We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Imagine you're streaming your favourite show, and the video plays seamlessly without a hitch. Behind this smooth experience lies an essential tool – the Content Delivery Network (CDN). But What is a CDN, and how does it ensure such flawless performance? It’s not just about speed; it’s about reliability, efficiency, and delivering content to users across the globe in the blink of an eye.
In the vast digital landscape, where seconds can make or break user engagement, understanding What is a CDN becomes crucial. It’s the invisible hand that accelerates website loading times and optimises the delivery of digital content. So, let’s dive into the world of CDNs, where faster and safer web experiences are just a click away.
Table of Contents
1) What is a CDN?
2) History of CDN Technology
3) How Does a CDN Improve Website Load Time?
4) How Does a CDN Work?
5) What are the Benefits of CDNs?
6) Who Uses CDNs?
7) Conclusion
What is a CDN?
A Content Delivery Network is a globally distributed network of servers designed to accelerate content delivery. It stores cached or temporary files on servers located in various regions to minimise latency.
When a user accesses a website or requests data, if the data server is far from the user, the data must travel across the internet, which can take a long time, especially for large files. CDNs solve this problem by storing data closer to the user, reducing the time it takes to access the content.
By increasing the efficiency of the internet, CDNs enable users to access large files more quickly from websites.
History of CDN Technology
Content Delivery Network technology emerged in the 1990s with the aim of speeding up content delivery across the internet. Nearly 30 years ago, CDNs were created to simply transfer data to users, and today they are the driving force behind every website delivering content.
Over time, developers have continuously improved and updated CDN technology to enhance User Experience within the internet ecosystem. Today, CDNs cover a significant portion of the internet, including web streaming, popular social media sites, downloadable software, hardware objects, and media.
Evolution of CDN by the Time
In the first phase, CDNs delivered only static content over the internet, focusing on networking principles and traffic management. The second generation saw the rise of demand for audio and video, transforming the concept to include on-demand videos and news on the internet.
Companies now use Cloud Computing techniques and peer-to-peer networks to boost content delivery. Currently, the third generation of CDN technology is still evolving, with AWS leading a new revolution among CDN service providers globally. The main focus of CDN providers is on managing bandwidth with the help of smart communication devices.
Master AWS skills with our AWS Certification Courses and accelerate your cloud career today!
How Does a CDN Improve Website Load Time?
When a website’s load time increases, traffic often drops as users shift to other sites. CDN services help mitigate this issue in several ways:
1) Global Network of Servers: CDNs consist of a worldwide network of servers that reduce the distance between users and website resources, resulting in faster content delivery.
2) Optimisation Techniques: Various hardware and software optimisation techniques enhance the speed of data transfer from the network to the user.
3) File Compression: CDNs use file compression methods to decrease file sizes, which reduces upload and browsing times, thereby improving overall site load times.
How Does a CDN Work?
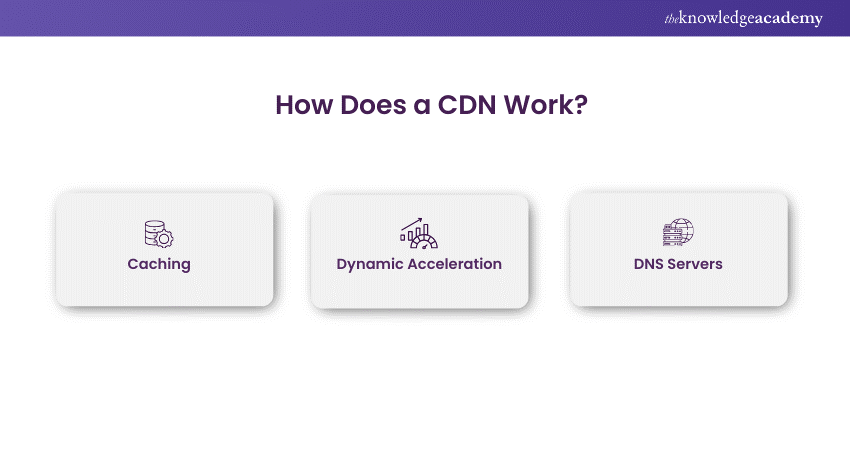
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) operate on principles such as caching, edge servers, dynamic acceleration, and DNS servers. They connect to multiple servers located globally to enhance performance.
Servers are placed at various network exchange points worldwide. These Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) are strategically located to boost speed and connectivity, reduce costs, and provide high-speed access. To understand how CDNs achieve this, let’s look at its key components:
1) Caching: Caching involves storing multiple copies of the same data for faster internet access. This principle can be applied to any memory or storage management system. Initially, a request reaches your static server, which stores a copy of the request. When the same request is made again, the static server responds instead of the origin server.
