We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Cryptocurrency, a revolutionary digital concept that emerged as a response to the traditional financial system's limitations, has taken the world by storm. In this age of technological progress and digital change, understanding "What is Cryptocurrency?" has become more critical than ever. With the rise of Bitcoin in 2009, the first-ever decentralised Cryptocurrency, a new era of financial possibilities was born, reshaping how we perceive and engage in transactions.
Cryptocurrency can be defined as a digital or virtual currency that utilises sophisticated Cryptographic methods to safeguard financial transactions, control the creation of new units, and verify asset transfers. Unlike traditional fiat currencies issued and controlled by central banks, Cryptocurrencies operate on decentralised networks powered by Blockchain Technology. Read the blog on What is Cryptocurrency and learn how cryptocurrencies work and their impact on the financial landscape. Dive into our in-depth analysis today!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Cryptocurrency
2) Types of Cryptocurrencies
3) How do Cryptocurrencies Work?
4) How to Buy Cryptocurrency?
5) How Can You Use Cryptocurrency?
6) How to Store Cryptocurrency?
7) Benefits of Cryptocurrencies
8) Risks of Cryptocurrencies
9) Conclusion
Understanding What is Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency is a form of currency taken to be either digital or virtual, characterised by advanced cryptographic techniques that allow it to secure its owner's financial transactions and control the creation of additional currency units and asset transfer verification.
Unlike traditional fiat currencies issued by a central authority and intermediated through banks, cryptocurrencies function on decentralised systems based on Blockchain Technology. These systems do not involve third-party intermediaries like banks or any government because ownership of the entities is individual; thus, it gives the people more autonomy and control over their finances. To stay informed about how these systems are evolving and shaping the future, keeping up with the Cryptocurrency Trends highlighting key developments in the block chain ecosystem is vital
It all started with Bitcoin, described in a whitepaper by Satoshi Nakamoto-an unidentified person-in October 2008. Nakamoto depicted a new peer-to-peer electronic cash that would render financial intermediaries useless. It was in January 2009 that the first block in the Bitcoin blockchain, named the "Genesis block," was mined, and thus began a journey that was to change the face of finance forever. Since then, many Cryptocurrencies have been developed with unique features and use cases.
With already global adoption, affecting industries and economies in many aspects, cryptocurrencies are no longer a subject for tech-savvy people or financial experts. It, therefore, becomes of paramount importance to understand their basics for individuals, businesses, and indeed policy framers.
On the other hand, Cryptocurrencies can empower finances-primarily those of unbanked, less fortunate people-by opening access to borderless, digital financial worlds that could transform traditional systems of finance and free individuals to operate in self-sovereignty from conventional banking systems.
Types of Cryptocurrencies
Most Cryptocurrencies are created to serve specific functionalities on the blockchains they function within. For instance, Ether (ETH) was originally designed for transaction validation and block creation fees in the Ethereum blockchain.
On implementing proof-of-stake from September 2022, ETH also plays an important role in staking on the blockchain. XRP was constructed by the XRP Ledger Foundation for financial institutions with the purpose of cross-border transfer activities. With numerous cryptocurrencies available, understanding each of them is crucial. Knowing the specific purpose of crypto currency can help assist in investment potential as those with defined used cases tend to carry lower risk.
Here are some common types of cryptocurrencies along with examples:
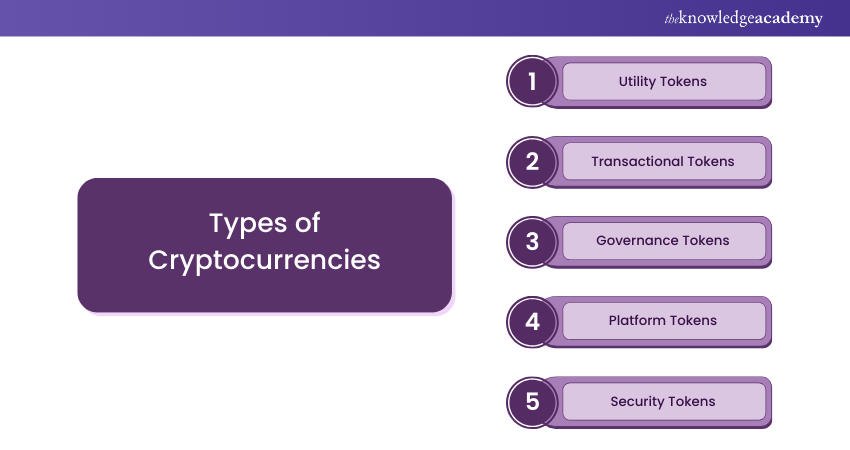
1) Utility Tokens: They have specific uses in their blockchains. Examples would include XRP and ETH.
