We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Imagine you’re at a trading table, and you want to control a hefty £100,000 position. Now, here’s where leverage comes in: instead of putting up the entire £100,000 yourself, your broker only requires a fraction of it as a deposit. This fraction is your “margin.” For instance, with 100:1 leverage, you’d need just £1,000 of your own money to control that £100,000 position. But What is Leverage in Forex exactly?
Leverage is a robust tool that can amplify both your profits and losses. Understanding this concept is important for anyone venturing into Forex Trading. By mastering leverage, you can streamline your strategies, assess risks more effectively, and take full advantage of the benefits it offers. Read this blog to learn more about What is Leverage in Forex and take your trading to the next level!
Table of Contents
1) Decoding What is Leverage in Forex Trading
2) Types of Leverage Ratios
3) How to Pick the Right Leverage Level?
4) How to Calculate Leverage in Forex?
5) Benefits of Using Leverage in Forex
6) Risks Associated with Forex Trading and Leverage
7) Conclusion
Decoding What is Leverage in Forex Trading
Leverage is a powerful financial tool used in trading that lets traders to control a larger position with a relatively small amount of capital. Essentially, it involves borrowing funds to increase the potential return on an investment. While Leverage can greatly amplify your profits, it can also magnify losses, making it a double-edged sword in the world of trading.
How Leverage Works
The idea behind leverage is borrowing money from the broker in order to increase the size of your position. This simply means that with a small investment, you could open a much larger position than you could otherwise with your own capital. The Leverage amounts are usually quoted as a ratio: for example, 10:1, 50:1, or even 500:1.
This means that, with a 50:1 Leverage ratio, an investor could control assets in the region of £50,000 by merely depositing £1,000. The position will register gains or losses on the total £50,000 amount, not just the initial £1,000 invested.
The Mechanics of Leverage
a) Initial Margin: This is the amount of money you need to open a Leveraged position. It acts as a security deposit that covers potential losses.
b) Borrowed Funds: The broker lends you the additional funds needed to control the larger position.
c) Position Size: The total value of the position you control, which includes your initial margin and the borrowed funds.
Gain expertise in trading psychology with our Cryptocurrency Trading Course – Register today!
Types of Leverage Ratios
Broker-specified initial margins fluctuate based on trade size. For example, a 100,000 GBP/USD trade might require a £1,000 margin, equating to a 1% requirement (£1,000 / £100,000). The resulting Leverage ratio, illustrating trade amplification due to the held margin, is calculated as 100:1 (£100,000 / £1,000). The subsequent outlines margin requirements and corresponding Leverage ratios:
a) A 2% margin necessitates a 50:1 Leverage ratio.
b) A 1% margin yields a 100:1 Leverage ratio.
c) A 0.5% margin corresponds to a 200:1 Leverage ratio.
Lower margin requirements in Forex trading determine the level of exposure a trader can achieve with their capital. Different Leverage ratios offer varying levels of risk and potential reward, making it crucial for traders to understand these ratios for effective trading. Common Leverage ratios include:
Table of Leverage Ratios:
|
Leverage Ratio |
Equity (£) |
Position Size (£) |
Risk Level |
|
1:1 |
1,000 |
1,000 |
Very Low |
|
1:5 |
1,000 |
5,000 |
Low |
|
1:10 |
1,000 |
10,000 |
Moderate |
|
1:25 |
1,000 |
25,000 |
Moderate |
|
1:50 |
1,000 |
50,000 |
Moderate to High |
|
1:100 |
1,000 |
100,000 |
High |
|
1:200 |
1,000 |
200,000 |
Very High |
|
1:500 |
1,000 |
500,000 |
Extremely High |
1) Low Leverage (1:1 to 1:10)
a) 1:1 Leverage: This is also known as trading without Leverage. The trader uses only their own capital without borrowing. For example, with £1,000, the trader can control a £1,000 position.
b) 1:5 Leverage: With a Leverage ratio of 1:5, a trader with £1,000 can control a £5,000 position. This ratio is considered relatively low risk as the exposure is not significantly magnified.
