We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

So, What is Logistics? It can be defined as the movement of items, services, and information from origin to state of use in the Supply Chain. It plays a crucial role in Supply Chain Management and is essential for businesses to meet customer demands while minimising operational expenses.
Efficient logistics relies on optimising routes, maintaining appropriate inventory levels, and utilising technology and automation. It also involves compliance with regulations, risk management, cost control, and a strong focus on customer service. In this blog, we will elaborate on "What is Logistics?" and how it significantly influences a product's journey from production to the end consumer.
Table of Contents
1) What is Logistics?
2) What are the Functions of Logistics?
3) Types of Logistics
4) The core components of Logistics
5)The Importance of Logistics in modern business
6) Challenges in Logistics
7) Future trends in Logistics
8) Logistics beyond Transportation
9) Role of Logistics in business operations
10) Difference of Logistics and Supply Chain Management
11) Conclusion
What is Logistics?
Logistics has its roots in ancient times. Trade routes, like the Silk Road, depended on it. Ancient empires rose with strong logistic capabilities. They organised large-scale Supply Chains, delivering food and weapons. The term itself originates from the Greek word "logistikos," related to calculating or reasoning. In military contexts, it meant supplying troops with necessary resources.
At the core of logistics lies a complex yet well-coordinated system that organises the efficient movement of goods, services, and information within the Supply Chain. This intricate network seamlessly integrates various elements, including transportation, Inventory Management, warehousing, packaging, information flow, and Supply Chain collaboration.
What are the Functions of Logistics?
Transportation and warehousing are the pillars of the Logistics sector. The role of transportation management is to design, refine, and add strategies for the proper movement of goods across various modes of transport—sea, air, rail, or roadways.
This domain is inherently intricate, encompassing the coordination of routes, optimisation of cargo loads, oversight of orders, and the financial aspects of freight, including auditing and payments. Additionally, it encompasses yard management, which regulates the transit of vehicles and fleet operations around the external areas of factories, storage facilities, and distribution hubs. The variability in cost, availability, and capacity of transport carriers makes carrier management a critical element.
Companies often employ Transportation Management Systems (TMS) and other specialised software for yard and warehouse management system (WMS). This is because it helps in navigating the complexities of transport Logistics,
Warehouse management, on the other hand, is concerned with inventory control and fulfilling customer orders. It also includes the administration of warehouse infrastructure and operational processes. For instance, in fulfilment centres, the reception, processing, and dispatching of orders to customers are managed.
Customs management, or global trade management, is frequently viewed as an integral component of logistics, dealing with the regulatory documentation required when merchandise crosses international frontiers or enters maritime ports.
The Core Components of Logistics
Understanding Logistics requires delving into its primary pillars. Here's a deeper look into each component:
1) Transportation
a) Mode selection: Choosing between road, sea, air, or rail impacts cost, speed, and environmental footprint.
b) Route planning: Efficient paths reduce fuel costs, delivery times, and environmental impacts.
c) Timeliness: Ensuring goods arrive when expected builds consumer trust and reduces storage costs.
d) Cost efficiency: Optimal transportation choices and negotiations reduce shipping expenses, benefiting both businesses and consumers.
2) Warehousing and Storage
a) Strategic locations: Placing warehouses in key areas minimises transportation costs and time.
b) Safety measures: Proper security protocols prevent theft or damage to stored goods.
c) Organisation systems: Effective layout and indexing ensure quick retrievals and reduce handling errors.
d) Climate control: Some goods, like perishables, require specific temperatures or humidity levels for preservation.
Inventory Management
a) Demand forecasting: Predictive tools help gauge future product demands, aiding stock decisions.
b) Stock levels: Maintaining optimal stock prevents overstock costs and product shortages.
c) Replenishment systems: Automated processes ensure stock is reordered at the right time, maintaining a flow.
d) Waste reduction: Efficient inventory management minimises expired or obsolete items, reducing losses.
