We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Imagine you’re working on your computer, creating a document, browsing the internet, or editing photos. All these tasks are made possible by Application Software. So, What is Application Software? It’s a type of program designed to help users complete specific tasks on a computer or device. Unlike system software, which helps the computer run, Application Software is created for tasks like writing, designing, or managing data. In this blog, we’ll dive into its functions, examples, benefits, and what you should consider when choosing the right software for your needs.
Application softwares are absolutely required to perform tasks for users. Whether it is creating a document, browsing the internet, or editing photos.
Table of Contents
1) What is Application Software?
2) Functions of Application Software
3) Need for Application Software
4) Types of Application Software
5) Examples of Application Software
6) Advantages and Disadvantages of Application Software
7) Differences Between System Software and Application Software
8) Factors you Should Consider When Choosing Application Software
9) Conclusion
What is Application Software?
Application Software is a type of program that helps you do specific tasks on a computer or device. It is different from system software, which helps the computer run. Examples include programs like word processors, web browsers, and games. Word processors help you write documents, while web browsers let you browse the internet.
Media players allow you to watch videos or listen to music. Application Software is made to help users complete everyday tasks. It can be installed on a computer, smartphone, or tablet, and is essential for completing various activities.
Functions of Application Software
Application Software is designed to help with various tasks. Here are some examples:
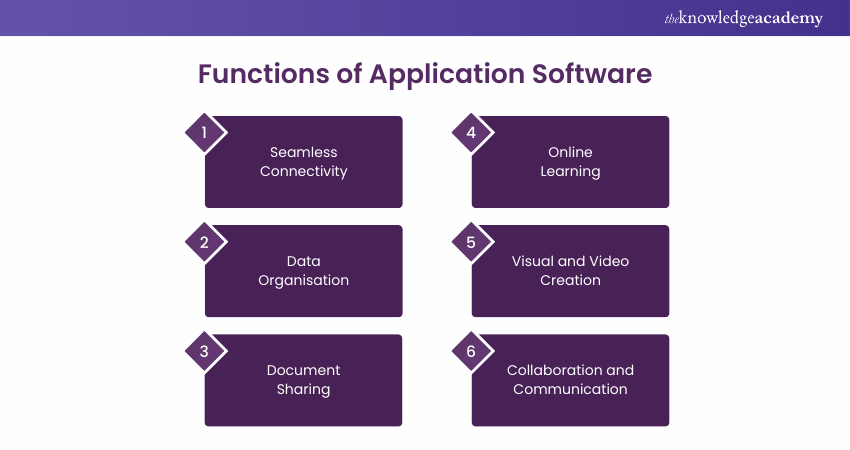
a) Healthcare Software: Ensures seamless connectivity and quick responses. It helps in managing patient records and scheduling appointments efficiently.
b) Information Management: Helps manage and organise data within an organisation. This software can streamline data storage and improve data retrieval processes.
c) Document Management: Assists in managing and checking documents. It allows for easy document sharing and ensures version control.
d) Educational Software: Includes Learning Management Systems (LMS) and e-learning platforms. These tools facilitate online learning and track student progress.
e) Visual and Video Development: Used for creating presentations. It helps in designing engaging visuals and editing videos for various purposes.
f) Communication Tools: Includes emails, text messaging, and audio/video conferencing. These tools enhance collaboration and ensure effective communication.
g) Accounting and Payroll Management: Supports HR and business financial tasks. It automates payroll processing and manages financial records accurately.
h) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Integrates core business processes. ERP systems improve resource planning and optimise operational efficiency.
i) Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Manages interactions with customers. CRM software helps in tracking customer interactions and improving customer service.
j) Project Management: Helps manage projects of any size. It assists in project planning, resource allocation, and tracking project progress.
k) Business Process Management: Ensures smooth and efficient business operations. This software helps in automating workflows and improving process efficiency.
