We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

A successful business in today's ever-changing world requires an effective strategy for managing its Supply Chain. This is where the Supply Chain Manager Role and Responsibilities come in.
Their job role include managing inventory, negotiating contracts, analysing data, solving problems, and collaborating with various stakeholders.
However, this is just the superficial view of their role, a Supply Chain Manager’s responsibilities encompass various aspects. In this blog, we will understand the Supply Chain Manager Role and Responsibilities, from planning and Logistics to technology integration and sustainable practices.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Who is Supply Chain Manager
2) Supply Chain Manager Role and Responsibilities
a) Supply Chain planning and strategy
b) Logistics and transportation management
c) Procurement and vendor management
d) Risk management and mitigation
e) Data analysis and technology integration
3) Conclusion
Understanding Who is Supply Chain Manager
Supply Chain Managers serve as the orchestrators of the entire Supply Chain process, ensuring the efficient movement of goods and services. They are responsible for designing, implementing, and optimising Supply Chain strategies that align with organisational goals and objectives.
The key Supply Chain Manager responsibilities, which directly contribute to the Objectives of Supply Chain Management, include risk management and mitigation, reducing costs, and staying updated with the latest industry practices. They collaborate with cross-functional teams, including procurement, logistics, and sales, to ensure seamless coordination and synchronization throughout the Supply Chain.
These professionals closely monitor inventory levels, demand forecasts, and production schedules to maintain optimal inventory levels while minimising carrying costs. Discussed below are some of the skills and qualifications of Supply Chain Manager:
a) Strong analytical skills: A Supply Chain Manager needs to be able to collect, process, and interpret data from various sources, such as inventory, sales, demand, and costs, to make informed decisions and optimise the supply chain performance.
b) High level of organisation: It is important for a Supply Chain Manager to plan, coordinate, and execute multiple tasks and projects simultaneously, while ensuring that the resources, timelines, and quality standards are met.
c) Excellent problem-solving mindset: A Supply Chain Manager needs to be able to identify, analyse, and resolve challenges that may arise in the course of action, such as delays, shortages, or excesses, by finding effective solutions.
d) Leadership abilities and interpersonal skill: A Supply Chain Manager needs to be able to lead, motivate, and communicate with a team of internal and external stakeholders to achieve the desired goals and objectives.
e) Rigorous attention to detail: A Supply Chain Manager needs to be able to monitor and review every aspect of the supply chain, such as inventory levels, delivery times, quality standards, and compliance regulations, to ensure accuracy, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.

