We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Money-making opportunities are everywhere—you just need to know where to look. Knowing about “What is Arbitrage” is about finding price differences: buying something where it’s cheaper and selling it where it’s more expensive. It’s a simple and century old idea, from trading goods between countries to swapping profitable currencies.
In this blog, we will break down What is Arbitrage, the different ways it’s done, how it works, and the pros and cons of this clever strategy, with real-life examples to show how it all comes together. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Arbitrage
2) Different Types of Arbitrages
3) How Does Arbitrage Work?
4) Arbitrage Trading Conditions
5) Benefits of Arbitrage
6) Drawbacks of Arbitrage
7) Conclusion
Understanding What is Arbitrage
Arbitrage is a trading form when someone buys an item in one place where it's comparatively cheaper and sells it in another place where it's significantly expensive, making a profit from the price difference. Professionals who do this are called Arbitrageurs, and they trade Stocks, Bonds, Contracts, commodities (like oil or grain), and currencies (like Dollars or Euros).

For example, imagine $1,800 per ounce is US gold price but is selling for $1,850 per ounce in the UK. An Arbitrageur could buy gold in the US and sell it at a higher price in the UK, making a $50 profit per ounce (minus any transaction costs). This is how arbitration works—taking advantage of price differences in two markets for profit earning.
Different Types of Arbitrages
Arbitrage can take diverse forms depending on the market or asset involved. It typically involves exploiting price differences across different locations, countries, or even currency markets.
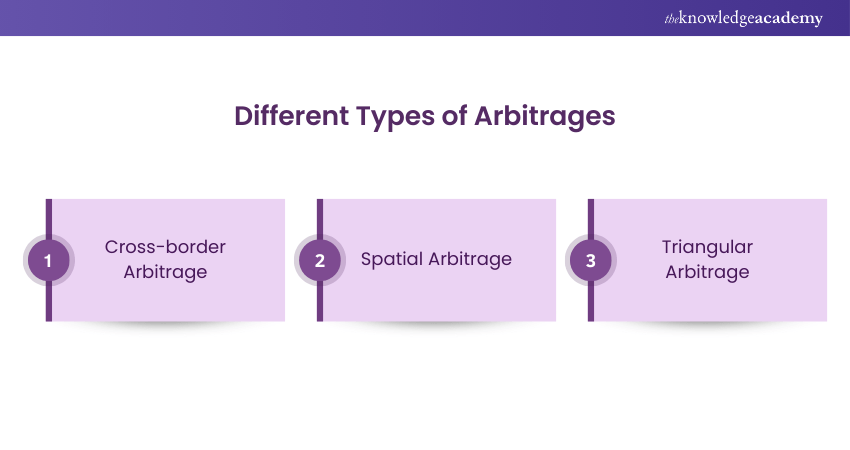
1) Cross-Border Arbitrage
a) This type focuses on exploiting price differences for assets or commodities in different countries.
b) Arbitrageurs take advantage of market exchange rates, tariffs, or differing conditions fluctuations between nations to buy low in one country and sell it at higher price in another country.
c) For instance, particular asset’s (like a stock or commodity) price might be cheaper in the U.S. than in Japan. An Arbitrageur could buy it in the U.S. and sell it in Japan, profiting from the differences in price.
2) Spatial Arbitrage
a) This involves product buying or assets in one location where it is lower priced and selling it in another location with a higher price.
b) The price differences can occur within a single country or between different states or cities.
c) This Arbitrage type relies on the fact that prices can differ between different locations due to local market conditions and supply chain.
3) Triangular Arbitrage
a) This Arbitrage form deals specifically with the foreign exchange (Forex) market’s currency.
b) The process involves exchange rates discrepancies of the three different currencies.
c) If the currency’s exchange rates don’t perfectly align, the trader can make a profit.
d) For example, if the exchange rates are off by small amounts, the trader will end up with more of the original currency (USD) than they started with, capturing the profit from the differences in conversion rates.
Master blockchain markets with Cryptocurrency Trading Training- Sign up today!
How Does Arbitrage Work?
Arbitrage is a strategy that allows traders to have an advantage over different market price differences. It involves a single market asset purchase where it’s cheaper and simultaneously selling it in another market at a higher price, making a profit from the difference.
