We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Have you ever downloaded a seemingly harmless app or clicked on a deceptive link only to find your system compromised? If so, you might have encountered Trojan Horse Malware, one of the digital world's most deceptive and dangerous threats.
So, how can you outsmart a threat designed to fool even the most vigilant users? The first step is knowledge. In this guide, we’ll delve into the world of Trojan Horse Malware, uncovering its secrets and showing you how to protect yourself from this digital deception. Ready to take back control of your Cyber Security? Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Trojan Horse?
2) How Trojans Horse Malware Work?
3) Different Types of Trojan Horse Malware
4) Real-world Examples of Trojan Horse Malware
5) How to Identify Trojan Horse Malware?
6) How to Safeguard Against Trojan Horse Malware?
7) Conclusion
What is a Trojan Horse?
When the horse’s belly opened under the cover of night, it was already too late. The Greeks had finally succeeded in capturing the long-besieged city of Troy, bringing the Trojan War to a dramatic end. Thousands of years later, the myth of the Trojan Horse endures, albeit with a less flattering connotation, much like the various Types Of Malware that use deceptive tactics to infiltrate systems.
What was once celebrated as a brilliant stratagem and a masterful feat of engineering is now synonymous with a malicious digital threat. This modern “Trojan Horse” infiltrates victims’ computers unnoticed, reading passwords, recording keystrokes, or opening the door for further Malware that can even take the entire system hostage. These actions can include:
a) Deleting data
b) Blocking data
c) Modifying data
d) Copying data
e) Disrupting the performance of computers or computer networks
Unlike computer viruses and worms, Trojans are not able to self-replicate.
How Trojans Horse Malware Work?
Here’s an explanation of how Trojans work:
1) Dependency on User Interaction:
Unlike viruses, Trojans need user action to activate, typically by downloading and running an executable (.exe) file.
2) Installation Process:
Once the user installs the Trojan, it embeds itself in the device’s system and begins its malicious operations.
3) Spread via Legitimate-looking Emails:
Trojans are often spread through seemingly legitimate emails and attachments, which are distributed widely through spam.
4) Automatic Execution:
After installation, the Trojan runs automatically every time the infected device is turned on.
5) Social Engineering Tactics:
Cybercriminals utilise deceptive methods, such as putting harmful files in banner advertisements, pop-up ads, or website links, to mislead consumers into accidentally downloading Malware.
6) Creation of Zombie Computers:
After infection, the hacker has the ability to control the computer that was infected, hence transforming it into a zombie which helps spread the Malware all over the network as part of a botnet.
Become a Certified Cyber Security Professional to protect digital environments with our Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO) Course. Sign up now!
Different Types of Trojan Horse Malware
Following are some of the most common types of Trojan Horse Malware:
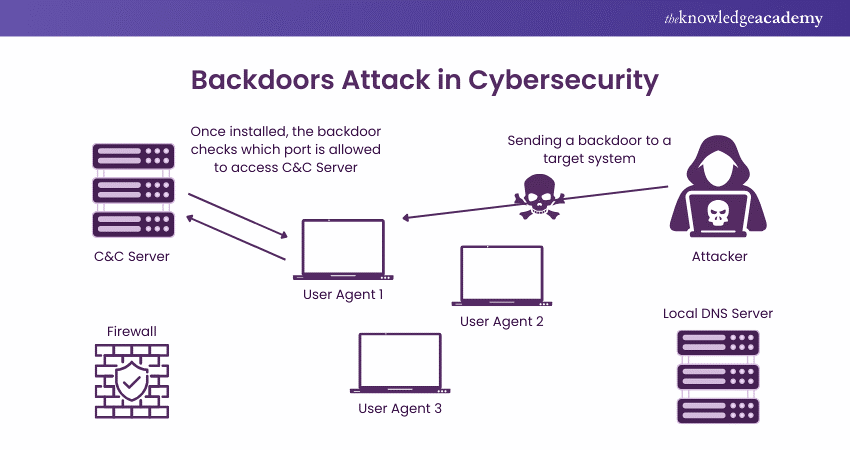
1) Backdoor Trojans
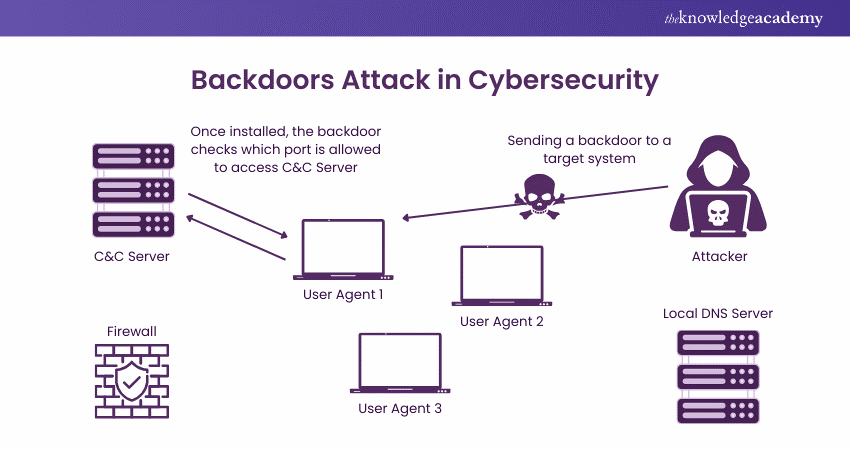
Function: These Trojans create a backdoor on a user’s system.
