We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Business Intelligence (BI) transcends the realm of mere spreadsheets and charts, weaving narratives from data that catalyse innovation. In today’s digital epoch, Business Intelligence is the bedrock of transformative insights, converting vast data arrays into strategic actions that thrust enterprises ahead. This blog will guide you through What is Business Intelligence (BI) is, highlighting its essential role in decision-making and its significant impact on the business world.
Table of Contents
1) What is Business Intelligence?
2) Importance of Business Intelligence
3) How does the Business Intelligence process work?
4) Types of Business Intelligence tools and applications
5) Advantages of BI
6) Examples of Business Intelligence
7) Key difference between traditional BI and modern BI
8) The future significance of Business Intelligence
9) Conclusion
What is Business Intelligence?
Business Intelligence (BI) encompasses many Data Management activities within a single field. It involves collecting, analysing, and visualising data, enabling organisations to gain insights into their strategies and operations for expansion. Seasoned professionals typically perform this task with a deep knowledge of BI tools and can transform raw data into insightful reports. These reports, generated through specialised BI software, are known for their accuracy and reliability. The essential benefits of BI include:
a) Converting raw data into actionable information that aids managerial decision-making for organisational growth.
b) Serving as the foundational architecture for managing organisational data, which includes gathering, storing, and analysing data.
As a pivotal element for product-centric companies, BI aids in examining customer behaviours and purchasing trends, which is crucial for devising marketing strategies.
Offering a variety of tools that facilitate effective Data Analysis, resulting in reports presented as spreadsheets and other formats that enhance user comprehension
Importance of Business Intelligence
Business Intelligence (BI) empowers organisations to enhance decision-making by leveraging current and historical data within the context of their business. Analysts utilise BI to establish benchmarks for performance and competition, streamlining organisational efficiency. Additionally, BI tools enable the identification of market trends, potentially boosting sales and revenue. When applied effectively, appropriate data can aid in various activities, from ensuring compliance to improving recruitment processes. Here are several ways in which Business Intelligence can facilitate more informed, data-driven decision-making for companies:
a) Uncover strategies to boost profitability
b) Study customer patterns and preferences
c) Conduct competitive analysis
d) Monitor organisational performance
e) Streamline business processes
f) Forecast future trends and successes
g) Detect emerging market shifts
h) Identify and address operational challenges
Use your expertise to fuel competitive strategies. Become our next Competitive Intelligence Analyst—apply now and make an impact!
How Does the Business Intelligence process work?
Business Intelligence (BI) is the framework through which companies and organisations address their inquiries and measure progress towards their objectives. This involves collecting, analysing, and applying data to inform strategic decisions.
Technically, BI entails gathering raw data from business operations, which is then processed and stored in data warehouses. Once archived, this data becomes accessible for analysis, providing insights to guide business decisions.
Unlock insights and drive smarter decisions! Apply now for the Business Intelligence Analyst position and help transform data into actionable business strategies.
BI, Data Analytics, and business analytics are interconnected components of a comprehensive process. BI facilitates the interpretation of Data Analysis, while Data Scientists delve into data intricacies using sophisticated statistical and predictive tools to identify trends and project future occurrences. Data Analytics explores the reasons behind events and anticipates what may happen next. BI translates complex models and algorithms into practical terms.
Gartner’s IT glossary explains that business analytics encompasses data mining, applied analytics, predictive analytics, and statistics, all of which are integral to an overarching BI strategy. BI is tailored to respond to specific questions and offer succinct analyses for decision-making or planning purposes. Nonetheless, analytics is not a one-way street but a continuous cycle of data retrieval, examination, experimentation, and knowledge dissemination, known as the analytics cycle. Through this iterative process, businesses can adjust to changing inquiries and expectations.
Learn to connect Power BI to various data sources with our Microsoft Power BI Course – join today!
