We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Understanding the fundamentals of computer systems starts with answering an essential question: What is BIOS? The BIOS is a crucial component that initialises the hardware, performs system checks, and loads the Operating System (OS) when a computer starts. Acting as the bridge between hardware and software, it ensures smooth communication and efficient functionality. Without BIOS, a computer wouldn't know how to start up or interact with its components.
As technology has evolved, traditional BIOS has largely been replaced by UEFI, offering enhanced security and faster boot times. However, learning What is BIOS remains essential for troubleshooting, updating firmware, and optimising system performance. In this blog, we’ll discuss its meaning, types, and how it works. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
1) What is BIOS?
2) Why is BIOS Required?
3) How Does BIOS Work?
4) Types of Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
5) Key Functions of BIOS
6) How to Update or Upgrade Your BIOS?
7) How to Fix BIOS?
8) How Do I Reboot My Computer Into the BIOS?
9) Conclusion
What is BIOS?
The BIOS is firmware stored in ROM or flash memory on a computer’s motherboard. It initialises hardware components and performs system checks when the computer starts. BIOS acts as an interface between the hardware and the Operating System, ensuring everything functions correctly before loading the OS.
Knowing the importance of BIOS is essential because it handles critical system settings like boot sequences, hardware setups, and security functionalities. Even though BIOS played a key role in old PCs, it has largely been replaced by the more advanced Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI), which offers enhanced speed, security, and compatibility with modern hardware, including RAM and ROM.
Why is BIOS Required?
The BIOS carries out numerous crucial functions for a computer's operation.

1) Checks System Power: The system's power is checked by the BIOS, which performs a Power on Self-Test (POST) to confirm hardware initialisation upon being switched on. A successful POST will generate a beep sound, while failures will produce distinct beep patterns to indicate errors.
2) Boot Process Assistance: BIOS is essential for finding software and starting the boot process, residing on a ROM or flash memory chip.
3) Security Protection: Enhancing system security is achieved through BIOS updates that patch security vulnerabilities, such as the Lenovo laptops update that addressed exploitable bugs.
4) Addresses Performance Issues: BIOS updates address motherboard-related issues impacting system performance, particularly for long-standing issues not addressed by OS updates.
5) Loads Operating System: BIOS loads the operating system (OS) by using a bootstrap loader to search for and load a functional OS and installs necessary drivers for controlling hardware.
6) Password Protection: Password protection feature in BIOS enables secure access to the system during boot up, however resetting forgotten passwords can be a challenging task.
7) Enhances IT Outcomes: Adjusting BIOS settings enhances PCIe speed, boosts data integrity, and lowers connectivity issues, enabling advanced IT capabilities such as AI and cloud services.
How Does BIOS Work?
Here are the steps on how BIOS works:
1) Power-On Self-Test (POST)
a) When the computer starts, BIOS performs a self-test to check the functionality of essential hardware components like RAM, CPU, keyboard, and storage drives.
b) If a problem is detected, BIOS may produce beep codes or error messages indicating the issue.
2) Initialising Hardware
BIOS configures and initialises system components such as:
a) Processor
b) Memory (RAM)
c) Hard drives or SSDs
d) Graphics card
e) Input devices (keyboard, mouse)
3) Finding the Boot Device
a) BIOS looks for a bootable device based on the boot sequence (set in BIOS settings).
b) It checks storage devices like HDDs, SSDs, USB drives, or network boot sources.
4) Loading the Bootloader
a) Once a bootable device is found, BIOS hands over control to the bootloader (like GRUB for Linux or Windows Boot Manager).
b) The bootloader then loads the Operating System into RAM.
5) Transition to the Operating System
a) After the OS takes over, BIOS is no longer actively used, but it may still provide low-level services via the System Management Mode (SMM).
Master essential tools and improve efficiency with our End User Training – join now!
Types of Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
The different types of BIOS play unique roles in handling hardware and ensuring seamless communication between the computer’s components and operating system.