Purpose: They allow attackers to gain remote control over the infected computer. This enables them to perform malicious activities like stealing data or installing additional Malware.
2) Exploit Trojans
Function: Exploit Trojans makes use of software mistakes.
Purpose: They enter a system by using those weaknesses, which frequently leads to unauthorised access or additional Malware installation.
3) DDoS Trojans
Function: These Trojans are utilised to launch DDoS assaults.
Purpose: They overload a target with traffic, disrupting regular processes and making it unavailable to consumers.
4) Rootkit Trojans
Function: Rootkit Trojans are designed to hide certain objects or activities in your system.
Purpose: They make detecting other types of Malware difficult, allowing malicious activities to continue undetected.
5) Banking Trojans
Function: Banking Trojans target online banking systems.
Purpose: They steal login credentials, financial data, and other sensitive information, often leading to financial theft.
6) Dropper/downloader Trojans
Function: These Trojans install other types of Malware onto a victim’s system.
Purpose: They act as a delivery mechanism for additional malicious software, which can perform various harmful actions.
7) Trojan-Ransom
Function: Trojan-Ransom Malware encrypts users' files.
Purpose: They seek a ransom to restore accessibility to the files that are encrypted, which often results in major disruption and financial loss.
8) Trojan-GameThief
Function: These Trojans steal user account information from online gamers.
Purpose: They target gaming accounts to steal credentials, in-game assets, or personal information.
9) Trojan-IM
Function: Trojan-IM targets instant messaging applications.
Purpose: They steal login credentials and other sensitive information from these applications.
10) Fake Antivirus Trojans
Function: These Trojans masquerade as genuine antivirus software.
Purpose: They confuse users into subscribing to fake safety services, leading to money loss and more Malware infection.
11) SMS Trojans
Function: SMS Trojans infect mobile devices.
Purpose: They can send SMS messages to premium-rate numbers, incurring charges for the victim without their knowledge.
12) Trojan-Spy
Function: Trojan-Spy Malware spies on the user.
Purpose: They capture screenshots, log keystrokes, or monitor other activities to steal sensitive information.
13) Trojan-Mailfinder
Function: These Trojans harvest email addresses from the victim’s computer.
Purpose: They collect email addresses for spamming or phishing purposes.
Develop advanced fraud detection strategies with our Fraud Analytics Course and build a secure future today!
Real-world Examples of Trojan Horse Malware
Trojan Horse Malware has been present for a long time, and Trojans were used in some of the most well-known cyber attacks. Here are some prominent examples:
1) Zeus Trojan:
a) Infamy: One of the most notorious financial Trojans in cyber history.
b) Discovery: First identified in 2007, primarily targeting Windows users.
c) Function: Steals confidential financial data, such as online banking credentials, by embedding itself in web browsers.
d) Detection Evasion: Known for its speed and ability to avoid detection.
e) Impact: It has stolen millions of pounds worldwide and facilitated the spread of other Malware, posing a significant risk to cybersecurity.
2) Emotet:
a) Origin: Initially detected as a banking Trojan in 2014.
b) Evolution: Evolved into a versatile and destructive botnet capable of distributing various Malware, including ransomware.
c) Spread: Primarily spreads through malicious email attachments and links.
d) Resilience: Recognised for its adaptability and ability to avoid traditional antivirus software.
e) Impact: Involved in multiple large-scale cyberattacks, resulting in considerable damage to companies and persons.
3) Trojan-Banker.AndroidOS:
a) Target: Specifically targets Android devices by masquerading as legitimate banking apps.
b) Function: Mimics real banking login screens to steal sensitive data such as credentials and financial information.
c) Stealth Operation: Operates silently in the background, often going undetected until the damage is done.
d) Significance: Demonstrates the increasing danger of mobile Malware as more individuals rely on their phones for financial transactions.
