We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Many economics scholars frequently inquire about the definition of Microeconomics in order to grasp its position within the broader field of economics. Microeconomics aims to comprehend actions and choices regarding resource distribution and the relationships among individuals and companies.
The field usually pertains to separate sectors, industries and markets, instead of national and global economies, which distinguishes it from macroeconomics. Microeconomics is the examination of small-scale financial resources and patterns of Production and consumption, as implied by its name.
The area is beneficial for studying the impact of Economic policies on individual Economic behaviour, such as raising taxes, and their potential influence on prices.
Table of Contents
1) What is Microeconomics?
2) How do People use Microeconomics?
3) Key Concepts of Microeconomics
4) The Importance of Microeconomics in Everyday Life
5) Difference Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
6) Method of Microeconomics
7) Conclusion
What is Microeconomics?
Microeconomics explores how incentives and decisions influence resource usage and distribution at an individual level. Microeconomics demonstrates the reasons for the varying values of different goods. It discusses how individuals and businesses engage in efficient Production and exchange, as well as how individuals can effectively coordinate and collaborate.
Key Points for Microeconomics:
a) Microeconomics focuses on analysing how individuals and businesses make choices regarding how to use resources for Production, trade, and consumption.
b) Microeconomics focuses on the relationship between prices and Production within individual markets and the connections between different markets.
c) Microeconomics focuses on individual markets, while macroeconomics studies the economy as a whole.
d) Microeconomists develop different kinds of Models by analysing logic and studying human behaviour, then they validate these Models using real-life data.
How do People use Microeconomics?
Businesses utilise Microeconomics to decide the quantity of goods they should produce or services they should offer and at what cost. The price may change depending on numerous factors such as resource and labor costs, as well as the amount customers are willing and able to spend. Professionals can apply Microeconomics in two ways.
Positive Microeconomics
This area of Microeconomics aims to forecast potential outcomes in a specific Economic scenario as circumstances evolve. If there is a drought in a region that produces a specific crop, such as cabbages, it will probably result in a scarcity of cabbages and an increase in their price at supermarkets.
Having a grasp on the microeconomic environment enables businesses to develop backup plans in order to mitigate the negative impacts of unexpected changes, given that markets are always changing.
Normative Microeconomics
This term refers to views on the most optimal financial choices for corporations and individuals. People's moral and political beliefs influence how they perceive Economic policies; some may see a policy as negative while others see it positively based on their views.
Key Concepts of Microeconomics
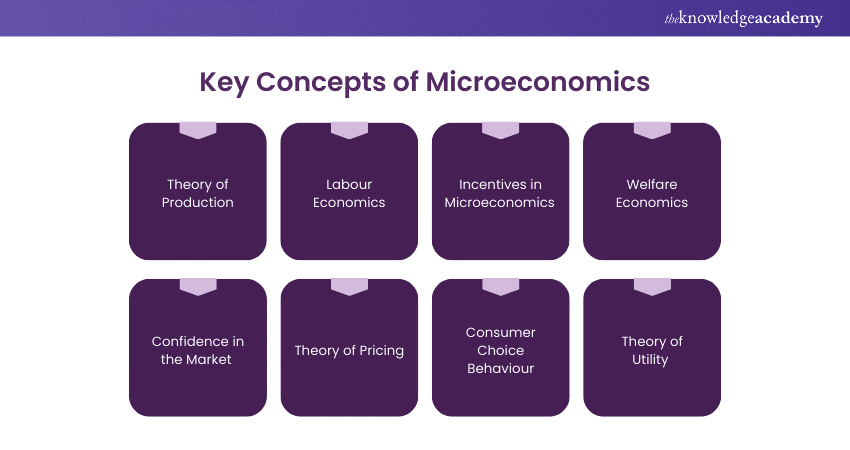
1) Theory of Production
Production involves a business transforming raw materials into products that can be sold. Companies aim to increase profits by manufacturing the greatest quantity of products while utilising the fewest resources possible.
The price and quantity of materials used in manufacturing greatly impact product costs and Demand. Businesses often consider extra expenses such as taxes, wages, and real estate.
2) Labour Economics
Labour is considered a crucial element in markets, making it vital for economists to have a grasp of its dynamics. The field of labour economics examines both workers and employers, as well as trends in salaries, job opportunities, and earnings.
This area concentrates on the evolving need for jobs that are compensated, as well as the operation and movement of these markets. Different Economic elements can influence labour economics on a small scale, like employee rights, overtime pay, and adjustments to minimum wage and taxes.
Empower your management journey with our Introduction To Managing People Course Register now!
3) Incentives in Microeconomics
Incentives are elements that drive individuals to make specific Economic or financial choices. For instance, tax incentives refer to tax reductions that the government offers on specific products to encourage consumers to make purchases. Additional kinds of motivators consist of tax refunds, state aid, and monetary motivators. Comprehending this is crucial to understanding specific market factors.
4) Welfare Economics
This Economic research seeks to determine how Economic policies affect the welfare of societies. It seeks to comprehend personal happiness as a type of well-being and to compare collective well-being across countries.
This aids Economic researchers in comprehending the impact of policies on communities, enabling them to assess policy effectiveness. It also pertains to the distribution of resources and how resource allocation affects well-being, like how funds are distributed by governments to specific sectors.
5) Confidence in the Market
This indicator is valuable in Economic analysis and research because it gauges the level of optimism individuals have regarding both their personal financial status and their country's overall economy. Consumer confidence is influenced by how people view things, a viewpoint often influenced by the media, as well as by the real condition of the economy and its effects on individuals.
