We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In the lightning-paced business landscape, vendors are more than just suppliers; they are the lifeline of efficiency and innovation. Consequently, effective Vendor Management is the fuel that drives successful partnerships and ensures long-term business success. From selecting the perfect partners to cultivating lasting relationships, the Vendor Management process is the expressway to improved business outcomes and assured competitive advantage.
This comprehensive blog will take you on a journey through the craft of Vendor Management, highlighting its benefits, essential steps, key features and more. Read on and elevate your vendor collaborations to new heights!
Table of Contents
1) What is Vendor Management?
2) Importance of Vendor Management
3) Vendor Management Process
4) Key Features of a Vendor Management Tool
5) Benefits of Using a Vendor Management Tool for Businesses
6) Common Challenges in Traditional Vendor Management
7) Conclusion
What is Vendor Management?
Vendor Management describes the processes organisations use to manage their suppliers, also known as vendors. These processes include choosing vendors, negotiating contracts, controlling costs, mitigating vendor-related risks, and ensuring service delivery.
The vendors a company uses will vary depending on the nature of the organisation and could include companies as diverse as IT vendors, seafood suppliers, cleaners and marketing consultants. Vendors can also range in size from sole traders to large organisations.
Importance of Vendor Management
Vendor Management is important for several reasons:
1) It plays a big role in choosing the right vendor for particular business needs.
2) Companies can use Vendor Management to accomplish business goals, like harnessing opportunities for cost savings and speeding up the onboarding process.
3) The process reduces the risk of supply chain disruption and ensures the goods and services are delivered on time and are up to the expected standard.
4) It helps companies nurture stronger relationships with their vendors, which may result in opportunities to negotiate better rates.
Vendor Management Process
The Vendor Management process includes numerous activities, including vendor selection, vendor onboarding, contract negotiation, risk monitoring and more. These activities are explored in detail below
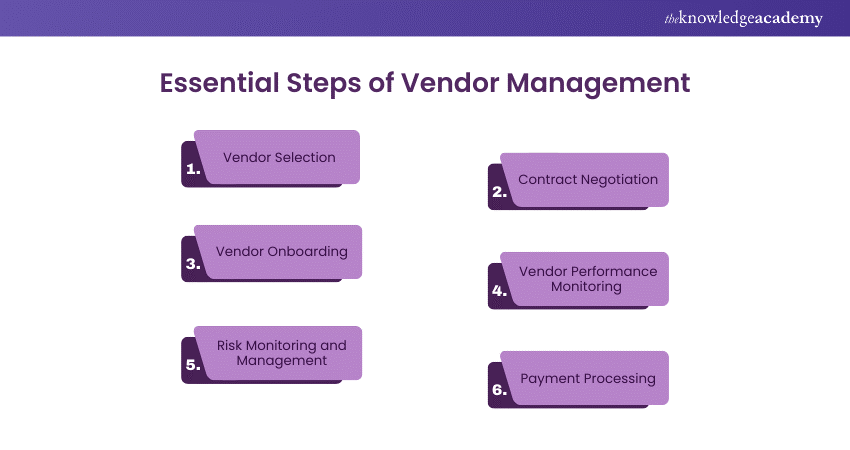
1) Vendor Selection
The vendor selection process includes:
a) Researching and sourcing suitable vendors
b) Seeking quotes via requests for quotation (RFQs)
c) Requests for proposals (RFPs)
d) Shortlisting vendors
While price will be an inevitable consideration during this process, companies must also evaluate other factors, such as a vendor’s reputation, track record, and communication ability, when deciding which vendors to appoint for a contract.
2) Contract Negotiation
It can take time to get the contract right at the outset and ensure the agreed terms benefit both parties. The contract negotiation process will include:
a) Defining the goods or services to be included
b) Start and end dates of the arrangements
c) All essential terms and conditions.
d) Focusing on confidentiality and non-compete clauses
3) Vendor Onboarding
This involves gathering documentation and information needed to establish the vendor as an approved supplier to the company and ensure the vendor can be paid for goods or services they supply. Essentially, the onboarding process includes:
a) The vendor's contact and payment information
b) Relevant licenses held by the vendor
c) Tax forms
d) Insurance details
4) Monitoring Vendor Performance
As part of the Vendor Management process, organisations monitor and evaluate their vendors' performance. This can include evaluating their performance against key performance indicators (KPIs) like delivery dates and quality and volume of goods.
