent the problem or failure from occurring again. It is the deepest level at which an issue can be traced.
5) Can you explain the difference between direct causes and root causes?
The following are the differences between direct causes and root causes:
|
Direct Causes |
Root Causes |
|
Immediate factors that directly contribute to a problem or an event. |
Underlying factors that give rise to the direct causes. |
|
Evident and observable. |
Often hidden or not immediately apparent. |
|
Addressing direct causes can resolve the immediate problem. |
Addressing root causes prevents the problem from recurring. |
|
Focuses on symptoms and visible effects. |
Focuses on the fundamental reasons behind the symptoms. |
|
Usually associated with short-term impact. |
Often associated with long-term impact. |
|
Examples: Human error, equipment failure, and miscommunication. |
Examples: Inadequate training, faulty design and lack of standard procedures. |
6) What are some common tools and techniques used in Root Cause Analysis?
There are several Tools and Techniques in Root Cause Analysis, including:
a) Fishbone diagrams (Ishikawa diagrams): Visual diagrams that help identify potential causes by categorising them into various factors.
b) 5 Whys: Involves asking "why" repeatedly to uncover the underlying causes of a problem.
c) Pareto charts: Graphical tools that display the frequency or impact of different causes in descending order.
d) Fault tree analysis: A systematic approach that uses logic diagrams to analyse and visualise the various combinations of events that led to a specific problem or failure.
e) Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): A proactive technique that identifies and assesses potential failure modes, their causes, and the effects of these failures.
f) Root cause mapping: A method that visually depicts the relationship between multiple causes and their effects.
g) Statistical analysis techniques: Statistical methods such as regression and correlation analysis can be applied to analyse data and identify patterns and trends.
7) What role do data analysts play in RCA?
Data analysts play a crucial role in Root Cause Analysis by:
a) Collecting and analysing relevant data to identify patterns, trends, and correlations
b) Applying statistical techniques to uncover insights and quantify the impact of potential root causes
c) Interpreting data to support evidence-based decision-making during the RCA process
d) Conducting data-driven investigations to validate hypotheses and eliminate biases
e) Collaborating with cross-functional teams to ensure accurate data collection and analysis
f) Providing objective analysis and recommendations for addressing Root Causes based on data findings
g) Monitoring and tracking key performance indicators (KPI) to evaluate the effectiveness of RCA interventions
h) Supporting the implementation of data-driven solutions and measuring their impact on problem resolution
i) Communicating data findings and insights to stakeholders in a clear and actionable manner
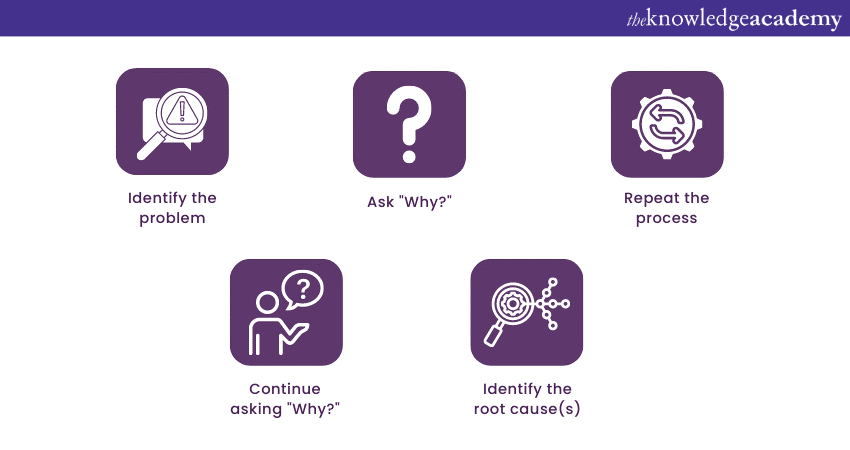
8) Can you explain the 5-Whys technique in detail?
The 5 Whys technique in RCA is a simple yet powerful problem-solving approach used to identify the underlying causes of a problem. By repeatedly asking “why” and delving deeper into the answers, this technique aims to uncover the root cause behind an issue. This technique involves the following steps:
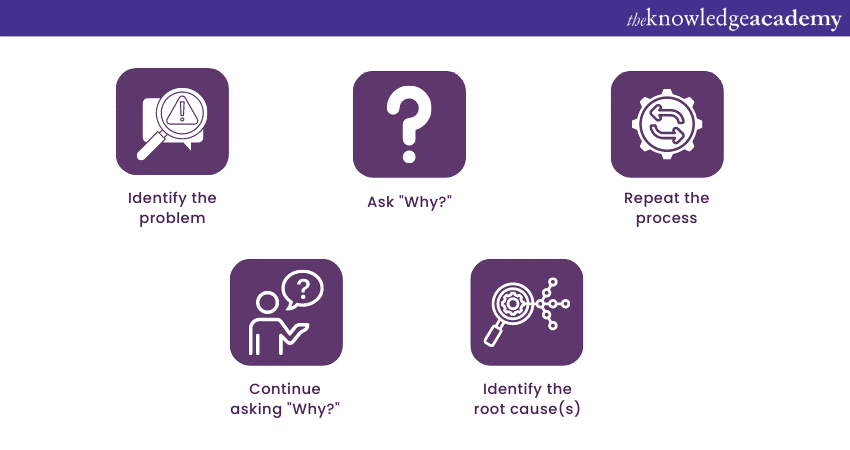
This technique is valuable because it helps move beyond surface symptoms and addresses the fundamental reasons behind an issue. It encourages critical thinking, exploration, and a deeper understanding of the problem.