Stay ahead of cyber threats with our Cyber Security Training. Sign up today!
How to Identify Trojan Horse Malware?
Identifying Trojan Horse Malware can be challenging because of its deceptive nature. However, some signs may indicate a Trojan infection:
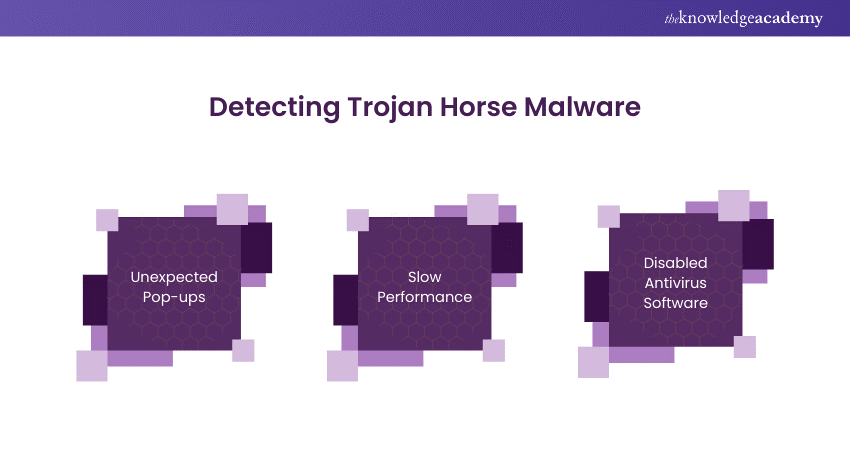
1) Unexpected Pop-ups: Frequent and unusual pop-up messages could signify a Trojan.
2) Slow Performance: If your system suddenly becomes sluggish, it could be a Trojan using your resources.
3) Disabled Antivirus Software: Some Trojans disable security programs to avoid detection.
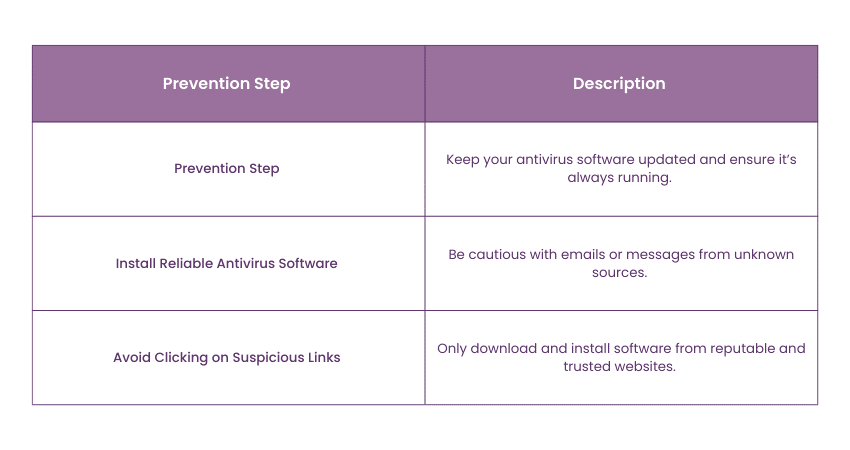
How to Safeguard Against Trojan Horse Malware?
Prevention is key to defending against Trojan Horse Malware. Here are some essential steps to protect your system:
Step into Cyber Security by mastering Malware Analysis Training to defend your systems and enhance your expertise!
Conclusion
In the digital battlefield, Trojan Horse Malware continues to be a cunning adversary, slipping through defences with deceptive ease. Understanding the difference between Malware vs Virus is essential to outsmart these digital invaders. By comprehending its tactics and fortifying your Cyber Security measures, you stay one step ahead. Be vigilant, informed, and proactive to keep your systems safe from Trojan Horse Malware.
Protect your organisation from cyber attacks – start your journey with our Cyber Security Awareness Course today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Goal of a Trojan Horse?

The goal of a Trojan horse is to deceive users into installing it. Once installed, attackers can steal data, gain unauthorised access, or control the infected system without the user’s knowledge.
Are Trojan Horses Easy to Remove?

Trojan horses can be challenging to remove because they often disguise themselves as legitimate files. Effective removal typically requires specialised antivirus tools and may involve restoring the system from backups.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cyber Security Training, including Malware Analysis Training, Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO), Cyber Security Awareness and Fraud Analytics Training Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Computer Worms.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to Malware Analysis, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cyber Security skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Malware Analysis Training
Malware Analysis Training
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