2) Transactional Tokens: Issued with the intent of being used as a transferable currency; Bitcoin is the most famous example.
3) Governance Tokens: Serves as representation of voting rights or other rights in a blockchain; an example would include Uniswap.
4) Platform Tokens: These tokens support applications built on a blockchain, such as Solana.
5) Security Tokens: This token represents ownership over an asset. Such as, tokenised stock. The MS Token gives partial ownership of the Millennium Sapphire.
How do Cryptocurrencies Work?
Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies. All transactions in the digital currency are recorded in a blockchain and it is a distributed public ledger. It is an updated list of all transactions in the cryptocurrency kept by the holders of the currency.
The generation of cryptocurrency units is frequently done via a process called mining. Miners must make substantial computational effort to solve complex mathematical problems in return for new coins. Alternatively, users may acquire cryptocurrencies by buying them from brokers and storing them in cryptographic wallets for spending.
Owning a cryptocurrency does not mean you are taking possession of a physical asset; rather, you gain possession of a private key that enables the transfer of some record or unit of value from one person to another without a trusted intermediary.
Since its inception in 2009, the use of cryptocurrencies and blockchain has continued to evolve. In their relative infancy regarding finances, these technologies are expected to extend beyond their conventional uses. For instance, blockchain technology could be applied to offer sale and purchasing of bonds, stocks, or other kinds of financial instruments in the future, and this is going to hugely revolutionise how financial transactions take place.
How to Buy Cryptocurrency?
If you are interested in investing in Cryptocurrency, it is extremely important to know which safe and efficient methods exist for buying and controlling digital currencies. The process usually occurs in three distinct steps:
1) Selecting the Appropriate Platform:
First, you must choose the right place for your crypto transactions. You have two basic variants:
a) Traditional Brokers: This service will provide a diversified set of financial assets, like cryptocurrencies, stocks, bonds, and ETFs. For the most part, the platforms are known to have lower trading costs and could offer more restrictions on cryptocurrency-specific features.
b) Cryptocurrency Exchanges: These have a strong focus on cryptocurrencies and could offer a diversified set of coins, wallet storage solutions, options for interest-earning accounts or even other services. For the most part, they use an asset-based fee structure.
When assessing exchanges, consider the variety of cryptocurrencies available, charge schemes, security measures, methods to store and withdraw your funds, and educational resources available.
2) Funding your Account:
After you have selected an exchange, you must fund your account to start trading. Most exchanges permit you to fund using fiat currencies such as USD, GBP, or EUR with debit or credit cards-but it varies. Also take into consideration:
a) Credit Card Purchases: The use of credit cards to buy Crypto is a very risky procedure and should not be allowed in all the major exchanges. This proves to be risky due to the high volatility associated with Cryptocurrencies, which would often cost a hefty amount with the chances of getting into debt.
b) Other Payment Systems: Most platforms also offer ACH, and wire transfer. The methods available and the time taken to process deposits and withdrawal are not similar for each of the platforms. Also keep in mind the various fees applied such as deposit, withdrawal, and trading fees, which also vary dramatically depending both on the platform and the payment system used.
3) Making a Purchase:
Now you can use the web or mobile interface of your chosen broker or exchange to buy Cryptocurrency. Most of the time, it will make you choose 'buy,' then select the type of order, enter in the amount of Cryptocurrency you want to buy, and confirm the order. The same process is above for selling.
Other than direct buying, there are also other forms of investment into Cryptocurrencies:
a) Payment Services: The services available include those from platforms such as PayPal, Cash App, and Venmo. These enable individuals to buy, sell, and hold Cryptocurrencies.
b) Investment Vehicles: They can be Bitcoin trusts available through most brokerage accounts, Bitcoin ETFs, or mutual funds. For indirect exposure to the Crypto market, one could invest in blockchain stocks or ETFs, which track companies developing Blockchain Technology or using it in their operations.
Navigation of the Cryptocurrency market safely would require careful consideration of a trading platform, an understanding of the funding methods and their associated fees, as well as other conditions under which to buy or invest in Cryptocurrencies, be it directly or through other financial instruments.
