We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +1800812339 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
If you're new to the world of Project Management or Software Development, you may have heard the term "Scrum Workflow" thrown around. But do you know what exactly does it mean?
According to the 17th State of Agile Report, 63% of Agile users implement Scrum methodology during their project workflow. Thus, you see that this Scrum methodology is the most popular among professionals. Thus, people implementing Scrum must be familiar with the term Scrum Workflow.
So, whether you're a novice or just looking to refresh your knowledge, you have come to the right place. This blog will provide you with a solid foundation to grasp the concept of Scrum Workflow and how it drives successful project outcomes. Let's dive in!
Table of contents
1) What is Scrum?
2) What is Scrum Workflow?
3) Roles in Scrum Workflow
4) Steps in the Scrum Workflow
5) Conclusion
What is Scrum?
Agile Project Management comprises of the Scrum framework that emphasises collaboration, flexibility, and iterative development. It enables teams to adapt to evolving requirements and deliver high-quality products efficiently.
At its core, Scrum revolves around the concept of Sprints, which are time-boxed iterations where teams work on delivering a potentially shippable product increment. Key components of Scrum include the following:
a) Product backlog
b) Sprint backlog
c) Daily stand-up meetings
d) Sprint reviews
e) Retrospectives
By embracing Scrum, organisations can enhance transparency, improve communication, and accelerate product delivery. This ultimately leads to enhanced business success and customer satisfaction.
What is Scrum Workflow?
Scrum Workflow is the structured approach followed within the Scrum framework to manage and execute projects effectively. It encompasses a set of roles, rituals, and artefacts designed to facilitate collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement throughout the development process.
At its core, the Scrum Workflow revolves around iterative cycles known as Sprints. Each Sprint essentially lasts between one to four weeks and aims to deliver a potentially shippable product increment. The Workflow begins with the product backlog, a prioritised list of features, enhancements, and fixes maintained by the Product Owner.
The Workflow also includes rituals such as Sprint retrospectives and artefacts to track the team's progress throughout the Sprint. It also includes product increment, which represents the work completed during the Sprint.
By embracing the Scrum Workflow, teams can foster a culture of collaboration, transparency, and continuous improvement. This, in turn, leads to faster delivery of high-quality products that meet customer requirements and drive business success.
Become familiar with the important terminologies used in Scrum – join our Scrum Overview Course today!
Roles in Scrum Workflow
In the Scrum framework, some professionals play a crucial part in ensuring the successful implementation of the Workflow. Each professional has distinct responsibilities that contribute to the overall effectiveness of the team and the project's success. Let's have a detailed look at each of these roles:
1) Product Owner
The Product Owner is a key stakeholder responsible for representing the interests of the business and ensuring that the team delivers value with each iteration. They act as the bridge between the Development Team and the stakeholders, conveying the vision, priorities, and requirements to the team.
They are tasked with maintaining the product backlog and ensuring that it aligns with the overall goals of the project. Moreover, they make decisions regarding what features to include in each Sprint, based on input from stakeholders and the team, and provide guidance and direction throughout the development process.
2) Scrum Master
The Scrum Master is a servant-leader responsible for ensuring that the Scrum framework is understood and followed by the team. They facilitate the team's progress by removing any impediments that may hinder their ability to deliver value.
The Scrum master coaches the team on agile principles and practices, fostering a collaborative and self-organising environment. They facilitate the various Scrum ceremonies, including Sprint planning, Daily stand-ups, Sprint reviews, and Retrospectives. The Scrum Master also acts as a mediator, resolving conflicts and promoting open communication within the team.
3) Software Development Team
The Software Development Team is a cross-functional group of individuals responsible for turning the product backlog items into working increments of software. They collaborate closely with each other and with the Product Owner to understand the requirements and deliver high-quality solutions.
The team self-organises and manages their work during the Sprint, deciding how best to accomplish the tasks at hand. They are also accountable for the success of the Sprint and work together to deliver value to the customer at the end of each iteration.
Understand the fundamental principles of Agile and Scrum methodology with our Scrum Certification Training – join now!