2) Moderate Leverage (1:10 to 1:50)
a) 1:10 Leverage: A trader with £1,000 can control a £10,000 position. This level of Leverage is often used by more conservative traders who want some amplification of their position without taking excessive risks.
b) 1:25 Leverage: This allows a trader with £1,000 to control a £25,000 position. It's a common Leverage ratio that balances potential returns with manageable risk.
c) 1:50 Leverage: With this ratio, a trader with £1,000 can control a £50,000 position. This Leverage level is popular among retail Forex Traders, offering significant exposure with moderate risk.
3) High Leverage (1:50 to 1:100)
a) 1:50 Leverage: As mentioned, a trader with £1,000 can control a £50,000 position. This ratio is still manageable for many traders.
b) 1:100 Leverage: With £1,000, a trader can control a £100,000 position. This level of Leverage is more aggressive and suitable for experienced traders who can manage higher risks.
4) Very High Leverage (1:100 and above)
a) 1:200 Leverage: A trader with £1,000 can control a £200,000 position. This level is highly speculative and can lead to significant gains or losses.
b) 1:500 Leverage: With this ratio, £1,000 can control a £500,000 position. This extremely high Leverage is typically offered by Forex Brokers in regions with fewer regulatory restrictions and is used by traders with a high-risk tolerance.
How to Pick the Right Leverage Level?
Selecting the appropriate Leverage level is crucial for successful trading and effective risk management. The right Leverage depends on various factors, including your risk tolerance, trading experience, and market conditions. It’s also important to know the difference between Scalping and Day Trading, as leverage might be used differently in each trading style depending on the time frame and frequency of trades. Here’s a guide to help you choose the right Leverage level for your Trading strategy:
1) Assess Your Risk Tolerance
Identifying your risk tolerance is the initial determinant of choosing the right level of Leverage. Leverage increases both the potential returns and the risk, making it critical to select the ratio of returns to risk that will give you the desired ratio.
a) Low Risk Tolerance: If you are conservative and prefer to minimise risk, opt for lower Leverage levels, such as 1:5 or 1:10. This will limit your exposure and potential losses.
b) High Risk Tolerance: If you are more aggressive and willing to take on higher risks for the possibility of greater rewards, you might consider higher Leverage levels, such as 1:50 or 1:100.
2) Consider Your Trading Experience
Your experience level in trading should also influence your Leverage choice.
a) Beginners: If you are new to trading, it’s advisable to start with lower Leverage levels. This will help you learn and understand the market dynamics without exposing yourself to excessive risk.
b) Experienced Traders: With more experience, you may feel comfortable using higher Leverage levels. Experienced traders often have better risk management strategies in place to handle the increased risk.
3) Analyse Market Conditions
Market conditions can greatly affect the appropriateness of your Leverage level.
a) Volatile Markets: In highly volatile markets, lower Leverage is recommended to avoid significant losses due to sudden market swings.
b) Stable Markets: In more stable and predictable markets, you might consider using higher Leverage to take advantage of steady trends.
4) Use a Forex Leverage Calculator
To simplify the decision-making process, use a Forex Leverage calculator. This tool can help you understand the potential outcomes of different Leverage levels based on your account balance and desired position size.
a) Input Your Equity: Enter the amount of money you have available for trading.
b) Input the Desired Position Size: Enter the total value of the position you wish to control.
c) Calculate: The calculator will show you the Leverage ratio and potential outcomes, helping you make an informed decision.
5) Implement Risk Management Strategies
Regardless of the Leverage level you choose, always implement robust risk management strategies:
1) Set Stop-Loss Orders: Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. This automatically closes your position when the market moves against you beyond a certain point.
2) Position Sizing: Ensure your position size is appropriate for your account balance and chosen Leverage level. Avoid over-leveraging, which can quickly lead to margin calls.