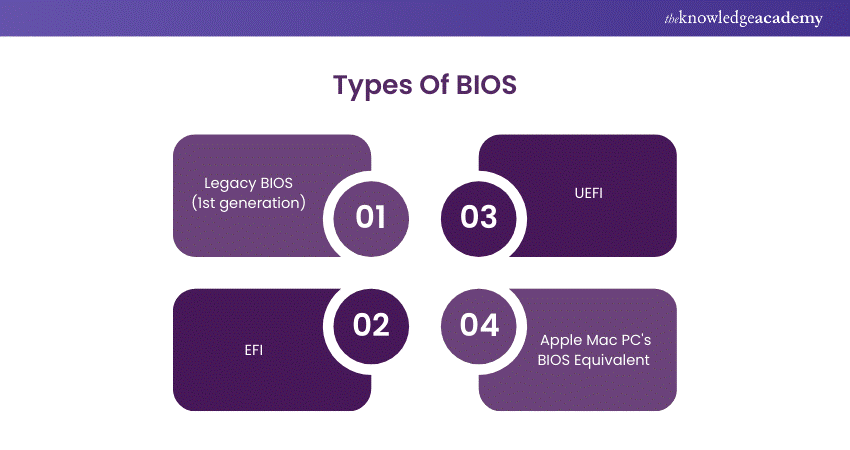
1) Legacy (1st generation) BIOS
In older motherboards, Legacy BIOS firmware is employed to boot up computers, featuring text-based menus and restricted compatibility. It is unable to detect disks over 2.1 terabytes and does not have contemporary flexibility in CPU and components.
2) EFI
Intel created Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) to fix issues with BIOS, establishing a universal firmware standard that does not require architecture-specific frameworks. The UEFI standards are maintained by the Unified EFI Forum, which consists of Apple, Intel, Microsoft, and IBM, and have evolved from EFI's original design.
3) UEFI
Launched in 2002, Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) enables disks larger than 2.2 TB with the GUID Partition Table (GPT) and provides enhanced scalability, security, and performance. Unlike BIOS, UEFI does not need a distinct bootloader and has an improved user interface, which increases performance.
4) Apple Mac PC's BIOS Equivalent
Apple Macs utilise Intel's EFI, which evolved into UEFI, as a substitute for BIOS, enabling compatibility with expansive boot disks and drivers integrated into the firmware. UEFI manages different boot procedures on Macs, such as selecting boot disks by pressing the option key but does not offer hardware configuration options in the traditional BIOS style.
Kickstart Your Tech Career with our LINUX Fundamentals Course – Sign up today!
Key Function of BIOS
The key functions of BIOS are vital for initialising hardware, managing system settings, and ensuring a smooth startup process.
1) Power-On Self-Test (POST)
The initial task done by BIOS after the computer is started is POST, which verifies all hardware parts. If a crucial part malfunctions, the system might not start up, and a sequence of beeps will show what the issue is.
2) Bootstrap Loader
Once POST is finished, the BIOS starts the bootstrap loader to locate the Operating System in its specified storage area. When located, BIOS transfers control to the Operating System, enabling the computer to complete its startup process.
3) BIOS Drivers
BIOS drivers are necessary software pieces that facilitate communication between the Operating System and hardware, like the keyboard, mouse, and display. These drivers make sure the system can identify and communicate with hardware prior to loading more drivers.
4) BIOS (CMOS) Setup
The BIOS setup, which is also called CMOS setup, enables users to modify system settings and hardware configurations. It allows for alterations such as controlling boot sequence, adjusting system time, and modifying hardware detection process at boot. This interface allows for the management of important system functions.
How to Update or Upgrade Your BIOS?
Updating or upgrading your BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) can improve system stability, compatibility, and performance. However, it carries some risks, so follow these steps carefully.
Step 1: Check Your Current BIOS Version
a) Before updating, check your BIOS version to see if an update is necessary.