5) Risk Monitoring and Management
Vendors must be monitored for risks that could impact the company, such as:
a) Compliance breaches
b) Lawsuits
c) Data security issues
d) Loss of intellectual property
Additionally, companies will need to monitor the risk that a vendor’s failure to provide goods and services may pose to company operations.
6) Payment Processing
This is the process of paying vendors for goods or services delivered to a business. The payment process ensures that vendors are paid accurately and in a timely manner. This process involves several steps, including:
a) Purchase order issuance
b) Invoice receipt and verification
c) Payment approval
d) Payment remittance
Looking to gain an in-depth understanding of the suppliers’ role in an organisation? Sign up for our Introduction to Supplier Management Course now!
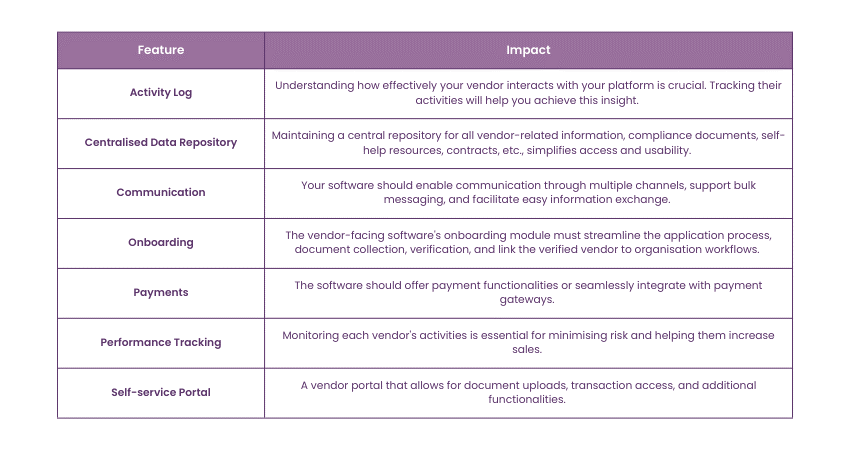
Key Features of a Vendor Management Tool
Vendor Management software tools make the process of onboarding and managing vendors easy, which includes merchants, suppliers, driving partners, and sellers. Here are the features of an ideal Vendor Management tool to consider:
Benefits of Using a Vendor Management Tool for Businesses
Once the right Vendor Management tool has been selected and implemented, it can offer numerous benefits and help streamline the Vendor Management process in various ways. These benefits are explored in detail below

1) Capture Inquiries and Conduct Screening
You may receive frequent business inquiries from sellers. In such cases, two main functions come into play:
a) Capture inquiry into your central system
b) Assign the request to the team for verification and onboarding
Sometimes, many of the inquiries might not fit your vendor selection criteria, such as the region they operate in or the scale they’re unable to meet. Manually vetting them could be a time-consuming process. A Vendor onboarding software qualifies leads based on predetermined criteria and ensures a high-quality funnel, preventing your team from wasting time on irrelevant merchants.
2) Automate Processes
Simple processes like applications, document collection, etc., can be automated by providing, for instance, self-serve portals to increase vendor self-listing. Vendor Management software can be used to map vendors to your team members for onboarding, vendor verification, and other operational tasks. Even if you are hosting an event, the tool can help you manage event ticketing and registration effortlessly.
Another use case of merchant management software is automating engagement campaigns. You can leverage software tools to ask for their feedback, share tips to increase sales, provide product and marketing updates and more.
3) Track Vendor Performance
You must keep an eye on vendor activities for two main reasons:
a) Mitigate risks like vendors supplying faulty products or not delivering on time
b) Identify best-selling products and top sellers
Vendor Management tools ease the process of tracking your vendors. You can utilise this information as part of your vendor risk management program to motivate sellers working hard to succeed on your platform. Additionally, software-driven insights will help you make informed business decisions.
4) Equip Teams with Advanced Tools
If your process requires your teams to, for instance, conduct field visits, Vendor Management tools can help. These software and apps allow your team to conduct field visits and update the vendor status easily.
