We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Picture this: you're working with simple int, char, or boolean values, and suddenly, you need them to act like objects. What if I told you there's a way to transform these basic types into full-fledged objects with just a bit of Java magic? That’s the power of the Wrapper Class in Java - it bridges the gap between Java's primitive data types and its object-oriented nature, opening up new possibilities for handling data.
In this blog, we’ll dive into how the Wrapper Class in Java works, explore the magic of autoboxing and unboxing, and guide you through creating your very own custom wrapper class to unlock even more coding potential. Ready to explore this hidden gem of Java? Let’s go!
Table of Contents
1) What is Wrapper Class in Java?
2) Use of Wrapper classes in Java
3) Autoboxing
4) Unboxing
5) Advantages of Wrapper Classes
6) Java Wrapper Classes Example
7) Custom Wrapper Classes in Java
8) Conclusion
What is Wrapper Class in Java?
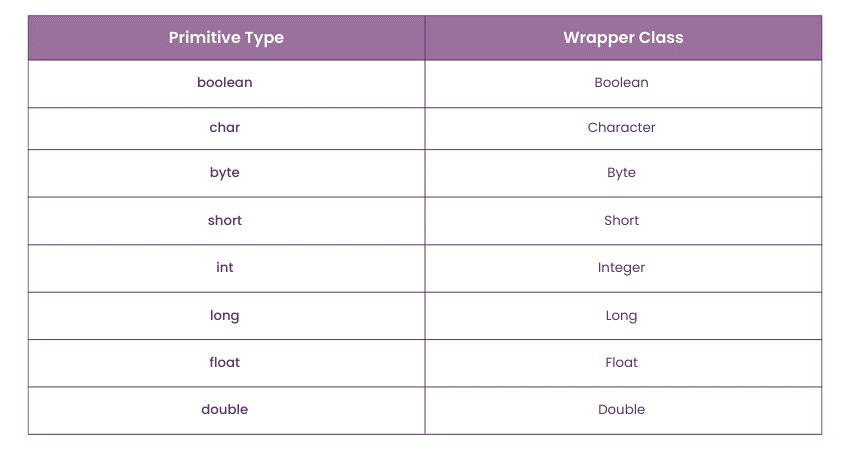
A Wrapper Class in Java is essentially an object representation of a primitive data type. Java provides these classes to convert primitive types into objects, which allows them to be used in various object-oriented contexts like collections (e.g., ArrayList, HashMap). For example, the wrapper class for the int primitive is Integer, and for float, it's Float.
Here are some common wrapper classes in Java:
Elevate your career by mastering the Java Programming Course – join our course and become a coding expert!
Use of Wrapper classes in Java
Here are some key situations where wrapper classes are essential:
1) Change the Value in Method: Java supports only call by value. When passing a primitive value, the original value remains unchanged. However, converting the primitive value to an object allows the original value to be modified.
2) Serialisation: Serialisation involves converting objects into streams. Primitive values need to be converted into objects using wrapper classes to be serialised.
3) Synchronisation: In multithreading, Java synchronisation works with objects, making wrapper classes necessary.
4) java.util Package: The `java.util` package provides utility classes that work with objects.
5) Collection Framework: The Java collection framework (e.g., `ArrayList`, `LinkedList`, `HashSet`, `TreeSet`, etc.) operates exclusively with objects, necessitating the use of wrapper classes for primitive types.
Autoboxing
Autoboxing is the automatic conversion of primitive data types into their corresponding wrapper class objects. Java introduced this feature in Java 5 to reduce manual coding efforts. For example, if you have an int variable but need an Integer object for a certain task, Java will automatically box the int into an Integer object.
Here’s an example of autoboxing:
|
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int num = 100; Integer boxedNum = num; // Autoboxing: Java converts int to Integer
System.out.println("Boxed Integer: " + boxedNum); } } |
Output:
|
Boxed Integer: 100 |
Become a certified Java expert and take your coding skills to the next level with our Java Courses – sign up now!
Unboxing
Unboxing is the reverse process of autoboxing, where a wrapper class object is automatically converted back into a primitive type. Java handles this conversion seamlessly, making it easier to work with both types interchangeably.
Here’s an example of unboxing:
|
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer wrappedNum = 200; int num = wrappedNum; // Unboxing: Java converts Integer to int System.out.println("Unboxed int: " + num); } } |
Output:
|
Unboxed int: 200 |
Elevate your skills with our Web Development Using Java Training – register now and become a Java web expert!
Advantages of Wrapper Classes
Wrapper classes bring several advantages that make them indispensable in Java development. Some of the key benefits include:
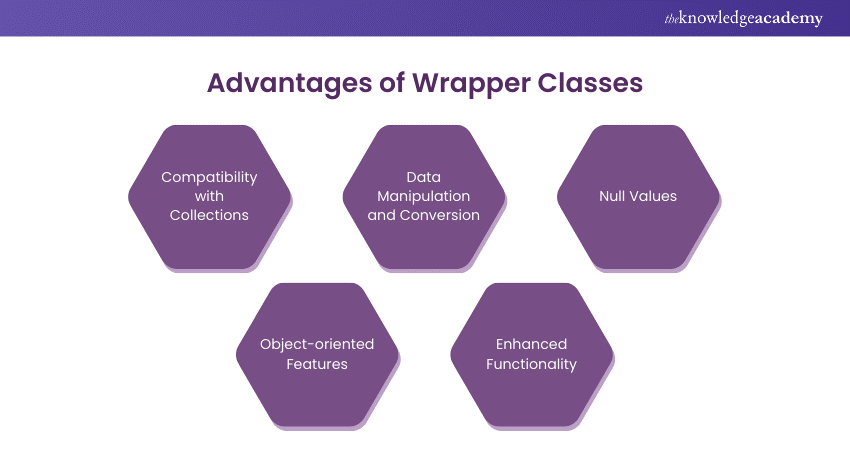
a) Compatibility with Collections: As mentioned earlier, collections in Java can only store objects. Wrapper classes ensure that primitive types can be easily included in collections.