Windows:
a) Press Win + R, type msinfo32, and hit Enter.
b) Look for BIOS Version/Date.
Command Prompt:
a) Open Command Prompt (Win + R, type cmd, hit Enter).
b) Type:
|
wmic bios get smbiosbiosversion |
c) Press Enter to see the current BIOS version.
Step 2: Identify Your Motherboard Model
a) If using a desktop, check the motherboard model using:
|
wmic baseboard get product,manufacturer |
b) If using a laptop, visit the manufacturer’s website and search for updates using your laptop model.
Step 3: Download the BIOS Update
1) Go to the Manufacturer’s Website
a) For prebuilt PCs (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo), visit their support page.
b) For custom-built PCs, visit your motherboard manufacturer’s website.
2) Find the Latest BIOS Version
a) Compare it with your current version.
b) Download the correct BIOS file.
3) Read the Release Notes
a) Ensure the update fixes an issue or provides improvements relevant to you.
Step 4: Prepare for the Update
a) Backup Important Data: A failed BIOS update can make your system unusable.
b) Ensure Stable Power: Use a UPS (for desktops) or keep your laptop plugged in.
c) Create a Bootable USB Drive (if required): Some updates require booting into a flash drive.
Step 5: Update the BIOS
Method 1: Using Windows Update Utility (If Available)
a) Some manufacturers provide an executable file to update BIOS directly from Windows.
Method 2: BIOS/UEFI Firmware Update
a) Copy the BIOS update file to a USB flash drive (FAT32 format).
b) Restart your PC and enter BIOS/UEFI (F2, F12, DEL, or ESC depending on your system).
c) Look for an option like "EZ Flash," "M-Flash," or "Q-Flash."
d) Select the BIOS file from the USB drive and start the update.
e) Wait for the update to complete (DO NOT turn off your PC during this process).
Step 6: Verify the Update
a) After restarting, enter BIOS again and check if the new version is installed.
b) Restore BIOS settings if necessary (some settings may reset to default).
Step 7: Reconfigure BIOS Settings
a) Enable or disable features based on your previous configuration.
b) Adjust boot order if needed.
How to Fix BIOS?
To repair BIOS problems, reset it by taking out and putting in the CMOS battery or applying the BIOS reset jumper. Alternatively, you may update the BIOS through the website of the manufacturer or enter the BIOS to default settings. In case the problem still exists, look for hardware malfunctions or consult a professional.
How Do I Reboot My Computer Into the BIOS?
To access BIOS, reboot your computer and tap the BIOS key (e.g., F2, F10, DEL, or ESC) on startup. The key depends on the manufacturer. If fast boot blocks access, utilise Windows' Advanced Startup (Shift + Restart) to go to UEFI settings and enter BIOS.
Conclusion
We hope now you know why it is crucial to comprehend What is BIOS. It helps us understand how a computer initiates and controls hardware. BIOS is essential for system startup, hardware setup, and performance optimisation. It serves as the link between your computer's hardware and operating system, ensuring seamless communication and operation. Although UEFI has largely replaced BIOS, its vital role in early computer development remains significant in modern system advancements.
Transform Your Career with Cutting-Edge Computer Skills with our Computer Science Course today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Main Purpose of BIOS?

The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) initialises the hardware, executes a Power-On Self-Test (POST), and loads an Operating System. It provides a bridge between system firmware and software to guarantee proper communication and hardware operation.
Where is BIOS Stored?

BIOS is retained in a non-volatile memory chip on the motherboard, usually EEPROM or flash memory. This enables it to retain its settings even when the system is turned off. Contemporary systems employ UEFI, a more sophisticated form of BIOS, retained in the same way for better performance and security.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy offers various End User Training, including the Computer Science Course, Administering Linux Systems, and LINUX Fundamentals Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into End User Testing.
Our Office Applications Blogs cover a range of topics related to Software, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Office Applications skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Office Applications Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Computer Science Course
Computer Science Course
Fri 6th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 3rd Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