Some of the benefits of using such tools for field teams are:
a) Share automated day plans with the team based on the leads assigned to them
b) Offer meeting recommendations
c) Track and ensure your team is at the right location and interacting with the right vendors
d) Gather documents and onboard vendors on the fly
Elevate your supplier quality assessment and enhancement skills in our comprehensive Supplier Quality Management Training - Sign up now!
Common Challenges in Traditional Vendor Management
Across regulated industries, procurement teams grapple with various challenges in traditional Vendor Management approaches, which, left unaddressed, could potentially have severe consequences. This includes the following challenges:
Limited Scalability and Flexibility
A combination of shared drives, spreadsheets, and emails lacks the scalability needed to adapt to evolving market dynamics and regulatory requirements. This lack of scalability hampers competitiveness, innovation, and agility, which could reduce competitive advantage and vendors' willingness to work with the business.
Manual, Paper-Based Processes
Procurement teams often put valuable time and resources into administrative tasks, leading to compliance breaches, missed deadlines, and increased operational costs. Manual processes also increase the risk of audit failures and data inaccuracies, which jeopardises regulatory compliance and tarnishes the organisation's reputation.
Difficulty in Risk Monitoring and Ensuring Compliance
Without systematic vendor monitoring and Risk Assessment capabilities, procurement teams struggle to detect, evaluate, and mitigate vendor risks effectively. Businesses may encounter quality issues, supply chain disruptions, data breaches, and compliance failures, leading to customer dissatisfaction, revenue loss, and regulatory scrutiny.
Lack of Centralised Visibility and Control
Relevant vendor information and contracts can be scattered across disparate documents and systems. This makes tracking vendor performance, monitoring compliance status and identifying potential risks challenging.
Due to this lack of visibility, the likelihood of missed renewal dates, contract discrepancies, and regulatory non-compliance increases, exposing the organisation to legal liabilities, financial penalties and reputational damage.
Get ready for your next role with top Management Interview Questions and Answers. Explore expert insights and ace your interview with confidence!
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective Vendor Management cultivates strong partnerships that drive long-term business success. As detailed in this blog, through strategic selection, continuous evaluation, open communication, and the use of Vendor Management tools, organisations can easily optimise their vendor relationships. This is the way to not only increase operational efficiency but create new avenues for innovation.
Learn the art of negotiating and managing supplier relationships in our Category Management Training - Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Considerations of Vendor Management?

Vendor Management involves several considerations to ensure efficient relationships with suppliers, including contract management, performance monitoring, Risk Management, legal considerations and communication.
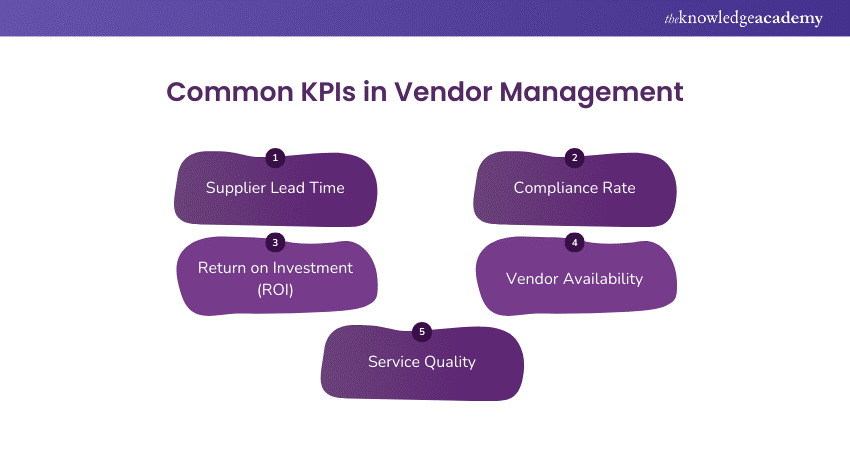
What is KPI in Vendor Management?

In Vendor Management, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) refers to the measurable metrics used to assess the performance of service providers and product suppliers.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Management Courses, including the Introduction to Supplier Management Course and the Business Process Improvement Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is Facility Asset Management.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Vendor Management, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Vendor Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Vendor Management Training
Vendor Management Training
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 17th Oct 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


