We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Ever wondered how much water fits in a perfectly round beach ball? Or perhaps you're baffled by the calculations needed to design a spherical spaceship? The answer lies in a powerful mathematical concept: the Volume of a Sphere. This seemingly complex idea unlocks the secrets of any object perfectly round.
This blog dives deep into understanding the Volume of a Sphere, offering a detailed explanation that goes beyond memorising a formula. We'll unveil the logic behind the volume equation, explore real-world applications, and equip you with the tools to solve any spherical volume problem with confidence!
Table of Contents
1) What is the Volume of a Sphere?
2) Volume of Sphere Formula with its Derivation
3) Formula for the Volume of a Sphere
4) Example for Volume of a Sphere
5) Applications of the Volume of a Sphere
6) What is the Ratio of the Volume of the Sphere and the Volume of the Cylinder?
7) What is the Relation Between the Volume of Sphere and the Volume of Cylinder?
8) Conclusion
What is the Volume of a Sphere?
The Volume of a Sphere is the total space enclosed within its surface. It is calculated using the formula V = (4/3) πr³, where r is the sphere's radius and π is approximately 3.1416. This formula helps determine the capacity of spherical objects like balls, planets, and bubbles. Similarly, the Volume of a Square follows specific geometric principles essential in various applications., similar to how the volume of a Cone can be calculated with a radius-dependent formula.
Volume of Sphere Formula with its Derivation
The Volume of a Sphere is given by the formula:
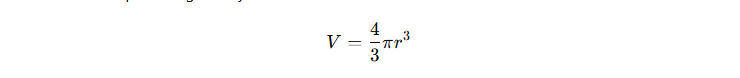
where:
a) V represents the volume of the sphere,
b) r is the radius of the sphere, and
c) π (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.1416.
Derivation of the Volume of a Sphere
The formula for the Volume of a Sphere can be derived using integral calculus. It involves revolving a semicircle around the x-axis to generate a three-dimensional sphere and then using the disk method to sum up the infinitesimally small circular slices of the sphere.
1) Consider a Sphere of radius r Centred at the Origin
The equation of a sphere in a Cartesian coordinate system is:
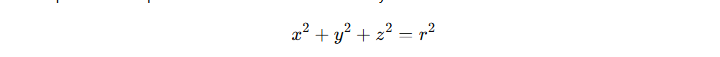
2) Using the Disk Method
A thin circular disk of radius y and thickness dx is taken along the x-axis. The volume of this small disk is:
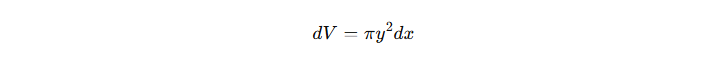
Since y^2=r^2+x^2 we substitute this into the equation:
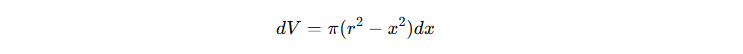
3) Integrating Over the Entire Sphere
To find the total volume, integrate from −r to r:
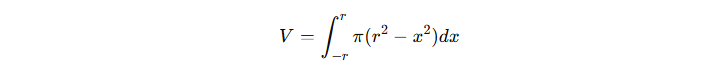
4) Solving the Integral
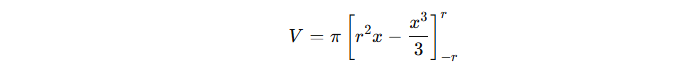
Evaluating the limits, we get:
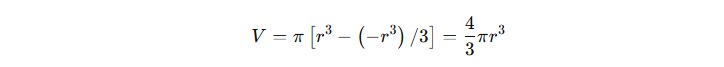
This derivation confirms the volume formula of a sphere, which is extensively used in geometry and applied sciences.
Formula for the Volume of a Sphere
Spheres, with their perfect roundness, are essential shapes in science, engineering, and even everyday life. Understanding their volume is crucial for tasks like calculating the amount of paint needed for a globe, the capacity of a spherical water tank, or even the volume of a basketball.
Volume of Solid Sphere
A solid sphere is a three-dimensional object where all the points on the surface are equidistant from the center. The formula for the volume of a solid sphere is the same as mentioned above:
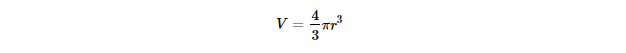
This equation means that to find the volume, you need to:
a) Cube the radius (r3).
b) Multiply by π.
c) Multiply by 4/3.
Example: If a solid sphere has a radius of 5 units:
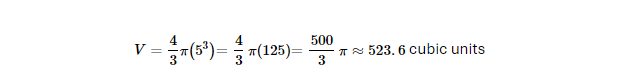
Volume of Hollow Sphere
A hollow sphere, also known as a spherical shell, has an inner radius (r1) and an outer radius (r2). The volume of a hollow sphere is the difference between the volume of the outer sphere and the volume of the inner sphere.
The formula for the volume (V) of a hollow sphere is:
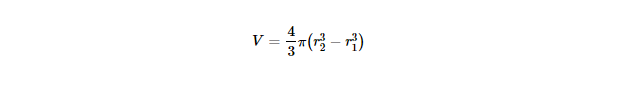
Where:
a) r2 is the outer radius.
b) r1 is the inner radius.