Steps in the Scrum Workflow
Scrum, as a framework, offers a structured approach to Project Management, guiding teams through a series of steps known as the Scrum Workflow. The following are the steps included within this Workflow:
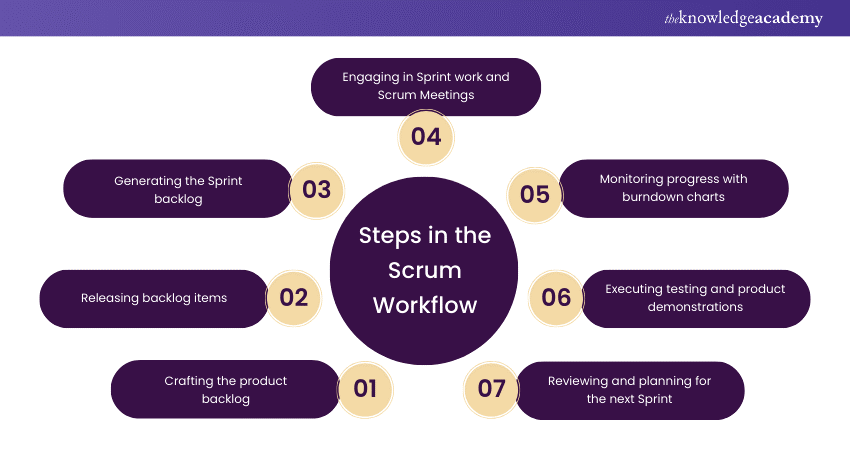
1) Crafting the product backlog
The first step in the Scrum Workflow is crafting the product backlog. It is the duty of the Product Owner to work with stakeholders to define and refine the backlog items, ensuring that they align with the vision and goals of the project. This backlog is the single source of truth for what is required to be done in the project, providing clarity and direction for the team.
2) Releasing backlog items
Once the product backlog is established, the team begins working on the highest-priority items. These items are broken down into much smaller tasks and implemented incrementally. This allows for regular releases and feedback from stakeholders. The goal of releasing backlog items is to deliver value to the customer early and often, enabling them to provide feedback that can inform future iterations.
3) Generating the Sprint backlog
At the beginning of each Sprint, the team selects a set of backlog items based on their capabilities and the priorities set by the product owner. The Sprint backlog outlines the tasks to be completed during the Sprint, providing clarity on the work to be done. The Sprint backlog is a comprehensive document that evolves as the team progresses through the Sprint, with new tasks added as needed and priorities adjusted based on changing circumstances.
4) Engaging in Sprint work and Scrum Meetings
During the Sprint, the team focuses on completing the tasks identified in the Sprint backlog. Daily stand-up meetings are held to synchronise efforts, discuss progress, and identify any obstacles that need to be addressed.
These Scrum meetings are time-boxed to ensure they stay focused and productive, with team members providing updates on what they have accomplished since the last meeting, what they plan to do next, and any impediments they are facing. By following the Scrum timebox, engaging in Sprint work, and attending Scrum Meetings, the team maintains momentum and keeps the project on track.
5) Monitoring progress with burndown charts
Throughout the Sprint, progress is monitored using burndown charts. Sprint Burndown charts track the remaining work versus time, providing visibility into the team's progress and helping to identify potential risks or bottlenecks. This enables the team to make sound decisions and adjust their approach as needed to meet sprint goals.
6) Executing testing and product demonstrations
As the Sprint progresses, the team executes testing to ensure quality increment. Product demonstrations are conducted at the end of the Sprint to showcase the completed work to stakeholders and gather feedback. This feedback informs future iterations and helps to ensure that the product meets customer needs.
7) Reviewing and planning for the next Sprint
At the end of each Sprint, the team hosts a Sprint review to inspect the increment and gather feedback from stakeholders. They also hold a Sprint retrospective to reflect on their process and identify areas for improvement. Based on this feedback, the team reviews and plans for the next Sprint, adjusting the product backlog accordingly.
Conclusion
The Scrum Workflow offers a dynamic and collaborative approach to Project Management, enabling teams to adapt to changing requirements and deliver value incrementally. By following the structured processes and roles outlined in the Scrum framework, organisations can enhance transparency, foster collaboration, and accelerate product delivery.
Learn how to work in iterations by joining our Scrum Developer Certification – register now!
Frequently Asked Questions

An example of a Scrum Flow involves iterative cycles called Sprints, with activities like backlog refinement, Sprint planning, daily stand-ups, retrospectives and Sprint reviews, ensuring collaborative and incremental product development.

The roles in Scrum Workflow include the Product Owner, responsible for prioritising tasks; the Scrum Master, facilitating the team; and the Development Team, executing the work and delivering increments iteratively.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Scrum Courses, including the Scrum Master Certification Course, Scrum Developer Training, and Scrum for Teams Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What are Project Controls.
Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to Scrum, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Scrum Master Certification
Scrum Master Certification
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 27th Feb 2025
Thu 27th Mar 2025
Thu 29th May 2025
Thu 3rd Jul 2025
Thu 4th Sep 2025
Thu 6th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