3) Diversification: Spread your risk by diversifying your trades across different assets or currency pairs.
6) Monitor and Adjust
Regularly review your Leverage levels and adjust them as necessary based on your trading performance, changes in market conditions, and your evolving risk tolerance.
Example Scenarios
1) Scenario 1: Conservative Approach: You have £1,000 and prefer low risk. Using 1:10 Leverage, you can control a £10,000 position. This provides some Leverage benefits while keeping potential losses manageable.
2) Scenario 2: Balanced Approach: With £5,000 and moderate risk tolerance, you use 1:25 Leverage to control a £125,000 position. This offers a good balance between risk and reward.
3) Scenario 3: Aggressive Approach: You have £2,000 and are experienced with high risk tolerance. Using 1:100 Leverage, you can control a £200,000 position, potentially yielding high returns but also exposing you to significant losses.
How to Calculate Leverage in Forex?
The basic formula to calculate Leverage is straightforward:
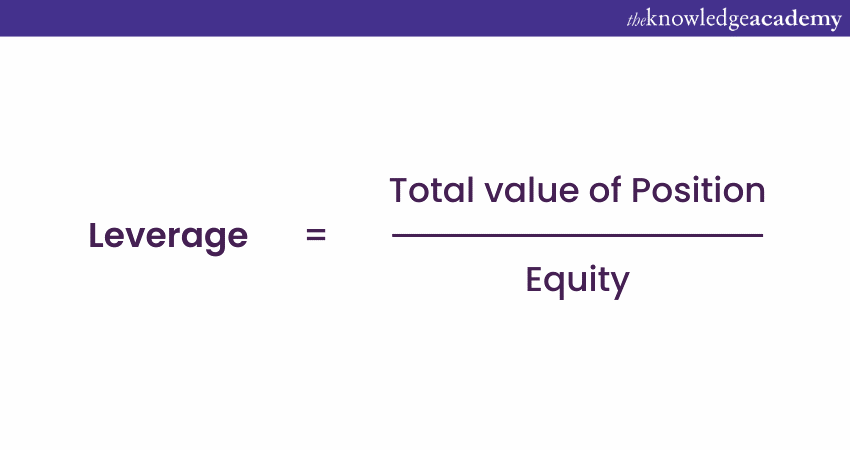
a) Total Value of Position: This is the size of the position you are controlling in the market. It is the total amount of money you are trading, including the borrowed funds.
b) Equity: This is the amount of your own money that you have put into the trade.
For example, if a trader uses £1,000 of their own money to control a £100,000 position, the Leverage ratio would be:
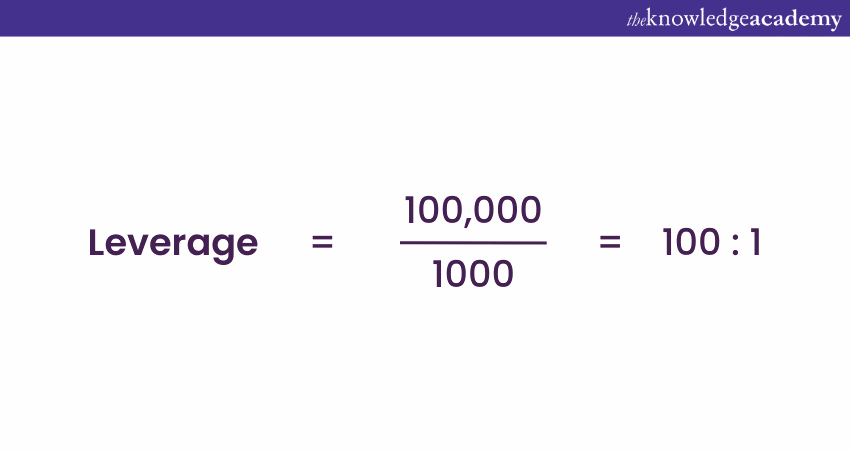
Practical Steps to Calculate Leverage
a) Determine Your Equity: Start by identifying the amount of capital you have available to trade. This is the money you have in your trading account that you are willing to use for trading.
b) Decide on the Position Size: This is the total amount of money you want to control in the market. Forex Brokers often allow traders to control large positions with relatively small amounts of equity.
c) Apply the Leverage Formula: Use the Leverage formula mentioned above to calculate your Leverage ratio.