b) Data Manipulation and Conversion: Wrapper classes come with utility methods for converting data from one type to another. For instance, you can convert a String to an int using the Integer.parseInt() method.
c) Null Values: Unlike primitive types, wrapper class objects can be null. This is useful in scenarios where a variable might not have a value, such as working with databases.
d) Object-oriented Features: Wrapper classes enable primitive types to benefit from object-oriented features, such as method overriding and inheritance.
e) Enhanced Functionality: Each wrapper class provides several methods that offer additional functionality compared to their primitive counterparts, like comparing values, converting strings, and more.
Build a strong coding foundation by understanding Object Oriented Programming (OOPs) Course and advance your development skills effortlessly!
Java Wrapper Classes Example
Here is a simple example demonstrating the use of wrapper classes in Java:
|
import java.util.ArrayList; public class WrapperExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // Autoboxing Integer boxedInt = 5; // int to Integer DoubleboxedDouble = 3.14; // double to Double // Unboxing int unboxedInt = boxedInt; // Integer to int double unboxedDouble = boxedDouble; // Double to double // Using wrapper classes in collections ArrayList intList.add(10); // Autoboxing happens here intList.add(20); // Retrieving and unboxing values from ArrayList int firstNum = intList.get(0); // Unboxing happens here System.out.println("First number: " + firstNum); } } |
Output:
|
First number: 10 |
Explanation:
1) Autoboxing:
a) `5` (int) is automatically converted to `Integer`, and `3.14` (double) to `Double`.
2) Unboxing:
a) `Integer` and `Double` objects are automatically converted back to `int` and `double`.
3) Using Collections:
a) An `ArrayList` stores `Integer` objects (autoboxed `int` values).
b) `10` is retrieved and unboxed from the `ArrayList` as an `int`.
Master Java EE Fundamentals with our comprehensive Introduction To Java EE Training Course and elevate your skills - join today!
Custom Wrapper Classes in Java
While Java provides a set of predefined wrapper classes, sometimes you might need to create custom wrapper classes for specific requirements. Custom wrapper classes allow you to wrap multiple related primitive fields or apply custom behaviours to objects.
Here’s an example of how to create a custom Wrapper Class in Java:
|
class CustomInteger { private int value; // Constructor public CustomInteger(int value) { this.value = value; } // Getter method public int getValue() { return value; } // Setter method public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } // Custom behaviour: Increment the value public void increment() { this.value++; } // Custom behaviour: Display the value public void displayValue() { System.out.println("The value is: " + value); } } public class CustomWrapperExample { public static void main(String[] args) { CustomInteger myValue = new CustomInteger(10);
// Accessing the custom wrapper class functionality myValue.displayValue(); // Output: The value is: 10 myValue.increment(); myValue.displayValue(); // Output: The value is: 11 } } |
Output:
|
The value is: 10 The value is: 11 |
Explanation:
1) Custom Wrapper Class (`CustomInteger`):
a) Field: The class contains a private `int` field called `value` that stores the integer.
b) Constructor: Initialises `value` when an object of `CustomInteger` is created.
c) Getter (`getValue`) & Setter (`setValue`): Methods to access and modify the `value`.
d) Custom Method (`increment`): Increases the `value` by 1.
e) Custom Method (`displayValue`): Prints the current value to the console.
2) Main Class (`CustomWrapperExample`):
a) Object Creation: `CustomInteger myValue = new CustomInteger(10);` initialises `myValue` with `10`.
b) Method Calls:
1) `myValue.displayValue();` prints the initial value, which is `10`.
2) `myValue.increment();` increases the value by 1.
3) `myValue.displayValue();` prints the updated value, now `11`.
Master Java Swing Development Training to build dynamic, user-friendly desktop applications and elevate your software development skills today!
Conclusion
Wrapper Class in Java transform basic types into versatile objects, making Object Oriented Programming smoother. With autoboxing and unboxing simplifying conversions and custom wrapper classes offering endless flexibility, you can enhance your code effortlessly. Embrace these tools to open up exciting new opportunities in your Java coding experience!
Achieve Java Engineering excellence and propel your career forward with our tailored Java Engineer Training - sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Use the Wrapper Class in Java?

The Wrapper Class in Java allows primitive types to be treated as objects, enabling their use in collections. It also facilitates autoboxing and unboxing, offering utility methods for data manipulation and conversion.
Is String a Wrapper Class?

No, String is not a Wrapper Class in Java. It is a separate class used to represent sequences of characters. Wrapper classes are specifically used to convert primitive types into objects.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Java Courses, including Java Programming, JavaScript for Beginners, Java Engineer Training and Web Development Using Java Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Java Developer Job Description.
Our Programming & DevOps Blogs cover a range of topics related to Java Programming, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Programming skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Programming & DevOps Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Java Programming
Java Programming
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