Unlock your potential in Software Engineering – sign up today for our Software Engineering Training
Need for Application Software
End-users use Application Software to perform single or multiple tasks. Here are a few reasons why Application Software is essential:
a) Helps the User in Completing Specified Tasks: It is designed with the user in mind. It assists users with specialised tasks in various industries, such as education, business, and entertainment. For example, Microsoft Word allows users to create, edit, and manage Word documents efficiently.
b) Manages and Manipulates Data: Businesses use Application Software to handle and manipulate data related to employees, customers, and other databases. Common examples include Enterprise Resource Management (ERM) systems and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems.
c) Allows Users to Effectively Organise Information: Application software helps users create and manage large amounts of data efficiently. For instance, Microsoft Excel is widely used to manage spreadsheets and perform data analysis.
Types of Application Software
Application Software can be categorised based on its cost and accessibility. Here are some types:
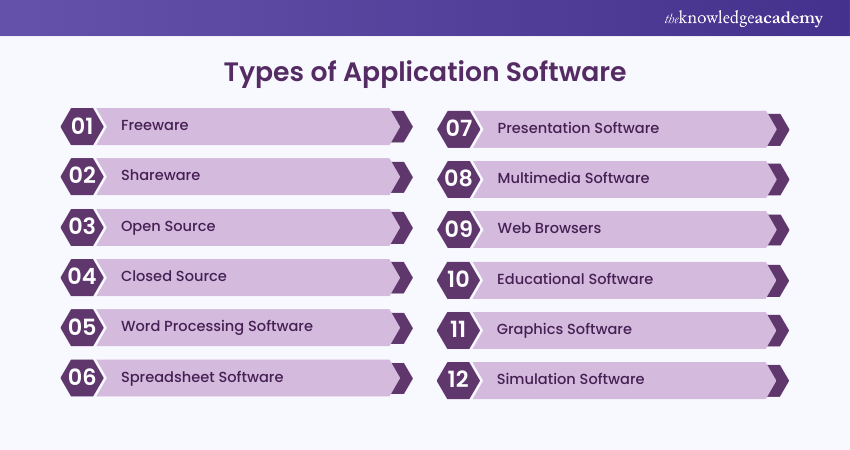
a) Freeware: This software is available for free. Users can download and use it without any cost, but they cannot modify or sell it. Examples include Adobe PDF, Mozilla Firefox, and Google Chrome.
b) Shareware: This software is provided for free on a trial basis, usually with a time limit. Users must pay to continue using it after the trial period. Examples include WinZip, antivirus programs, and Adobe Reader.
c) Open Source: This software comes with its source code, allowing users to modify and add features. It can be free or paid. Examples include Moodle and Apache Web Server.
d) Closed Source: Most Application Software falls into this category. It is usually paid, and the source code is protected by intellectual property rights (IPR) or patents. Examples include Microsoft Windows, Adobe Flash Player, WinRAR, and macOS.
e) Word Processing Software: This software allows users to create, edit, and save documents. An example is Microsoft Word.
f) Spreadsheet Software: This software is used for managing worksheets and performing numerical calculations. An example is Microsoft Excel.
g) Presentation Software: It is used to create and display presentations. An example is Microsoft PowerPoint.
h) Multimedia Software: This software handles a mix of audio, video, images, and text. Media players are common examples.
i) Web Browsers: These applications are used to access the internet. Examples include Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox.
j) Educational Software: This software supports learning and education. Examples include language learning software and classroom management tools.
k) Graphics Software: This software is used for creating and editing images and graphics. Examples include Canva and Adobe Photoshop.
l) Simulation Software: It is used to simulate real-world processes and evaluate different scenarios. It is often used in training and research.