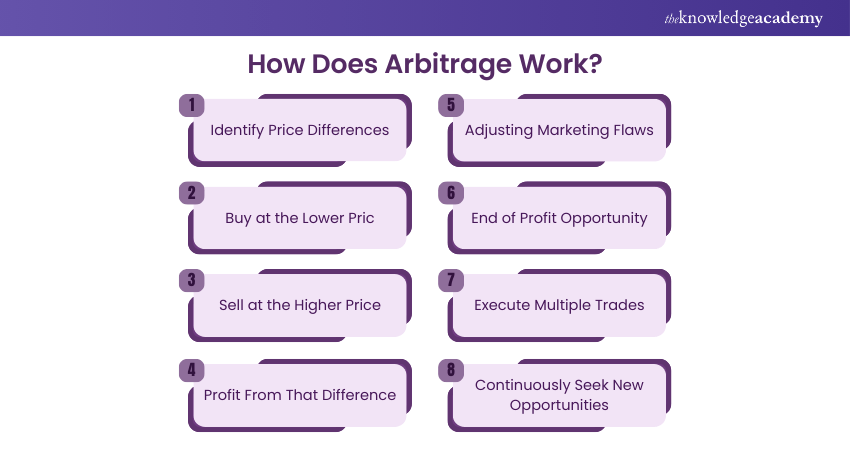
1) Identify Price Differences: The first step in identifying the same asset’s price, security, or commodity differences is to identify them across two different markets or exchanges. For example, a stock might be at a lower price on one exchange and higher on another.
2) Buy at the Lower Price: Once there is a price difference identification, the Arbitrageur buys the asset at the lower price in the first market or exchange.
3) Sell at the Higher Price: The Arbitrageur then performs the same asset selling in the second market or exchange with the higher price.
4) Profit: From That Spread The prices difference between the two markets is known as the Spread, and this spread is the profit the Arbitrageur makes.
5) Adjusting Marketing Flaws: By exploiting the price difference, the Arbitrageur helps improve market efficiency by correcting the pricing flaw. As the market adjusts, there is a considerable shrinking of the price difference.
6) Market Correction Phase: Once the market corrects itself, the price difference disappears, and the opportunity for Arbitrage profit ends.
7) Execute Multiple Trades: In efficient markets, prices are stable and don’t drastically change. Therefore, to make a meaningful profit, arbitrageurs often need to execute multiple trades across different markets.
8) Continuously Seek New Opportunities: Since Arbitration opportunities are usually short-lived, arbitrageurs must constantly look for new price differences to exploit and make profits.
Arbitrage Trading Conditions
Arbitrage opportunities arise during the prices discrepancies between different markets or assets. These price differences can create profit chances under certain conditions.
1) Same Asset Price Difference: If the same asset is differently price in two markets, an Arbitrageur can buy it where it's cheaper and sell it where it's more expensive.
2) Similar Assets Price Difference: If two assets with the same value (like Stocks) are differently priced in two markets, an Arbitrageur can profit from the price difference. This can happen if there is better performance performing better than another.
3) Future Price Differences: Sometimes, assets or commodities may have a known future price but are today priced lower. If this happens, an Arbitrage opportunity exists where the asset can be bought at a comparatively lower price now and sold for a higher price in the future.
Trade smarter with advanced Forex market insights- Join our Forex Trading Course today!
Benefits of Arbitrage
Arbitrage offers various traders and financial market benefits. By exploiting price differences across different markets, Arbitrage helps improve market efficiency and provides unique profitable opportunities.
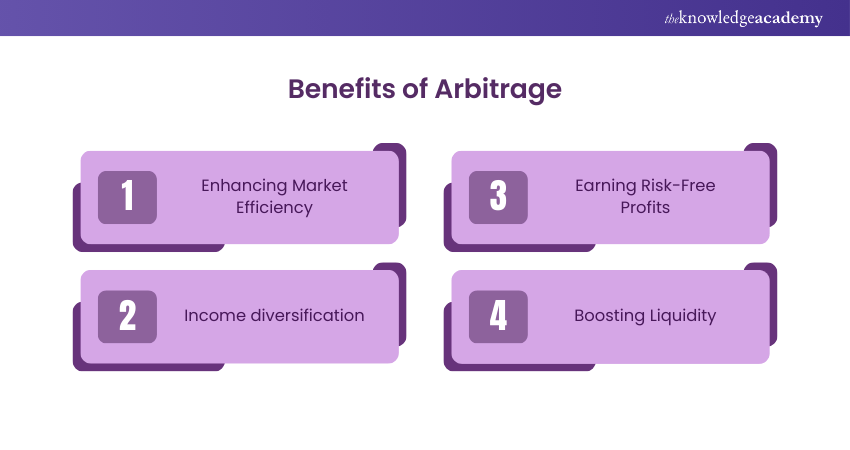
1) Enhancing Market Efficiency
Arbitrage helps improve market efficiency by correcting price discrepancies. When Arbitrageurs exploit price differences, they bring the asset prices closer to their true value. This ensures that prices are more accurately aligned across markets.