Example of Leverage Calculation
Suppose you have £5,000 in your trading account, and you want to open a position worth £250,000. To find out the Leverage ratio, you would use the formula:
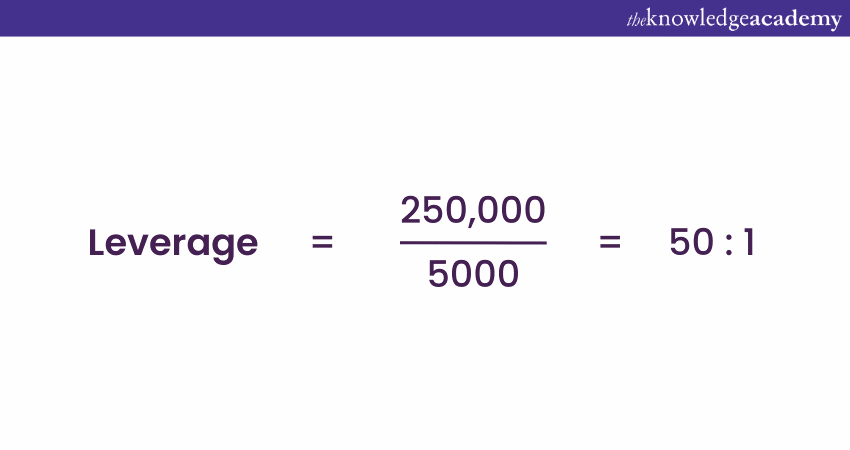
This means you are using a Leverage of 50:1, allowing you to control a £250,000 position with just £5,000 of your own money.
Using a Forex Leverage Calculator
To simplify the process, many brokers offer online Forex Leverage calculators. These Forex Trading Tools automatically calculate the Leverage based on the input values of equity and position size. Here’s how to use a Forex Leverage calculator:
a) Enter Your Equity: Input the amount of money you have available to trade.
b) Enter the Position Size: Input the total value of the position you wish to control
c) Calculate: The calculator will automatically compute the Leverage ratio for you.
Benefits of Using Leverage in Forex
Leverage is an integral part of the Forex market, offering both risks and advantages. When used judiciously, Leverage can be a significant asset to traders. Let’s explore its numerous benefits.
1) Maximising Capital Efficiency
Leverage enables traders to control quite large trading exposures for relatively small amounts of capital. For example, a 100:1 Leverage ratio means that with £1000, a trader is able to manage a £100,000 trade. This capability can lead to potentially higher profits without having to commit all their capital. This allows the trader to make optimal use of the capital at his or her disposal.
2) Potential for Enhanced Returns
The amplifying effect of Leverage means that even minor price shifts can lead to substantial profits. For instance, a 1% shift in a currency’s value can result in a 100% return on investment with the right Leverage. This magnification can turn small market movements into significant profit opportunities, making Leverage a powerful tool for increasing trading returns.
3) Opportunities for Diversification
By accessing larger positions, traders can spread their capital across various trades, reducing the impact of a poor-performing trade on the overall portfolio. Diversification serves as a risk management strategy, providing a safety net that ensures not all capital is at risk in a single position. This ability to diversify can enhance the overall stability and performance of a trader's portfolio.
4) Engaging in Higher Value Trades
Leverage also allows one to participate in trades of higher value than they would be able to without Leverage, which is generally a domain of larger institutions or banks. Thus, if applied correctly, it levels up the playground. An individual trader would then be allowed to compete with other big boys, taking part in markets far beyond their financial capability.