Examples of Application Software
A wide range of Application Software programs are available to help you manage tasks, take notes, conduct online research, set alarms, maintain logs, and even play games. It is designed to perform specific tasks, streamline workflows, and enhance team communication. Here are some of the most commonly used applications by millions of people daily:
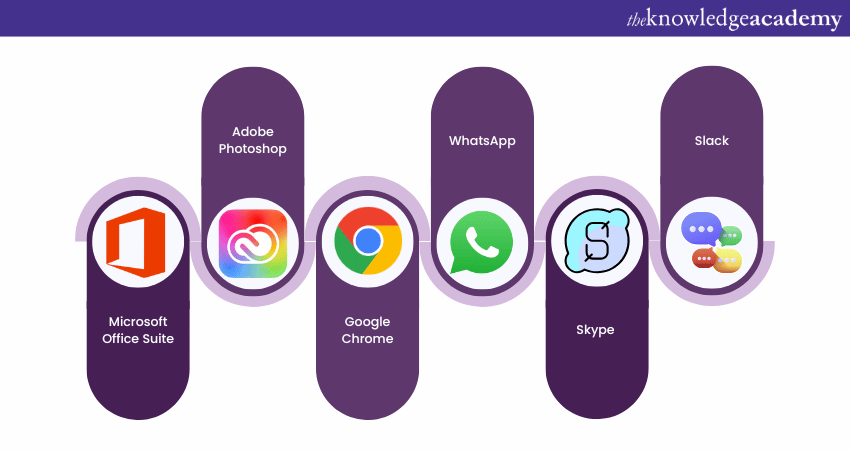
a) Microsoft Software Suite: Includes MS Office, PowerPoint, Word, Excel, and Outlook. These tools are essential for creating documents, presentations, spreadsheets, and managing emails.
b) Internet Browsers: Popular browsers like Google Chrome, Safari, and Firefox are used for accessing the web and conducting online research.
c) Graphics and Design Software: Tools such as Canva, Adobe Photoshop, CorelDraw, and AutoCAD are used for creating and editing graphics and designs.
d) Real-time Communication Tools: Applications like Skype, Hangouts, Google Meet, Zoom, and WhatsApp facilitate video and audio calls, as well as messaging.
e) Multimedia and Music Streaming Software: Programs like Wynk, Gaana, MX Player, VLC Media Player, Spotify, and Pandora are used for entertainment, including streaming music and videos.
f) Project Management Software: Tools such as Teams, Asana, Zoho, Slack, and Forecast are used for managing projects and enhancing team collaboration.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Application Software
Application Software, with its diverse range of functions and capabilities, plays an integral role in our digital lives. However, like any tool, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let's explore these in detail:
Advantages of Application Software
The following are some advantages of Application Software:
1) Enhanced Productivity: Application Software streamlines tasks, making them more efficient and less time-consuming. For example, word processing software automates formatting, saving users hours of manual effort when creating documents.
2) Specialisation: One of the key benefits of Application Software is its specialisation. Users can choose software tailored to their specific needs. This ensures that the software they use is optimised for the task at hand, whether it's graphic design, accounting, or Project Management.
3) Improved Creativity: Many Application Software tools are designed to foster creativity. Graphic Design Software, for instance, provides a platform for artists and designers to bring their vision to life. This encourages innovation and artistic expression.
4) Convenience: Application Software simplifies complex processes, making them accessible to users with different levels of expertise. This convenience is particularly important in a world where technology plays a key role in our daily lives.
5) Scalability: Application Software often offers the advantage of scalability. Businesses can start with a basic version of the software and then scale up as their needs grow. For example, a small business may begin with a simple accounting software package and later transition to a more comprehensive solution as it expands. This scalability ensures that the software can adapt to changing requirements without the need for a complete overhaul.
6) Collaboration and Connectivity: Many Application Software tools are designed with collaboration in mind. They offer features that enable users to work together seamlessly, even if they are geographically dispersed. For instance, cloud-based office suites like Google Workspace facilitate real-time collaboration on documents, enabling multiple users to edit and comment on files simultaneously. This connectivity promotes teamwork and productivity, especially in today's global and remote work environments.
Disadvantages of Application Software
The following are some disadvantages of Application Software:
1) Cost: High-quality Application Software can be expensive. Licenses, subscriptions, and upgrades can add up, making it a significant investment for individuals and businesses. This cost can be a barrier to access for some users.
2) Compatibility Issues: Not all Application Software is universally compatible. Some software may work seamlessly on one Operating System but encounter challenges on another. Similarly, hardware limitations can restrict the use of certain software.
3) Security Risks: Security is a significant concern with Application Software. Malicious software, commonly known as malware, can compromise the integrity of a system or steal sensitive data. Users need to be vigilant and use reputable software from trusted sources to mitigate these risks.
