We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Ever wondered how strategic goals become actionable plans within an organisation? In every successful company, a key leadership layer is responsible for this transformation. This crucial tier is known as Middle Management. So, What is Middle Management?
Middle Management acts as the vital link between Senior Executives and the broader workforce, converting strategic goals into actionable plans. They oversee lower-level supervisors and employees, ensuring daily operations align with company objectives.
Continue reading this blog to understand What is Middle Management and how it can elevate your business to new heights.
Table of Contents
1) What is Middle Management?
2) Advantages of Middle Management
3) The Levels of Managerial Hierarchy
4) Responsibilities and Duties of Middle Managers
5) Challenges of Middle Management:
6) Career Strategies for Middle Managers
7) Conclusion
What is Middle Management?
Middle Management serves as the bridge between Executive-level Managers and First-line Managers. These managers have various responsibilities, but their primary role is to communicate upper management's goals to front-line employees and ensure these objectives are achieved. Additionally, Middle Managers often oversee training and development programs and manage employee performance.
Advantages of Middle Management
Middle Management plays an important role in ensuring an organisation operates smoothly. Without Middle Managers, upper management would be overwhelmed with day-to-day tasks, and front-line employees would lack clear direction and the necessary support to succeed in their roles.
Middle Managers are often strategically hired to enhance business functions, bringing valuable skills and advantages to their employers. Some of these advantages include:
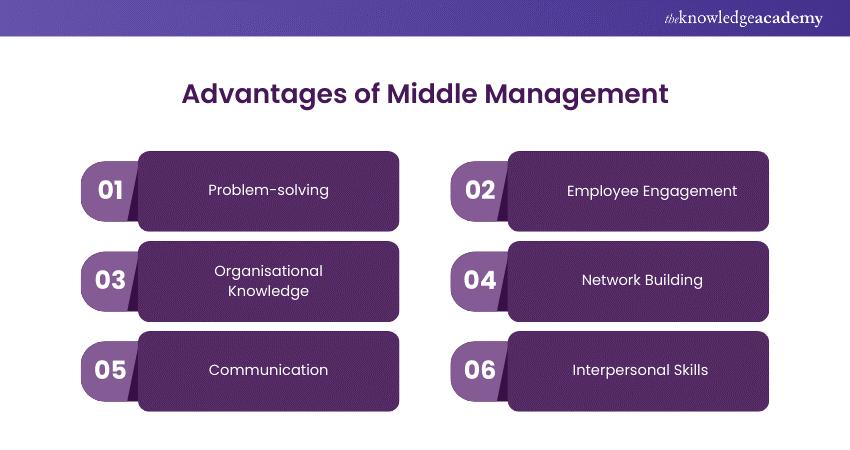
1) Problem-solving: Handling everything from staffing issues to conflict resolution.
2) Employee Engagement: Using positive reinforcement (recognition and rewards) or negative reinforcement (disciplinary action) to motivate employees.
3) Organisational Knowledge: Leveraging a deep understanding of the organisation, its structure, and its culture to make informed decisions and solve problems.
4) Network Building: Utilising a vast network of contacts within the organisation to troubleshoot issues and identify new opportunities.
5) Communication: Facilitating the smooth flow of information between different organisational levels.
6) Interpersonal Skills: Working effectively with people at all levels, making strong interpersonal skills essential for Middle Managers.
Build your workplace decision-making and problem-solving skills with our CMI Level 4 Training – Sign up today!
The levels of Managerial Hierarchy
There are basically three traditional levels of management, including top level, middle level, and first line. This structure is known as the managerial hierarchy, with each level having distinct focuses and responsibilities.
Top-Level Management
Top-level management also referred to as C-suite executives, oversees company strategy with a broad perspective on the organisation and its industry position. They are responsible for setting objectives that employees must achieve, with these goals trickling down to front-line employees.
Top-level management typically handles significant items such as:
a) Company vision and strategy
b) Long-term planning
c) Resource allocation
d) Corporate policies
Here are the common titles within top-level management:
1) Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
2) Chief Operating Officer (COO)
3) Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
4) Chief Information Officer (CIO)
5) President
6) Vice President (VP)
These managers usually possess extensive industry experience and a deep understanding of business, often holding at least a bachelor’s degree, with many having an MBA or other advanced degrees like a Doctor of Management. Strategic thinking, problem-solving, and leadership skills are also crucial for these roles.
Become familiar with how to assume human nature and managerial behaviour with our CMI Level 4 Certificate in Management and Leadership Training.
Mid-Level Management
Middle Management, or executory management, refers to managers positioned between Senior Executives and First-line Managers. They are tasked with implementing the decisions made by upper management and ensuring directives are executed.
Middle Managers have various responsibilities that vary depending on the size and structure of the organisation. In smaller organisations, they might handle all day-to-day operations, including planning, budgeting, and staffing. In larger organisations, they might oversee specific functions or departments, including Human Resources, marketing, or sales.
Some of the most common responsibilities of Middle Managers include:
a) Overseeing and mentoring First-line Managers
b) Managing inter-departmental coordination
c) Creating and executing operational plans
d) Tracking progress towards departmental and business goals
e) Facilitating communication between senior executives and First-line Managers
f) Establishing sales or operational targets for departments
g) Addressing and resolving employee conflicts
Common job roles for Middle Managers include Business Manager, General Manager, Operations Manager, and Store Manager. Middle Managers often hold a bachelor’s degree, and some roles may require a management master’s degree or an undergraduate management certificate to acquire critical skills for positions such as general or operations manager, which can also impact the Chief Operating Officer Salary.