Supply Chain Manager Role and Responsibilities
Let's look at some of the responsibilities of a Supply Chain Manager to gain a better understanding of their role:
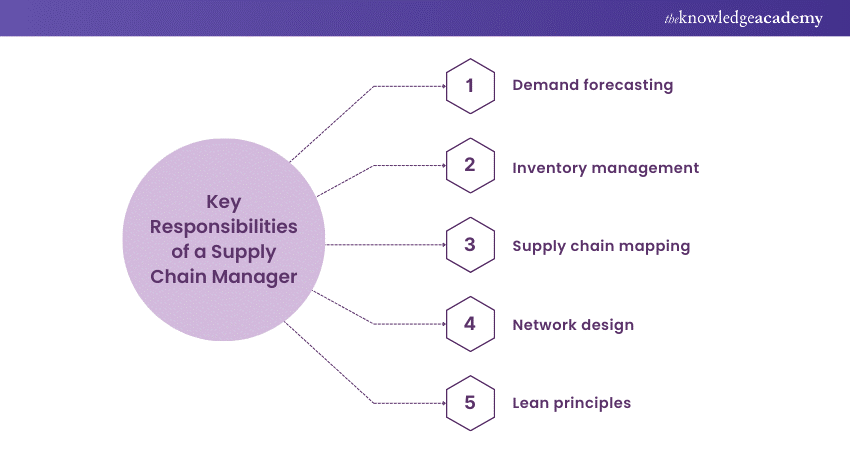
Supply Chain planning and strategy
Supply Chain planning and strategy form the foundation for efficient and effective Supply Chain Management. It involves a comprehensive approach to streamline operations, optimise resources, and align Supply Chain activities with organisational goals. Here are key points highlighting the significance of Supply Chain planning and strategy:
a) Demand forecasting: Accurate demand forecasting is essential for predicting customer requirements and planning production and inventory levels accordingly.
b) Inventory management: Efficient inventory management ensures the right quantity of goods is available at the right time, minimising carrying costs and stockouts.
c) Supply Chain mapping: Supply Chain Managers develop a comprehensive Supply Chain plan to pinpoint improvement areas and identify bottlenecks.
d) Network design: Strategic network design involves determining the optimal number and location of warehouses, distribution centres, and suppliers to enhance efficiency.
e) Lean principles: Applying Just-In-Time (JIT) principles and continuous improvement help eliminate waste and streamline processes.
Join our renowned Train the Trainer course and gain the expertise you need to inspire and educate others effectively.
Logistics and Transportation Management
In the intricate landscape of Supply Chain Management, the dynamic interplay between Logistics and transportation are crucial components of elements of supply chain management, as they ensure the smooth transfer of goods from suppliers to customers in a complex business environment. these critical components orchestrate the seamless transfer of goods from suppliers to customers within the complexities of the business environment. By strategically navigating the intricacies of distribution, storage, and transportation, logistics not only facilitates efficient supply chain operations but also plays a pivotal role in optimising overall business performance.
Effective logistics management involves streamlining the entire flow of materials, from procurement and warehousing to distribution and delivery. Benefits of green supply chain management include careful planning and coordination to minimize inventory carrying costs while ensuring sufficient stock levels to meet customer demands promptly.
Transportation management is equally vital, as it encompasses the selection of appropriate transportation modes, carriers, and routes to ensure timely and cost-effective deliveries. Moreover, Supply Chain Managers leverage technology and data analysis to monitor transportation performance, identify bottlenecks, and implement continuous improvements.
Ready to enhance your Supply Chain Management skills? sign up for our Industry Training now!
Procurement and Vendor Management
Procurement and vendor management are critical functions within the Supply Chain, ensuring the sourcing of goods and services from reliable suppliers and maintaining fruitful partnerships. Supply Chain Managers are responsible for these processes and for fostering collaboration with vendors. Here are key points highlighting the significance of procurement and vendor management:
a) Supplier selection: Supply Chain Managers conduct thorough assessments to identify suitable suppliers who meet quality, cost, and delivery requirements.
b) Competitive bidding: They leverage competitive bidding processes to obtain favourable pricing and terms from potential suppliers.
c) Contract negotiation: Negotiating contracts and agreements with vendors ensures clear expectations and terms for both parties.
d) Cost optimisation: Supply Chain Managers aim to reduce procurement costs through efficient negotiation and bulk purchasing.
e) Supplier relationship building: Building strong relationships with vendors fosters trust and mutual cooperation, ensuring smooth operations.
Acquire skills and knowledge for successful logistics route planning and strategy, sign up for our Logistics Management Training now!
Risk Management and Mitigation
Effective risk management and mitigation are crucial for ensuring the resilience and continuity of the Supply Chain, and Vendor Risk Management plays a key role in identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities. Supply Chain Managers employ various strategies to identify, assess, and address potential risks, minimising the impact of disruptions and enhancing overall Supply Chain performance. Here’s how Supply Chain Managers are involved in risk management and mitigation:
a) Risk identification: Supply Chain Managers conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats throughout the Supply Chain.
b) Risk analysis: They analyse each risk's probability and potential impact to prioritise mitigation efforts.
c) Diversification: Supply Chain Managers diversify suppliers, transportation routes, and sourcing locations to reduce dependency on single sources and minimise the risk of disruptions.
d) Contingency planning: They develop robust contingency plans and alternative strategies to respond swiftly in case of unexpected events.
e) Technology integration: By leveraging advanced technologies like data analytics and AI, Supply Chain Managers gain real-time insights into potential risks, enabling proactive decision-making.
Data Analysis and Technology Integration
Data analysis and technology integration are integral to modern Supply Chain Management, enabling Supply Chain Managers to make informed decisions, optimise operations, and enhance overall efficiency. Here are key points on the significance of data analysis and technology integration in the Supply Chain:
a) Data-driven insights: Supply Chain Managers use data analytics to extract valuable insights from large datasets, identifying patterns, trends, and performance indicators.
b) Demand forecasting: Data analysis aids in accurate demand forecasting, allowing managers to align production and inventory levels with market demands.
c) Inventory optimisation: By analysing inventory data, Supply Chain Managers can determine the optimal stock levels, reducing carrying costs while meeting customer expectations.
d) Supply Chain visibility: Technology integration provides real-time visibility into Supply Chain processes, enabling proactive monitoring and faster issue resolution.
e) Internt of Things (IoT) and sensors: Integrating IoT devices and sensors in the Supply Chain provides data on the temperature, location, and condition of goods, ensuring quality control and compliance.
Conclusion
In this blog, we covered the key Supply Chain Manager Role and Responsibilities, which include orchestrating an efficient and resilient Supply Chain. While understanding the broader Scope of Supply Chain Management from strategic planning and risk management to vendor collaboration and technology integration, their expertise ensures streamlined operations, mitigates risks, and drives organisational success in the competitive marketplace.
Understand the Supply Chain structure with its planning and distribution process, sign up for our Supply Chain Management Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the scope of Supply Chain Managers in future?

The future of Supply Chain Managers is promising, as it is expected to evolve with the advancement of technology, such as Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, automation, Blockchain, and digital twins. These technologies can help Supply Chain Managers improve their resilience, risk management, optimisation, prediction, and decision-making. Therefore, there are ample opportunities for professionals who are skilled and interested in SCM to pursue a rewarding career in this field.
What are the five main decisions made by operations and Supply Chain Managers?

The five main decisions made by operations and Supply Chain Managers are:
a) Location: This involves choosing the best places for the facilities, suppliers, and customers of the organisation. It affects the cost, speed, and quality of the operations.
b) Production: This involves deciding what products or services to offer, how to design and produce them, and how to manage the capacity and quality of the operations.
c) Inventory: This involves determining how much and when to order, store, and distribute the materials, components, and finished goods of the operations.
d) Transportation: This involves selecting the best modes and routes for moving the goods and services along the supply chain.
e) Sourcing: This involves choosing the best suppliers and partners for the organisation and negotiating the contracts and terms of the relationships.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy's Knowledge Pass, a flexible prepaid voucher system, offers the freedom to enrol in courses over a 12-month period. Start your limitless learning adventure with us and embrace education that knows no bounds.
What are related Industry Training courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Industry Training, including Facilitation Skills Training, Facilities Management Training, Product Management Training and more. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Supply Chain Risk Management.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Logistics, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Logistics skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Supply Chain Management Training
Supply Chain Management Training
Fri 2nd May 2025
Fri 4th Jul 2025
Fri 5th Sep 2025
Fri 7th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