4) Learning Curve: Complex Application Software often has a steep learning curve. Users may need to invest time and effort in learning how to use the software effectively. This initial learning period can slow down productivity.
5) Maintenance and Updates: Application Software requires regular maintenance and updates to remain secure and functional. Users need to ensure they keep their software updated, which can be time-consuming and occasionally disruptive.
6) Resource Intensive: Some Application Software can be resource-intensive, requiring powerful hardware to run smoothly. This can be a disadvantage for users with older or less powerful devices, as they may experience performance issues.
Unlock your potential in Software Development with our comprehensive Software Development Lifecycle Training
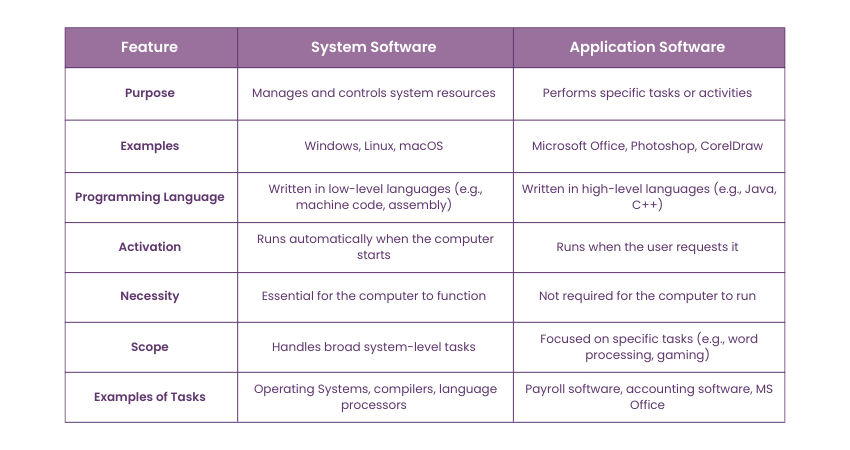
Differences Between System Software and Application Software
System Software and Application Software serve different purposes on a computer. The Windows Operating System is a good example of System Software, while programs like Microsoft Office, Photoshop, and CorelDraw are examples of Application Software.
Factors you Should Consider When Choosing Application Software
The following are some factors you need to consider before you choose the Application Software that best suits your needs:
a) Purpose: Ensure the software is designed for the specific task you need to complete. It should match your requirements, whether it's for writing, design, or data management.
b) Ease of Use: The software should have a user-friendly interface. You want to be able to use it easily without needing a lot of training.
c) Cost: Compare prices to see if the software fits your budget. Some software offers free versions, while others may charge a one-time fee or subscription.
d) Compatibility: Make sure the software works well with your Operating System and other programs you use. It should integrate smoothly into your existing setup.
e) Features: Check if the software provides the features you need. It should offer the right tools without being too complex or missing key functions.
f) Support and Updates: Look for software that provides reliable customer support. Regular updates help improve performance and fix any bugs or security issues.
g) Security: Ensure the software protects your data from potential threats. It should have strong security measures to keep your information safe.
Conclusion
We hope this blog has helped you understand “What is Application Software” and its importance in our daily lives. Application Software is designed to perform tasks on a computer or device. Whether it’s for work, entertainment, or communication, it plays a key role in enhancing productivity. By considering the right factors, you can choose the best software to suit your needs.
Unlock the world of software design and architecture with our comprehensive Software Design and Architecture Training.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Difference Between "On-premises" and "Hosted" Application Software?

"On-premises" software is installed and run on a company's own computers or servers. "Hosted" software, on the other hand, is stored and managed on remote servers, often by a third party, and accessed via the internet.
How can you Differentiate Between an App and an Application?

An app is typically a smaller, simpler program designed for mobile devices or specific tasks. An application is a broader term that can refer to any software designed to perform a set of tasks, often including larger programs for computers.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Software Engineering Courses, including the Software Design and Architecture Training, Systems Engineering Training, and Software Development Lifecycle Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Information Importance of Technology.
Our Programming & DevOps Blogs cover a range of topics related to Software Application, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Software Application knowledge, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