9) Explain the main types of Root Causes
In RCA, the main types of root causes can be categorised as follows:
a) Physical causes: These relate to tangible aspects such as equipment malfunction, structural failures, material defects, or physical conditions.
b) Human causes: They are attributed to actions, decisions, or behaviours of individuals involved in the process. These can include inadequate training, awareness, errors, or procedure deviations.
c) Organisational causes: These are associated with systemic issues within the organisation, including ineffective policies, inadequate communication, poor management practices and lack of resources.
Enhance your skills in ITIL and boost your career with our ITIL® Certification Training.
10) What are the challenges associated with conducting Root Cause Analysis?
Conducting Root Cause Analysis can present several challenges, including the following:
a) Limited or incomplete data
b) Lack of clear problem definition
c) Identifying the true root cause among multiple contributing factors
d) Dealing with biases and assumptions
e) Time constraints
f) Resistance to change from stakeholders
11) What is the ideal time to perform Root Cause Analysis, and how often should you perform it?
The ideal time to perform Root Cause Analysis is immediately after an incident or problem occurs. Promptly initiating RCA allows for fresh information, better recollection of events, and higher accuracy in identifying the root cause(s).
The frequency of performing RCA depends on the nature of the organisation and the occurrence of problems. Generally, RCA should be conducted whenever significant incidents, failures, or recurring problems arise.
12) How do you prioritise the identified Root Causes?
Prioritising root causes involves considering factors such as the following:
a) The severity of the problem
b) Frequency of occurrence
c) Potential impact on critical processes or systems
13) How do you prevent biases from influencing the RCA process?
Influencing the Root Cause Analysis process by preventing biases, it is important to create an environment that encourages open and honest discussions. Employing diverse perspectives and involving multiple stakeholders can help mitigate individual biases. Additionally, using data-driven analysis techniques and maintaining objectivity throughout the process can minimise the impact of biases.
14) How do you ensure effective communication during the Root Cause Analysis process?
During RCA maintaining communication crucial for gathering accurate information, sharing findings, and gaining consensus. It involves the following:
a) Actively listen
b) Ask clarifying questions
c) Document information accurately
d) Employ visual aids such as diagrams or flowcharts
15) Can you share an example of a successful RCA you performed?
Let’s assume that there is a software system failure in an organisation.
Problem: A critical software system used by a company experienced a sudden failure, leading to system downtime and disruption of operations.
Root Cause Analysis steps:
a) "Sudden failure and system downtime of the XYZ software system.”
b) Collect relevant data about the incident, including system logs, error messages, and user reports.
c) Identify the immediate causes that directly contributed to the system failure.
d) Begin the Root Cause Analysis process by asking "Why?" to delve deeper into the factors contributing to the immediate causes. For example, “Why did the error message occur? Why did the component malfunction?
e) Keep asking "Why?" for each answer obtained in the previous step, uncovering underlying factors until reaching the root cause(s) of the problem.
The root cause(s): The root cause(s) may be identified through this iterative process, which could include inadequate testing procedures, software bugs, or inadequate system maintenance.
Take the first step towards enhancing your IT service management skills with our ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Training Course.
16) How would you handle a situation where the root cause cannot be identified?
In such situations, it is crucial to acknowledge the limitations and communicate transparently with stakeholders. Alternative strategies can be employed, such as implementing preventive measures based on the identified contributing factors or conducting further investigations in collaboration with subject matter experts.
17) Can you use software tools to automate the RCA process? If yes, then how?
Yes, software tools can be utilised to automate the Root Cause Analysis process, streamlining and enhancing its efficiency. Here’s how software tools can be beneficial in automating RCA:
a) Software tools automate data collection and storage for Root Cause Analysis
b) Advanced tools analyse data, identify patterns, and visualise insights
c) Workflow management features to guide and tracks the RCA process
d) Collaboration tools facilitate team communication and knowledge sharing
e) Software tools also enable systematic documentation of root causes and actions
f) Reporting and analytics features generate comprehensive RCA reports
18) What is the major mistake people make while asking Root Cause Analysis questions to diagnose a problem?
The main mistake teams make when asking Root Cause Analysis questions is focusing too much on immediate or superficial causes rather than digging deeper to identify the underlying and systemic Root Causes.
Conclusion
By preparing for Root Cause Analysis Interview Questions, you can demonstrate your proficiency in problem-solving, critical thinking, and analytical skills. By mastering the art of RCA, you can position yourself as an asset to organisations across industries.
Master the essential problem-solving techniques with our Root Cause Analysis Course.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis
Fri 7th Feb 2025
Fri 30th May 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