Example: If a hollow sphere has an outer radius of 6 units and an inner radius of 4 units:
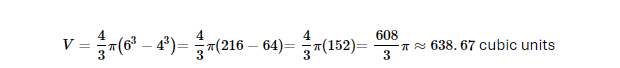
Unlock your potential! Register for our Personal Development Courses today to enhance your skills, boost your confidence, and realise your goals.
Example for Volume of a Sphere
Calculating the Volume of a Sphere is essential in various fields, including engineering, physics, and real-life applications. The formula for the Volume of a Sphere is:
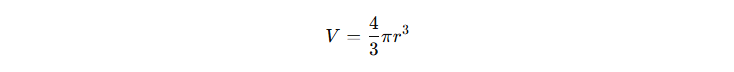
So, the volume of the sphere is approximately 1436.76 cubic units.
Real-Life Example: Basketball
Imagine you have a basketball with a radius of 12 cm. To find how much air it can hold, we use the formula:
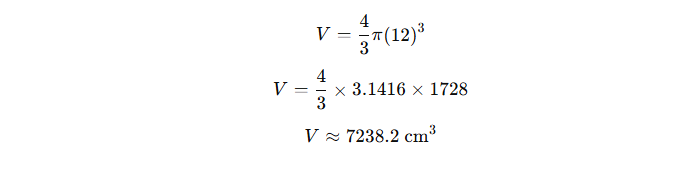
So, the basketball can hold approximately 7,238.2 cm³ of air.
Scientific Example: Water Droplet
A perfect spherical water droplet has a radius of 0.5 mm. Let’s calculate its volume:
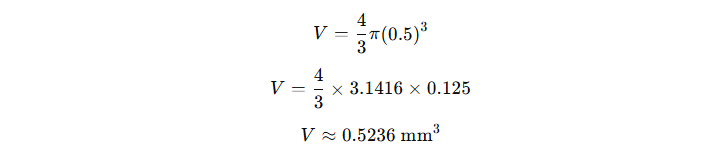
Even tiny water droplets hold measurable volume, which is crucial in meteorology and fluid dynamics.
Space Example: The Moon
The Moon is roughly a sphere with a radius of 1,737 km. Using the formula, its volume is:
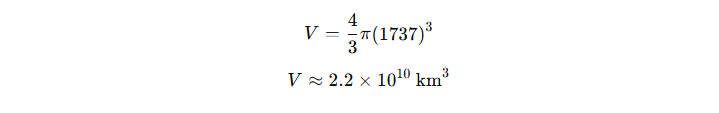
This immense volume helps scientists understand planetary mass and density.
Unlock the secrets of geometry, refer to our blog on the Volume of a Cuboid
Applications of the Volume of a Sphere
Here are 3 applications of the Volume of a Sphere:
1) Calculating Material Needs: The volume formula helps determine the amount of material needed for spherical objects. This applies in construction (concrete for spherical water tanks), manufacturing (metal for ball bearings), or even cooking (batter for round cakes).
2) Resource Measurement: Spheres are all around us! Scientists use volume to estimate resources like the amount of water in a spherical water droplet or the volume of oil in a spherical oil reserve. Understanding the volume of a cylinder and how it compares to spherical volumes allows us to manage these resources effectively and make accurate calculations in various scientific fields.
3) Engineering & Design: Spherical shapes are used in many engineered objects due to their efficient design. Engineers might use the volume formula to calculate the capacity of spherical pressure vessels, the volume displaced by a submarine, or even the volume of air a spherical parachute can hold.
Sharpen Your Skills. Train to Become a Top Engineer with our Engineering Skills Training now!
What is the Ratio of the Volume of the Sphere and the Volume of the Cylinder?
The ratio of the Volume of a Sphere to a cylinder (with the same radius and height as the sphere’s diameter) is 2:3. The sphere’s volume is (4/3)πr³, while the cylinder’s volume is πr²(2r) = 2πr³, giving a ratio of (4/3)πr³ : 2πr³ = 2:3.
What is the Relation Between the Volume of the Sphere and the Volume of the Cylinder?
A sphere and a cylinder with the same radius r and height 2r have related volumes. The sphere’s volume is (4/3)πr³, while the cylinder’s volume is 2πr³. The sphere occupies 2/3 of the cylinder’s volume, meaning one-third of the cylinder remains empty when a sphere is placed inside it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, calculating the Volume of a Hemisphere and sphere is straightforward with the formulas provided. Whether dealing with solid, hollow, or partial spheres, understanding these calculations is essential for various practical applications in geometry and engineering. Accurate volume measurement enhances our ability to design and analyze three-dimensional objects effectively.
Take charge of your future! Join our Career Development Course today and unlock the skills and strategies to advance your professional journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Rule for the Volume of a Sphere?

The rule for a sphere's volume is V = (4/3)πr³, where V is volume, π (pi) is a constant, and r is the sphere's radius.
Do Spheres Maximise Volume?

No, spheres don't always maximise volume! For a given amount of material, a sphere is efficient, but a cylinder can hold more volume with a flat top and bottom. Think tall cans versus round balls.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development Courses, including the Engineering Skills Training, Time Management Training and the Supervisor training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Best Courses After 12th.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Personal Development, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Engineering skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Engineering Skills Training
Engineering Skills Training
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