Types of Business Intelligence tools and applications
Business Intelligence (BI) professionals utilise various BI tools, each falling into one of five primary categories based on their functionality and output. Here’s a refined overview of these categories:
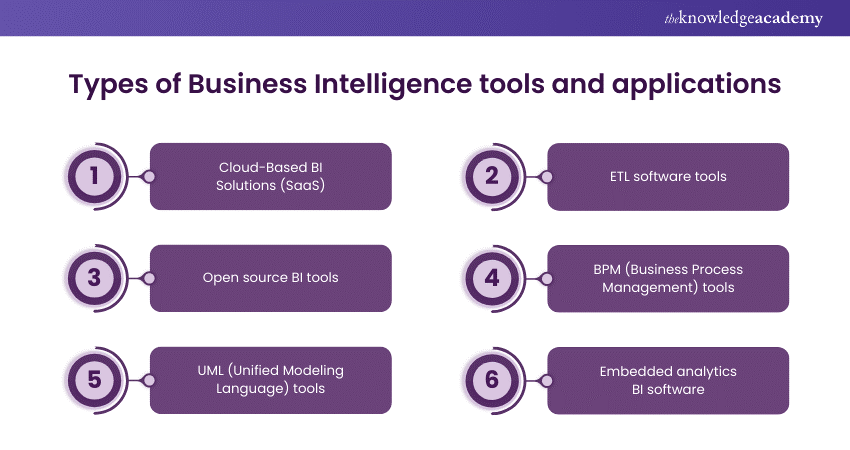
a) Cloud-Based BI Solutions (SaaS) : They provided by external vendors who manage BI applications and Data Analysis through cloud-based data warehouses.
b) ETL software tools: It extracts, transforms, and loads data, integrating information from diverse sources to produce required insights.
c) Open source BI tool: These tools are self-service platforms with inherent features, offering a more limited range than fully licensed BI solutions.
d) BPM (Business Process Management) or UML (Unified Modeling Language) tools: These tools are tailored for comprehensive project management or specific tasks within projects.
e) Embedded analytics BI software: This category comprises tools crafted to streamline the Data Analysis process, rendering it accessible and user-friendly to a wide spectrum of users.
Considering these categories, numerous tools are available, each boasting features that can significantly aid business analysis. Selecting the most suitable tool will depend on your specific needs and can greatly enhance your analytical capabilities.
Understand reporting tools and visualisation techniques with our Business Intelligence Reporting Course – join today!
Advantages of BI
Business Intelligence (BI) is instrumental in guiding business leaders to make well-informed choices. Beyond aiding in decision-making, BI offers a multitude of advantages, as highlighted by Tableau, a leader in Data Visualisation:
Data-Driven Decision Making: At the heart of BI is its capacity to inform decisions through data. A robust BI framework ensures business users receive precise data and reports swiftly, enabling more effective and timely decisions.
a) Accelerated analysis & user-friendly dashboards: BI enhances reporting efficiency by distilling complex reports into user-friendly dashboards, streamlining the process for non-experts to extract valuable insights from data.
b) Enhanced organisational efficiency: BI provides a comprehensive view of business operations, allowing leaders to align performance with overarching goals and pinpoint opportunities for improvement.
c) Elevated Customer Experience: Immediate access to data equips customer service staff to offer superior experiences.
d) Boosted employee satisfaction: Empowering business users with direct data access, bypassing the need for analyst or IT intervention, minimises delays, boosts productivity, and yields quicker outcomes.
e) Reliable and controlled data: Contemporary BI systems merge internal and external data into a unified data warehouse, granting simultaneous data access to various departments.
f) Greater competitive edge: A well-executed BI strategy enables businesses to keep a pulse on market dynamics and foresee customer requirements, thereby gaining a competitive edge.
Ace your next interview! Prepare with these top Competitive Intelligence interview questions.
Examples of Business Intelligence
Business Intelligence (BI) is a pivotal element in the corporate landscape, and dashboards epitomise this technology. These hosted applications amalgamate data into visual representations like charts and graphs, providing a snapshot of a company’s current status.