Information Management
a) Real-time tracking: Modern tools offer real-time insights into shipments, enhancing transparency for consumers.
b) Data analytics: Analysing Logistics data can spotlight inefficiencies and suggest optimisation strategies.
c) Integrated systems: Connecting all Logistics components digitally ensures synchronised operations digitally.
d) Decision support: Accurate, timely data empowers businesses to make informed logistical choices, boosting efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The Importance of Logistics in Modern Business
Logistics serves as the intricate thread weaving together various elements. This sector doesn't just move goods; it facilitates connections, drives efficiency, and shapes customer experiences. Here's an expanded view of its indispensable role:
Global Reach
a) Connecting markets: In an interconnected world, Logistics forms bridges, enabling businesses to tap into distant markets and diversify their consumer base.
b) Cultural understanding: Different regions have unique regulations and preferences. Logistics helps businesses tailor their approach, respecting local nuances.
c) Supply Chain flexibility: The unpredictable nature of global events requires an agile Supply Chain. Logistics provides the adaptability to manoeuvre through challenges and maintain business flow.
Customer Satisfaction
a) Timely deliveries: Delivering on promises is crucial. When Logistics ensures punctual deliveries, it solidifies consumer trust.
b) Product availability: A seamless shopping experience relies on product availability. Logistics manages inventory to prevent disappointing stockouts.
c) Returns and exchanges: A hassle-free return process can make or break customer loyalty. Efficient Reverse Logistics makes this possible.
Operational Efficiency
a) Cost management: By optimising routes, storage, and transport modes, Logistics plays a pivotal role in cost-saving.
b) Resource utilisation: Maximising the use of assets, from trucks to warehouse space, ensures higher productivity and fewer overheads.
c) Data-driven decisions: Logistics offers a treasure trove of data. Analysing this can spotlight areas for improvement and streamline operations.
Sustainability and Ethics
a) Eco-friendly operations: Conscious consumers demand sustainability. Logistics responds with green transport modes and packaging solutions.
b) Ethical sourcing: Ethical Logistics ensures products are sourced responsibly, supporting fair labour practices and sustainable methods.
c) Waste reduction: Reducing product waste isn't just eco-friendly, it's also cost-effective. Logistics aids in this mission with efficient inventory management.
Technology Integration
a) Automation: From robot-assisted warehousing to automated delivery schedules, Logistics harnesses technology for increased efficiency.
b) Digital tracking: Real-time tracking tools empower consumers, offering them visibility into product journeys.
c) Predictive analysis: Predicting market trends and demands helps businesses stay prepared. Logistics technology offers this foresight.
Elevate Your Career: Discover Industry Training Courses Now!
Challenges in Logistics
Logistics not only facilitates global commerce but also presents multiple challenges that require attention for seamless operations. Here's a more comprehensive dive into these challenges:

Infrastructure Limitations
a) Underdeveloped regions: Some areas lack proper roads or transport networks, making delivery and procurement challenging.
b) Urban congestion: Dense city traffic can escalate fuel consumption, extend delivery times, and amplify logistic costs.
c) Lack of facilities: Limited or outdated storage and handling facilities can reduce the storage quality and increase spoilage or damage risks.
d) Transport maintenance: Aging vehicles or transport modes can lead to frequent breakdowns and inefficiencies.
Technological Gaps
a) Outdated systems: Relying on old systems might result in slow processes, missed opportunities, and poor data analysis.
b) Integration issues: Blending old and new tech can lead to data discrepancies and system crashes.
c) Cybersecurity threats: Without secure platforms, sensitive data can be at risk, potentially harming business reputation.
d) Tech adoption resistance: Employees accustomed to traditional methods may resist adopting modern solutions, slowing progress.