2) Dynamic Acceleration: Dynamic Acceleration reduces server response time for dynamic content requests. Direct requests to the server can be lost or delayed due to traffic. To prevent this, nearby CDN servers forward your request directly to the main server using a trusted connection, minimising network latency.
3) DNS Servers: The Domain Name System (DNS) tracks processes and supplies IP addresses for the origin server. When a user sends a request, it is saved on the DNS with the same name, allowing faster content delivery.
What are the Benefits of CDNs?
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) handle a significant portion of internet traffic and are widely used by both small companies and large corporations to provide optimal services to their customers. Here are some key benefits of using CDNs:
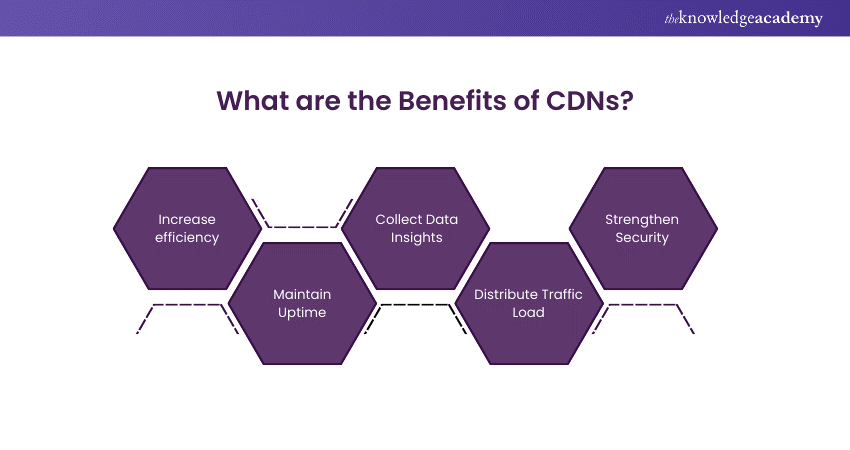
Increase Efficiency
CDNs increase efficiency and boost network performance, providing instant access to content. They minimise buffering time, which is the delay experienced while loading videos or websites. By delivering content quickly, CDNs significantly reduce loading times.
Maintain Uptime
CDNs are designed to maintain uptime by storing cached data at the network edge. Even if the hosting server is unavailable, edge servers can deliver the cached data to users. Technologies like load balancing and anycast routing help resolve issues and ensure continuous availability.
Collect Data Insights
CDNs collect valuable data insights using monitoring tools and software. This data includes user location, device type, browsing behaviour, and browser type, helping businesses understand and optimise user interactions.
Distribute Traffic Load
CDNs distribute traffic load across multiple servers and use load balancing software in data centres. This division of requests increases content delivery speed and balances data and traffic loads, enhancing overall performance.
Strengthen Security
CDNs protect data networks from attacks and unauthorised access. Key security practices include DDoS protection, SSL, and TLS encryption, which safeguard data and strengthen the security of the CDN.
Want to be a Backend Developer? Then this HTML and CSS Course is for you. Sign up now!
Who Uses CDNs?
Almost everyone who uses and browses the internet benefits from CDNs, as they were created to provide a better and faster online experience. Network service providers, content owners, and application owners use CDNs to deliver content smoothly and enhance speed for their users.
1) CDN for End Users:
Content delivered through CDNs, such as websites, videos, and applications, provides a more consistent online experience. Behind the scenes, technology works efficiently to ensure users enjoy these benefits seamlessly.
2) CDN for Network Service Providers:
Many network service providers deploy CDNs to enhance their services for customers. This facilitates the deployment of value-added services and reduces traffic on the origin network.
3) CDN for Content Owners:
Content and web application owners use CDNs to improve their customers’ online experience. CDNs also help secure networks and reduce the risk of DDoS attacks on data centres and networks.
Conclusion
In this blog, we've broken down What is a CDN and how it can drastically improve your website's speed and User Experience. With this knowledge, you now have the tools to enhance your website's infrastructure and ensure a seamless experience for your audience. Your passion for optimising web performance can now be turned into reality by implementing these simple yet powerful strategies. Let your website thrive with the support of a CDN!
Interested in learning Web Development? Sign up for our Web Development Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is CDN Good or bad?

Yes, Using CDN is good as it has many advantages, such as scalability, security and faster loading times. It reduces the gap between the user and content by lowering latency and improves user satisfaction and conversion rates.
What is a CDN Host?

It is the service that is provided by the content and application owners which gives access to the Content Delivery Network. CDN hosting platform can be a good alternative for web providers as it is cost efficient and more effective.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various App & Web Development Training, including the HTML, CSS and Node.JS Course, and the Web Development Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Web Development Training.
Our Programming and DevOps Blogs cover a range of topics related to CDN, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Programming and DevOps skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Programming & DevOps Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 MEAN Stack Web Development Training
MEAN Stack Web Development Training
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