First-Line Management
First-line Managers are also known as front-line or supervisory managers. They directly supervise front-line employees, ensuring they complete their tasks on time and to standard. Despite being among the lower management levels, their role is crucial.
Typical responsibilities of First-line Managers include:
a) Hiring and training employees
b) Setting work schedules
c) Assigning tasks and responsibilities
d) Enforcing company policies
Common titles for First-line Managers include Supervisor, Team Leader, Floor Manager, and Shift Manager. Most organisations require at least a high school diploma for first-line management positions, although industry experience can sometimes suffice.
For example, an employee who advances from barista to store manager in a coffee shop might not need formal education for the position. However, roles in industries like healthcare may require at least a bachelor’s degree and further education can help enhance skills and promote career advancement.
Responsibilities and Duties of Middle Managers
Middle Managers address everyday issues at a specific business site or within a particular department of the organisation. While top management focuses on overall strategy and long-term planning, Middle Management emphasises interactions with employees and the daily operations of a specific site, office, or department. Common duties and responsibilities of middle-level managers include:
a) Developing and implementing daily routines for a specific office, branch, or department
b) Monitoring employee performance
c) Assigning and supervising specific work tasks
d) Ensuring processes and procedures comply with the organisation’s overall guidelines
e) Inspiring and encouraging employees to perform at their best
f) Generating ideas to improve productivity at a specific business location or within a department
g) Recruiting and retaining hourly or salaried employees
h) Interpreting top-level management strategy and translating it into everyday policies
i) Allocating resources within a branch, office, or division
j) Reporting issues and performance metrics to top-level management
Challenges of Middle Management
Middle Managers possess some of the most valuable skills in any industry. Their multifunctional work is crucial to the everyday operations of many organisations. Recognising and supporting Middle Managers is essential for maintaining effective and productive teams. However, they face some challenges in their job role. Some of them are mentioned below.
Increased Difficulty in Leadership
Leadership has become increasingly challenging over the past few years. With the rise of remote work and the accompanying feelings of isolation, engaging team members and encouraging stellar performance have become more difficult. Middle Managers now struggle to balance their responsibilities while managing group demands and expectations.
The Messy Middle
A primary challenge lies in the very nature of their role: being in the middle. Middle Managers often feel caught between leading teams and reporting to higher-ups. They are tasked with directing work while also performing it, creating a dual role that demands high dedication and focus.
Additionally, they frequently mediate conflicts between those above and below them in the hierarchy, a difficult task when trying to satisfy both sides.
Stress and Burnout
Middle Managers experience significant stress from solving problems across the hierarchy, coaching teams, organising tasks, and maintaining communication. The pressure to deliver exceptional results, meet deadlines, and satisfy customer and leadership expectations can lead to burnout.
It is crucial to provide strong support systems for Middle Managers to help them manage their workload and support their teams effectively.
Feeling Undervalued
Middle Managers often report low job satisfaction and feeling undervalued despite their critical role. The perception of Middle Managers as mediocre supervisors is a gross underrepresentation of their value.
They are the glue that holds companies together, offering essential guidance and support. Without their organisational and communication skills, teams would struggle to function smoothly, impacting overall company success and productivity.
Understand how to implement and evaluate the personal development plan with our CMI Level 4 Diploma in Management and Leadership.
Career Strategies for Middle Managers
Middle managers are pivotal to the success of nearly every organisation. For them to thrive, they need to feel respected and valued. Organisational leaders can provide the necessary support to help Middle Managers prosper in their careers. The key tips for helping Middle Managers succeed are:
1) Learning and Development Opportunities: Offer programs to enhance decision-making and communication skills.
2) Reskilling and Upskilling: Provide chances to develop new skills that strengthen their leadership abilities.
3) Support and Recognition: Ensure Middle Managers feel respected and valued within the organisation.
Register for our CMI Level 4 Award in Management and Leadership and learn about the internal and external factors influencing organisational culture.
Conclusion
Understanding What is Middle Management highlights its important role as the bridge between senior executives and front-line employees. Middle Managers translate strategic goals into actionable plans, ensuring smooth day-to-day operations. Their effectiveness in managing, motivating, and mediating is key to organisational success and operational efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can Middle Managers Enhance Their Leadership Capabilities?

Middle Managers can enhance leadership by seeking mentorship, pursuing leadership training, and setting clear goals for their teams.
How can Middle Managers Improve Communication Within Their Teams?

Improve team communication by fostering open dialogue, actively listening, and providing regular feedback.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various CMI Level 4 Training, including CMI Level 4 Award in Management and Leadership Training and Health and CMI Level 4 Certificate in Management and Leadership Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Leadership and Management Skills.
Our ILM, CMI Leadership & Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to CMI Level 4, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Leadership Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming ILM, CMI Leadership & Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CMI Level 4 Award in Management and Leadership Training Course
CMI Level 4 Award in Management and Leadership Training Course
Fri 25th Apr 2025
Fri 20th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 17th Oct 2025
Fri 19th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