Regulatory Constraints
a) Customs and duties: Each country has customs protocols, sometimes leading to unexpected fees or shipment delays.
b) Environmental regulations: Meeting ever-changing eco-friendly standards may involve constant adaptation and financial outlays.
c) Local laws: Compliance with diverse local Logistics-related laws can complicate cross-border operations.
d) Trade tariffs: Unanticipated tariffs or trade wars can disrupt established Supply Chains.
Human Resource Challenges
a) Skill gaps: As Logistics evolves, the need for upskilling becomes critical to meet industry demands.
b) Labour shortages: Peak seasons or regional labour shortages can disrupt normal operations.
c) Safety concerns: Ensuring staff welfare reduces turnover and accidents, especially in physically demanding roles.
d) Communication barriers: Working globally might introduce language or cultural communication challenges.
Environmental Concerns
a) Carbon footprint: Identifying and switching to low-emission transportation modes is crucial for sustainability.
b) Waste management: Efficiently managing and reducing logistical waste, especially plastics, is essential for eco-friendliness.
c) Sustainable sourcing: Finding suppliers prioritising eco-friendly practices while maintaining quality is challenging.
d) Energy consumption: Warehouses and transport modes consume energy, emphasising the need for green energy solutions.
Mitigating these challenges not only streamlines Logistics but also bolsters business reputation, ensuring they remain competitive and responsive to global market demands.
Master the Supply Chain: Enrol in our Supply Chain Management Training today!
Future Trends in Logistics
The trajectory of trends suggests a future where Logistics is not only more efficient but also more aligned with environmental needs and customer preferences. Here's a glimpse of emerging trends shaping its future:
Automation and Robotics
a) Warehouse robots: Automated robots are streamlining storage and retrieval tasks, enhancing warehouse efficiency.
b) Autonomous vehicles: Self-driving trucks and drones are on the horizon, promising faster and safer deliveries.
c) Smart sorting: Advanced systems auto-sort packages by size, destination, or priority, speeding up processing.
Digital Transformation
Blockchain offers transparent, tamper-proof records, improving Supply Chain authenticity.
a) Internet of Things (IoT): Sensors and smart devices provide real-time data, ensuring efficient tracking and resource utilisation.
b) Cloud-based systems: Centralised, cloud-based platforms allow for easy data access and management across global operations.
Sustainability Drives
a) Green vehicles: Electric and hybrid vehicles are reducing Logistics' carbon footprint.
b) Eco-packaging: Biodegradable or reusable packaging materials are gaining traction, addressing environmental concerns.
c) Energy-efficient facilities: Warehouses with solar panels or smart energy systems reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Shape tomorrow's products: Dive into Product Management Training now!
Logistics Beyond Transportation
People mistake Logistics for transportation of goods, but it is more complicated than transport. It intertwines various sectors, creating a cohesive system. For instance, when you order a book online and receive it on the estimated date of delivery, it’s because Logistics ensure timely delivery. This process begins much before you click, starting with raw materials sourced globally. These materials transform into a finished product through manufacturing.
Logistics dictates how raw materials are stored. It determines the most efficient transport modes. It even decides the optimal stock levels at warehouses. But Logistics isn't confined to tangible products alone. Ever received an international invoice or a digital download link? That’s Logistics in the digital realm, streamlining information flow.
Technology continually reshapes Logistics. Innovative systems now manage fleets, optimising routes based on real-time data. Drones and autonomous vehicles are no longer just science fiction; they're part of the evolving Logistics landscape, ensuring quicker, safer deliveries. Sustainability is now central to Logistics, bringing eco-friendly packaging, green transport methods, and waste reduction strategies into focus. Logistics adapts, striving for both economic and environmental efficiency.
Logistics meets consumer demands while navigating global challenges. It’s an intricate ballet of processes, all working in synchrony for a world constantly on the move.