This process benefits the market comprehensively, making it more efficient and ensuring that assets are fairly priced, which ultimately leads to markets that is more stable and transparent.
2) Earning Risk-Free Profits
Arbitrage provides a distinct trader’s opportunity to earn profits with minimal or no risk. By identifying the same asset’s price differences in different markets, traders can buy low in one market and sell high in another.
Since the transactions simultaneously occur, the trader’s market fluctuations fluctuation is very limited, making it one of the safest profitable ways in the financial markets.
3) Boosting Liquidity
The Arbitrageurs' activities increase market liquidity by narrowing the bid-ask spread, which is the price difference a buyer is willing to pay and the price a seller asks for an asset. By doing so, they help create a more efficient market where prices reflect true value more accurately.
Drawbacks of Arbitrage
While Arbitrage can be a significant and profitable strategy, it also comes with certain levels of minor risks and drawbacks for beginner-level traders. Let’s unveil those below:
1) High Transaction Costs
Beginners often overlook the various Arbitrage Trading’s transaction costs, such as broker fees, commissions, and taxes. These costs can quickly perform the potential profit addition, reduction, and elimination, especially if there is a small price difference between markets. Moreover, it’s important to account for all these costs before making profitable trades
2) Potential Model Risk
Using information that is not accurate can significantly impact trading decisions. Market conditions, prices of assets, quick economic factor changing, and relying on old Data can lead to poor judgment and missed opportunities. Beginners need access to data in real-time and the ability to make quick, informed decisions for Arbitrage Trading success.
3) Liquidity Risk
Arbitrage Trading requires quick multiple trades execution. If there is a slow market or low liquidity (i.e., not enough buyers and sellers), there are price-changing risks before the completion of trades, leading to losses.
4) Regulatory and Legal Risk
Different markets have different regulations that can affect trading strategies. Beginners might not be fully aware of the legal constraints or market rules that govern trade in different countries or exchanges.
Real-World Examples of Arbitrage
Arbitrage is a strategy with the profit of the traders by taking advantage of different market price differences. The following examples show how this strategy works in various situations.
1) Stock Arbitrage: A phone company’s stock is priced at $25 on the NYSE and $25.50 in Shanghai. The trader buys the stock for $25 on the NYSE and sells it for $25.50 in Shanghai, making a 50-cent profit.
2) Art Arbitrage: An Impressionist painting costs $10,000 in London but only $4,000 in America. The trader buys the painting in America and sells it in London for a $6,000 profit.
3) Currency Arbitrage: A trader has 1 million Canadian dollars (CAD) and exchanges it through three banks at different rates. After converting the money between Euros, USD, and CAD, the trader ends up with 1,000,896.13 CAD, earning a profit of $896.13.
Streamline results with advanced Sales Analytics techniques- Our Sales Analytics techniques awaits!
Conclusion
Understanding “What is Arbitrage” and its potential to generate profits from price differences across various markets opens exciting and lucrative opportunities. While the strategy offers minimal risk when it is effectively executed, incorporating Forex Market Analysis is crucial to be aware of the associated costs, regulatory requirements, and challenges. By mastering the Arbitrage complexities, traders can transform market inefficiencies into profitable ventures.
Drive results with advanced selling methodologies- Register for our Value Based Selling Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Arbitrage Good or Bad?

Arbitrage is neither inherently good nor bad; it’s a kind of strategy. It benefits traders by exploiting profit’s price differences while enhancing the efficiency of the market. However, it requires expertise and risks, costs, and regulations awareness. If done in a responsible way, it can be a valuable financial growth tool.
Why Is Arbitrage Illegal?

Arbitrage itself is not illegal; it is a legitimate trading strategy. However, it becomes unlawful when it involves unethical practices, such as market manipulation insider trading, or exploiting privileged information. Regulations ensure fair markets and prevent unfair advantages in Arbitrage activities.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Investment and Trading Training, including Investment Management Course, Cryptocurrency Trading Training, and Forex Trading Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Revenue Forecasting.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to professional development and workplace efficiency, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your business and leadership skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Investment Management Course
Investment Management Course
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