5) Flexibility in Trading Strategy
Finally, Leverage enables the trader to engage in many Forex Trading Strategies that would not be possible without it. Whether he is involved in short-term scalping or long-term position trading, Leverage can be adapted to fit many trading styles. This makes it possible to optimise the outcomes of trading by giving traders the tools they need to reach their particular financial goals.
Understand effective risk management strategies to protect your capital with our Day Trading Course – Sign up right now!
Risks Associated with Forex Trading and Leverage
Forex trading offers the potential for lucrative returns but comes with its fair share of risks. The use of Leverage amplifies these risks, making it imperative for traders to approach with caution. Here are the primary risks associated with Forex trading and Leverage.
1) Magnified Bosses:
Leverage can magnify losses just as it can amplify profits. A slight adverse movement in currency values can result in significant losses when trading with high Leverage. This means that one could potentially lose more than their initial investment, highlighting the importance of careful risk management.
2) Margin Calls:
Margin calls are another significant risk. Brokers require traders to maintain a minimum balance, known as the "margin requirement." If a Leveraged position moves against the trader, their balance might fall below this requirement. In such cases, brokers can initiate a margin call, liquidating positions to cover the shortfall. This can lead to unexpected and substantial losses.
3) Overtrading:
Overtrading is a common pitfall for traders attracted by the prospect of high returns. The allure of significant gains can tempt traders to take on excessive positions. Overtrading, especially when fueled by high Leverage, can lead to substantial losses. It's crucial to maintain discipline and not let greed dictate trading decisions, ensuring a more balanced and thoughtful approach.
4) Interest Rate Fluctuations:
Interest rate fluctuations also pose a risk in Forex trading. Trading often involves borrowing one currency to purchase another, and fluctuations in interest rates can affect the cost of borrowing, impacting profitability. An unfavourable shift in interest rates can erode potential profits or exacerbate losses, making it essential to stay informed about economic indicators.
5) Complexity and Speed:
Lastly, the complexity and speed of the Forex market add to the risk. Operating 24 hours a day, the market experiences rapid price changes. Leveraged positions are particularly sensitive to these swift fluctuations, requiring traders to stay alert and make quick decisions, informed by Forex Market Analysis, to protect their investments. This high-speed environment can be challenging to navigate without a robust understanding of the market.
Try our Forex Trading Course today and become a successful Forex Trader.
Conclusion
Understanding What is Leverage in Forex is important for every aspiring trader aiming for success. Leverage can greatly magnify both potential gains and potential losses, making it a powerful yet risky tool. While it offers numerous opportunities, it demands respect and a thorough understanding. Making well-informed decisions in the Forex market is the foundation for sustainable trading success.
Explore our Investment and Trading Training today and become an expert in Forex Trading!
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Leveraging Pave the way for Better Risk Assessment and Management in the Forex Market?

Leveraging in the Forex market enhances risk assessment and management by allowing traders to control larger positions with relatively little capital. While it amplifies potential profits, it also magnifies potential losses. Traders can assess and calibrate risk exposure by understanding and effectively utilising Leverage ratios.
Can Traders with Varying Levels of Experience Effectively Utilise Leverage in Their Forex Transactions?

Traders with varying experience levels can use Leverage in Forex transactions, but effectiveness depends on risk awareness. Novice traders may benefit from conservative Leverage to minimise potential losses, while experienced traders may Leverage more aggressively based on a thorough understanding of market dynamics.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is Knowledge pass and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Investment and Trading Training, including Forex Trading Course, Day Trading course and Stock Trading Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Best Forex Trading Strategies.
Our Investment and Trading Blogs cover a range of topics related to Investment and Trading, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Investment and Trading skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming ISO & Compliance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Cryptocurrency Trading Training
Cryptocurrency Trading Training
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