Role of Logistics in Business Operations
Logistics holds a depth that's worth exploring. To truly grasp its intricacies, let's dissect its essence step by step:

a) Central nervous system: Much like our body’s coordination system, Logistics intertwines various business functions. It ensures that production, distribution, and sales work harmoniously, enabling smooth business operations and customer satisfaction.
b) Product journey: From the drawing board to a customer's hands, Logistics plays a role. It determines how raw materials are sourced, products are manufactured, and goods are finally delivered.
c) Planning and execution: Planning is not about mere movement but strategic actions. Logistics entails detailed forecasts, understanding market demands, and efficiently orchestrating resources to meet these demands.
d) Information management: Today, data is as valuable as gold, if not much more. Logistics oversees the flow of vital data – determining production rates, gauging inventory levels, and setting delivery schedules, all based on real-time insights.
e) Bridging distances: Sometimes, a product must travel continents in our globalised world. Logistics ensures it reaches its destination promptly, whether a handicraft from a remote village or a tech gadget from a bustling city.
f) Maintaining quality: Receiving poor-quality products is unappealing. Logistics ensures products are stored and transported under ideal conditions, maintaining their quality and freshness.
g) Adaptability: Markets are dynamic. A sudden trend or global event can shift demands. Logistics adapts swiftly, rerouting supplies, adjusting storage, or changing transport modes as required.
h) Rapid deliveries: The digital consumer is impatient. They crave instant gratification. Logistics rises to this challenge, leveraging technology to ensure faster deliveries and real-time tracking for eager customers.
i) Modern backbone: Behind every successful e-commerce giant or retail store is a robust Logistics framework. It's the silent force ensuring businesses thrive in today's fast-paced commercial landscape.
Difference Between Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Let’s simply the difference between Logistics and Supply Chain for you:
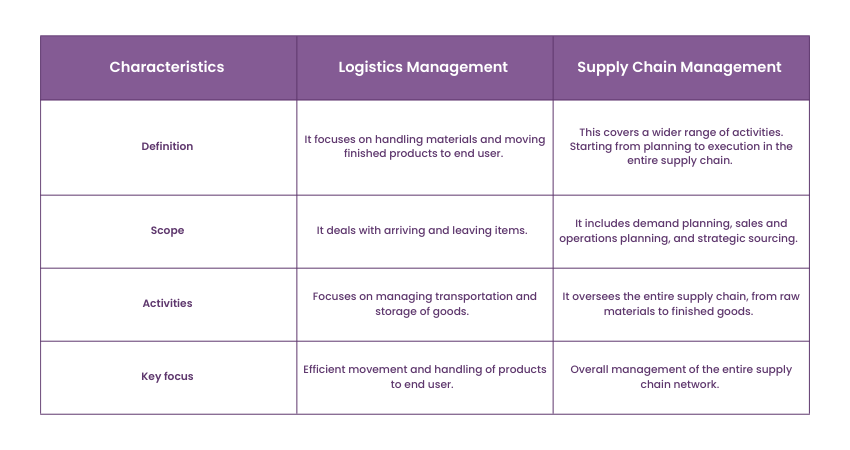
Conclusion
We hope after reading this blog, you now understand What is Logistics. It's evident that Logistics is not a mere cog in the business machine, but it's the very lifeblood. Its evolving nature, marked by upcoming trends and solutions to challenges, indicates its resilience and crucial role in shaping global commerce. As global connectivity increases, streamlined Logistics becomes ever more vital, solidifying its position in modern business.
Unlock your Logistics potential with our Logistics Management Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions

The roles include storage, packing, transportation, delivery, cargo handling, distribution processing, and information processing. It starts from the production location or factory to sending it off to the consumer on time.

Transport can be defined as the movement of goods from one location to another. Whereas Logistics is an all-encompassing term. It includes all activities needed to coordinate and manage the movement of goods to the end destination.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Business Skills Courses, including the Facilitation Skills Training, Floristry Training, Product Management Training, and Supply Chain Management Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Supervisor Responsibilities.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Earned Value Management, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Logistics Management Training
Logistics Management Training
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