Increases in inflation, unemployment rates, and living costs have a negative impact on consumer confidence, whereas decreases in these factors have a positive impact on it.
6) Theory of Pricing
Price theory combines Production theory and utility theory to explain the formation of prices in competitive markets. Production and utility theory aid Economic researchers in developing theories regarding prices by focusing on supply and Demand. Economic equilibrium is reached in a perfectly competitive market when the prices consumers are willing to pay match the prices offered by producers.
7) Consumer Choice Behaviour
Consumer choice refers to the choices that consumers make when buying goods and services. Factors like needs, perceptions, desires, location, information, and income play a role in shaping consumer choices. Economists can better predict individual consumption levels by studying consumer choice patterns.
Manage behaviour and foster harmony with our Anti Social Behaviour Management Training Sign up now!
8) Theory of Utility
The process of inducing raw materials into goods available for purchase is known as Production in business. Businesses strive to increase profits by manufacturing the highest quantity of products while utilising the fewest resources possible.
The cost and Demand for products mostly depend on the type, amount, and cost of materials used in the Production process. Businesses often take into account extra expenses such as taxes, wages, and real estate.
The Importance of Microeconomics in Everyday Life
Microeconomics plays a vital role in everyday life, sometimes in ways that may not be directly apparent to participants. Consider the example of an individual in search of purchasing a vehicle. Microeconomic principles are essential in decision-making for individuals. When deciding whether to buy a vehicle, they will probably take into account different incentives like rebates or low interest rates.
They are likely to choose a specific make and Model that will provide the greatest amount of utility while also fitting within their financial limits. A car manufacturer would have taken similar microeconomic factors into account when producing and supplying cars to the market.
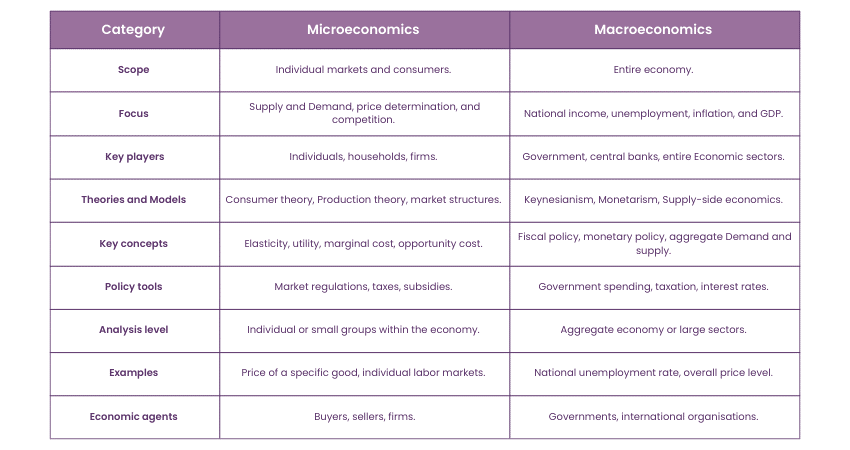
Difference Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Microeconomics: Microeconomists examine how goods and services are produced, traded, and consumed in markets, and how producers' and consumers' actions are influenced by factors like incentives, Production techniques, and taxes.
Macroeconomics: Macroeconomics is a division of economics that examines the behaviour of an entire economy, including markets, companies, individuals, and authorities. Macroeconomics studies broad Economic aspects like inflation, price levels, Economic growth rate, national income, GDP, and unemployment fluctuations.
Method of Microeconomics
The study of Microeconomics involves several techniques such as conducting empirical research, using mathematical Models, and analysing real-world data. Economists utilise these techniques for examining theories, studying market patterns, and creating strategies to enhance market effectiveness. Microeconomics delves into particular markets and behaviours to grasp how individual choices influence the overall economy.
The analysis of Microeconomics has traditionally been based on two theories: general equilibrium theory by Leon Walras and partial equilibrium theory by Alfred Marshall.
The Marshallian and Walrasian techniques are both part of the broader field of neoclassical Microeconomics. Neoclassical economics examines how individuals and businesses make logical decisions to maximise their Economic welfare based on their available income and resources.
These techniques aim to describe human behaviour using practical mathematical terms. This enables economists to create mathematically verifiable Models for specific markets. Neoclassicals advocate for creating testable hypotheses about Economic events and then using data to identify the most effective hypotheses.
Conclusion
The study of Microeconomics is essential for understanding how individual decisions impact the overall economy. Exploring ideas such as Production, labor economics, pricing, and consumer behaviour provides us with an important understanding of market operations. Understanding Microeconomics is beneficial for making informed decisions and navigating Economic complexities, whether you are an individual consumer, a business owner, or a policymaker.
Economic insights for leaders with our Economics For Managers Course Register now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Main Problem of Microeconomics?

Microeconomics is the study of how people make decisions when allocating scarce resources. Some of the main problems in Microeconomics include:
a) Inequality
b) Monopoly
c) Externalities
d) Resource Allocation
What is the Heart of Microeconomics Analysis?

Microeconomics focuses on how individuals, businesses, and economic entities make decisions about allocating limited resources, shaping supply, demand, and market dynamics.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Management Courses, including the Economics for Managers Course, and the Personal and Organisational Development Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Transformational Leadership Theory.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Business Process Improvement Training, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Economics for Managers Course
Economics for Managers Course
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