Join our Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Course today to equip yourself with essential insights and tools for navigating this dynamic market!
How Can You Use Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrencies, such as Litecoin, Bitcoin, and Ethereum, have become popular means of purchasing goods and services and have also turned into alternative investment means aside from traditional stocks and bonds.
It is among the most recognised cryptocurrencies. As David Zeiler, a cryptocurrency specialist in Money Morning, explains, Bitcoin has been a secure, decentralised currency that morphed into a store of value, like gold. Therefore, Bitcoin has been referred to as "digital gold" because it must be capable of protecting value for an extended period.
Crypto investments create a potential avenue for diversification in one's investment portfolio. Unlike traditional assets, cryptocurrencies work on a blockchain-a guarantee of transparency and security. This, therefore, implies that they are decentralised, not at the discretion of one controller, hence there is a minimum probability of manipulation.
How to Store Cryptocurrency?
Once you buy it, you should store your cryptocurrency safely to avoid hacks or thefts. Cryptocurrencies can be stored in wallets. The wallet, for one, can either be a physical appliance or online software which was designed to secure the private key of a user.
Some exchanges also allow consumers to store their assets on their own platform, though not all exchanges or brokers automatically include this service. There are several options in choosing a wallet provider; however, this basically falls under two major categories:
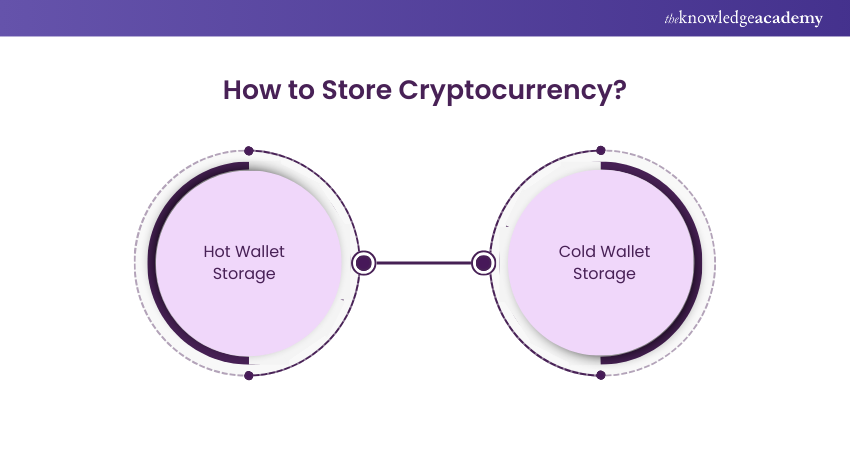
1) Hot Wallet Storage: These wallets utilise online software to secure the private keys to your assets. Hot wallets are very useful for asset access but relatively more exposed to online dangers.
2) Cold Wallet Storage: It uses offline electronic devices. It is generally known as a hardware wallet, and it stores private keys securely by means of offline electronic devices. Its security is significantly better because it operates with the internet off thus no hackers can hack them easily.
Benefits of Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies introduce a new idea of decentralised finance, or the removal of intermediaries like banks. In the system, the speed and security of transactions are enhanced because any individual can transfer funds directly to others and over borders. Here are a few benefits of cryptocurrencies:
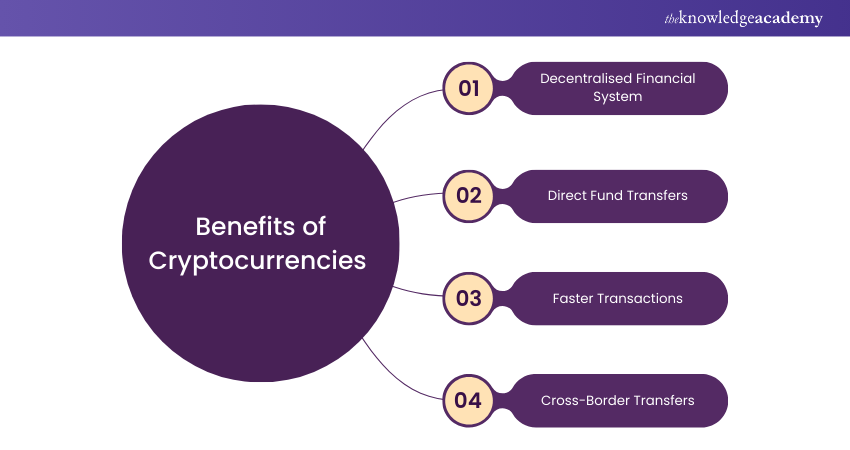
1) Decentralised Financial System:
Cryptocurrencies introduce a new, decentralised approach to money, eliminating the need for centralised intermediaries like banks and financial institutions. This would mean that risks such as the most publicised point of failure of a single point of failure - that was the case of 2008 - when the crash came on major investment banks.
