We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Unity is one of the most widely used engines for game development, known for its versatility, robust features, and cross-platform compatibility. Although Unity was initially created for Windows and Mac OS, Unity Technologies has made strides in making Unity available for Linux users as well.
If you're interested in using Unity for Linux, you're in the right place. This step is pivotal for game developers using Linux, as it opens a world of possibilities. Installing Unity on Linux will ensure that you are well-equipped to kickstart your game development journey.
In this blog, we will learn the process of installing Unity on Linux. Follow the step-by-step instructions and set up your Linux environment to start creating amazing games.
Table of Contents
1) What are the prerequisites for installing Unity on Linux?
2) Step-by-step guide on how to install Unity on Linux
a) Download Unity Hub
b) Installing Unity Hub
c) Sign in to Unity Hub
d) Install Unity Editor
e) Select the Modules
f) Accept the terms and conditions
g) Track installation progress
h) Create a new Unity Project
3) What are common troubleshooting issues?
4) Conclusion
What are the prerequisites for installing Unity on Linux?
So, you understand what is Unity. However, you are still unsure about the requirements that you need to install Unity on Linux. These points will show you what are the prerequisites that you need to have for smooth operation and top-notch performance of Unity on your system. Let’s have a look:
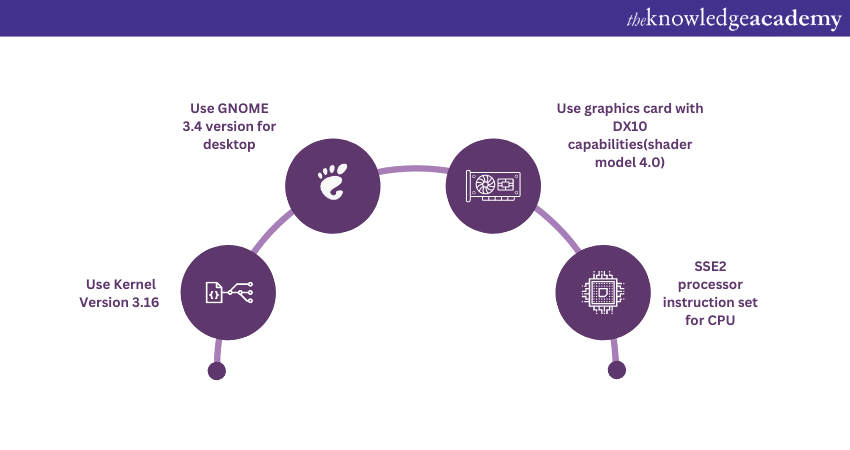
a) Your Linux OS needs to use Kernel version 3.16 or newer. The Kernel is the core of the system, and having an updated version ensures compatibility and optimal operation.
b) The GNOME desktop environment version needs to be 3.4 or newer. Unity has chosen GNOME as the reference desktop environment due to its extensive user base and compatibility with Unity's features.
c) Your computer needs to have a graphics card with DX10 capabilities (shader model 4.0) or better. This is essential for rendering complex graphics in the games you'll be developing.
d) Your CPU needs to support the SSE2 instruction set. These are specific processor instructions that Unity utilises for efficient operations.
Take your Game Development Skills to the next level with our course on Game Development Training .
Step-by-step guide on How to install Unity on Linux
Unity on Linux offers a flexible and efficient platform for creating immersive and interactive games. For a smooth and successful game development in your system, you need to follow this step-by-step guide on how to install Unity on Linux:
a) Download Unity Hub:
The first step in installing Unity on Linux is to download Unity Hub. Unity Hub is a standalone application developed by Unity Technologies, which helps manage different Unity versions and projects on your system. Head over to the Unity Download page on Unity's official website and download the Unity Hub AppImage for Linux.
b) Installing Unity Hub:
Once the Unity Hub AppImage file is downloaded, you need to install it. To do this, open a terminal window and go to the directory that contains the downloaded file. You must grant permissions for execution to the UnityHub.AppImage file before you can run it. This can be done using the command chmod +x UnityHub.AppImage. Once this is done, you can run the Unity Hub using the command ./UnityHub.AppImage.
c) Sign in to Unity Hub:
After running the Unity Hub, the application will open, and you will be prompted to sign in to your Unity account. You can always create an account if you don't have one. Creating an account is free on Unity's official website. Once your account is set up, sign in to the Unity Hub.
Master the world of open-source operating systems with our Linux Training .
d) Install Unity Editor:
The next step in the process is to install the Unity Editor. To do this, navigate to the 'Installs' section in the Unity Hub. Here, click on the 'Add' button. A list of different Unity versions will be displayed. You can choose the one that you want to install and then click on 'Next'. The Unity Editor is the main application where you will be developing your games.
e) Select the modules:
Unity provides additional modules that can be installed along with the Unity Editor. These modules provide extra functionalities that can be beneficial in your game development process. For example, if you want to create games that can run on Linux, you should install the 'Linux Build Support' module. After selecting the necessary modules, you can proceed with the installation by clicking on 'Next'.
f) Accept the terms and conditions:
Before installing, you will be prompted to accept Unity's terms and conditions. Ensure that you read through these terms and conditions before accepting them. Once you have accepted, click on 'Done' to begin the installation.
g) Track installation progress:
The installation progress can be tracked from the 'Installs' section in the Unity Hub. Once the installation is complete, the new Unity version will appear in this section.
h) Create a new Unity project:
Once Unity is installed, you can create a new Unity project. To do this, navigate to the 'Projects' section in Unity Hub. Here, click on the 'New' button. A dialogue box will be displayed where you can specify late. Once these details are filled in, click on 'Create' to create your new Unity project.
Elevate your game design skills with our course on Game Design And Development With Unity Training .
What are common troubleshooting issues?
Now you know how to install Unity on Linux. But you are facing some challenges while installing. In this section, we have discussed some common troubleshooting errors that you may encounter. These are:

a) Unity Hub not starting: Check for necessary executable permissions on UnityHub.AppImage file.
b) Graphics-related issues: Keep your graphics card drivers up-to-date or consider reinstalling them if problems persist.
c) Unity Editor not launching: Force Unity to use OpenGL by starting it with the command ./Unity -force-opengl.
d) Installation errors: Check your internet connection, ensure there is enough hard drive space, and verify the integrity of your UnityHub.AppImage file.
e) Version compatibility: Confirm that the Unity version you're installing is compatible with your Linux distribution.
f) Unity Projects not opening: Try opening them directly from Unity Hub and verify the project's files and directory permissions.
g) Performance issues: Ensure your system meets the minimum requirements for running Unity, and free up resources if necessary.
h) Software conflicts: Temporarily disable other software to check if they're causing conflicts with Unity.
Conclusion
Installing Unity on Linux enables game developers like you to leverage this powerful engine on an open-source platform. With careful attention to prerequisites, you can approach a step-by-step installation process. Fixing all your troubleshooting errors, you'll be ready to bring your gaming visions to life using Unity for Linux.
Start your journey towards Linux mastery with our comprehensive Course on LINUX Fundamentals.
Upcoming Programming & DevOps Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Game Design and Development with Unity Training
Game Design and Development with Unity Training
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