BI transcends mere report generation; it empowers users to sift through data, discern patterns, and glean insights, facilitating informed decision-making without prescribing specific actions or predicting outcomes.
Consider a corporation aiming to optimise its supply chain. BI tools can pinpoint bottlenecks and inconsistencies in the shipping process and identify frequently delayed products or problematic transportation methods.
BI’s applicability is not limited to enhancing sales or curtailing expenses. For instance, Tableau and G2 highlight practical BI applications:
a) A cooperative could leverage BI to track membership dynamics.
b) BI solutions can seamlessly produce sales and delivery summaries from CRM databases.
c) Sales personnel might utilise BI to craft a dashboard that visualises the progression of potential deals through the sales funnel.
These examples underscore BI’s versatility in fostering organisational efficiency and strategic planning.
Learn how to add new reports to a document with our Business Objects Reporting Course – join today!
Key Difference between traditional BI and modern BI
The evolution from traditional to modern Business Intelligence (BI) reflects a shift towards empowering users with self-service analytics and rapid insights.
In the past, BI tools adhered to a conventional model characterised by a hierarchical, IT-driven process. Analytics were predominantly disseminated through static reports, and any subsequent inquiries would be relegated to the end of a lengthy queue, resulting in protracted and often exasperating reporting cycles. This structure hindered the ability to leverage up-to-date data for timely decision-making. While traditional BI remains prevalent for routine reporting and fixed queries, modern BI stands out for its dynamism and user-friendliness.
Stay ahead of the competition! Learn what Competitive Intelligence is and why it's crucial for business success.
Modern BI is distinguished by its interactive nature and user-centric design. It doesn’t solely rely on IT departments for data access management; instead, it enables users at various levels to tailor dashboards and compile reports promptly. With the right tools, users gain the autonomy to visualise data and independently seek answers to their questions.
These examples underscore BI’s versatility in fostering organisational efficiency and strategic planning.
Unlock the power of data with the latest Business Intelligence platforms. Find the right solution for your business!
The future significance of Business Intelligence
The realm of Business Intelligence (BI) is dynamic, adjusting to evolving business needs and technological progressions. Annually, we spotlight emerging trends to keep users informed about the latest innovations. It’s anticipated that Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) will continue to expand, providing valuable insights that can be incorporated into a comprehensive BI strategy. As organisations aim to become more data-centric, the emphasis on data sharing and collaboration is expected to rise.
Curious about a Business Intelligence Analyst’s earning potential? Check out the latest salary trends in your area!
Data Visualisation will become increasingly crucial for cross-team and interdepartmental cooperation. This article serves as a primer to the expansive domain of BI. BI systems can track sales near-real-time, uncover customer behaviour patterns, project profits, and more. Various sectors, including retail, insurance, and energy, have embraced BI, and the trend is set to continue. BI platforms are designed to evolve in tandem with new technologies and user-driven innovations.
Master the competitive landscape! Learn the step-by-step Competitive Intelligence process to stay ahead.
Conclusion
In exploring the core of Business Intelligence, we confront a crucial question: What is Business Intelligence (BI)? BI transcends a mere collection of tools; it serves as a strategic guide leading businesses to triumph in a data-centric world. BI embodies the foresight to navigate through market complexities, offering clarity amidst information chaos. As a strategic beacon for companies, BI illuminates the path to innovation and competitive advantage.
Discover the top tools for effective Competitive Intelligence. Enhance your strategic decision-making!
Frequently Asked Questions

BI focuses on past and present data to drive business operations, while Data Analytics focuses on predictive modelling and statistical analysis to foresee future trends.

BI levels the playing field, allowing small businesses to harness data insights that were once exclusive to larger corporations.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Business Intelligence Reporting Course, including Microsoft Power BI Course, Business Objects Reporting Course and Crystal Reports Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Power BI.
Our Office Applications Blogs cover a range of topics related to Microsoft Excel, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Intelligence skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