2) Direct Fund Transfers:
Cryptocurrencies allow for the direct transfer of funds between two parties without the trusted third party of a bank or credit card company. This can be facilitated through a public and private key as well as incentive mechanisms including but not limited to proof of work or proof of stake.
3) Faster Transactions:
Cryptocurrency transactions do not entail the use of a third-party intermediary, and they can be faster than the transactions traditional money transfers involve. Such examples include flash loans in decentralised finance that can be executed without collateral and process settlement within a few seconds for trading purposes.
4) Cross-Border Transfers:
Cryptocurrencies Come in Handy in the Remittance Economy Intermediate currencies, such as Bitcoin, help speed cross-border money transfers. A fiat currency may be first transformed into Bitcoin (or another cryptocurrency), sent across borders, and then transformed back into the destination fiat currency-all without third party facilitation.
Risks of Cryptocurrencies
Due to the very significant losses from scams, hacks, bugs, and volatility, cryptocurrencies have obtained a bad reputation for their instability as investments. Aside from the inherent market risks, which come with all speculative assets, there are several other risks of cryptocurrency which investors should be aware:
1) User Risk:
Once cryptocurrency is sent, unlike traditional finance, it cannot be reversed or cancelled. It's estimated that about one-fifth of all bitcoins are now inaccessible either due to lost passwords or incorrect sending addresses.
2) Regulatory Risks:
As a rule, the regulatory status of cryptocurrencies is far from certain in most regions; different governments are still considering how to handle their regulation-as securities, as currencies, or as both. A sudden regulatory crackdown might make the sale of cryptocurrencies difficult or even plunge prices across the market.
3) Counterparty Risk:
Most of the investors and traders keep their cryptocurrency with exchanges or custodians. Any theft or misplacement by these third parties means the total loss of one's investment.
4) Management Risks:
Without proper and clear regulations, there is limited protection against deceitful or unethical management. Many investors have been thrown off guard whereby they lost a large sum to teams of managers that failed to deliver their promise.
5) Programming Risks:
Many investments and lending platforms utilise automated smart contracts to manage user deposits. Investors in those platforms are generally taking on the risk that some sort of bug or exploit in the code would result in lost investment.
6) Market Manipulation:
Another big issue in the cryptocurrency space is market manipulation. Influential individuals, organisations, and exchanges sometimes act unethically.
Gain knowledge on creating and deploying your tokens; sign up for our Ethereum Developer Training now!
Conclusion
Understanding What is Cryptocurrency? is essential as we navigate an increasingly digital landscape. These innovative currencies are more than just a trend; they constitute a fundamental shift in how we think about money and transactions. By eliminating intermediaries, Cryptocurrencies empower individuals with greater control over their finances. To explore how this revolutionary technology is expected to evolve, we should closely monitor the Future of Cryptocurrency and its potential impact on the global economy.
Learn how to develop a private Blockchain using Multichain and acquire valuable skills; sign up for our Blockchain Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Learning About Cryptocurrencies help me Adapt to the Future of Finance and Technology?

Learning about Cryptocurrencies can surely help you adapt to the future of finance and technology. Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are becoming integral to the global financial markets. By understanding them, you will in fact gain important insight into Blockchain Technology, which underpins these currencies.
What are the Long-Term Prospects and Growth Opportunities Within the Cryptocurrency Market?

The cryptocurrency market's long-term outlook involves ongoing innovation, wider adoption, and deeper integration with mainstream financial systems. Growth opportunities lie in areas such as decentralised finance (DeFi), Blockchain applications, and global financial inclusion, driving market expansion and maturity.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers Investment and Trading Training, including Cryptocurrency Trading Training, Foreign Exchange Training, Day Trading Course, Stock Trading Masterclass and more. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into various Types of Investments.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to PRINCE2, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Investment and Trading skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Cryptocurrency Trading Training
Cryptocurrency Trading Training
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


