We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +1800812339 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Have you ever marvelled at how data glides effortlessly through your network, connecting devices and enabling smooth communication? This seamless communication is made possible by the switch; which is a crucial component in networking. But What is a Switch in Networking exactly, and why does it matter for networks of all size
In this captivating exploration, we’ll unravel the mysteries of network switches. We’ll delve into their functions, explore different types, and reveal why they’re the backbone of modern network infrastructure. Let’s dive into this blog on "What is a Switch in Networking?" and demystify the beating heart of efficient data transfer and robust network performance!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is a Network Switch?
2) Types of Network Switches
3) What Problems do Switches Solve?
4) How to Set up a Network Switch?
5) Network Switch vs Router
6) Conclusion
Understanding What is a Network Switch?
A network switch links devices within a network, letting them to communicate by exchanging data packets. These switches can be either hardware devices managing physical networks or software-based virtual devices. Operating at the data-link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model, network switches play a crucial role in local area networks (LANs) using Ethernet.
In such networks, switches determine the destination of each incoming message frame by examining the Media Access Control (MAC) address. Their primary functions include learning MAC addresses, forwarding data packets, and ensuring the protection of these packets.
Types of Network Switches
Network switches come in various types and categories to address different use cases. These various types of switches cater to different networking needs, from simple home setups to complex enterprise environments. Let's explore them in detail:
1) Fixed-Configuration Switches
Such switches have a fixed number of ports and are not expandable, making them cost-effective. They typically come with 8, 16, 24, or 48 Ethernet ports, with speeds usually starting at 1 Gbps. Connectivity options include wired electrical ports (RJ45) or optical fibre ports.
2) Stackable Switches
These switches allow for network optimisation and increased reliability. They function as a single switch with a unified management interface, enabling link aggregation, traffic mirroring, and Quality of Service (QoS) across multiple units.
3) PoE Switches
Power over Ethernet (PoE) switches supply DC power to low-power devices over LAN cables, eliminating the need for separate power supplies. This simplifies installation and enhances safety by managing low power output intelligently.
4) LAN Switches
They are also known as Ethernet or data switches and are used to connect devices within a company’s internal LAN. They efficiently allocate bandwidth to prevent data packet collisions and alleviate network congestion by directing packets to their intended recipients.
5) Smart Switches
Smart or intelligent switches are a type of managed switch that offers more features than unmanaged switches but fewer than traditional managed switches. This makes them more advanced than unmanaged switches while being more cost-effective than fully managed ones.
6) Routing Switches
Routing switches connect Local Area Networks (LANs) by performing both MAC-based Layer 2 switching and routing functions at OSI Layer 3 (network layer). They direct traffic based on the IP address in each packet, ensuring efficient data flow across the network. Additionally, they support advanced features like Quality of Service (QoS) and security protocols.
7) Managed Switches
These switches offer advanced features beyond unmanaged switches but are less complex than fully managed ones. They are suitable for smaller networks with limited budgets, providing options like VLANs and basic QoS.
8) Unmanaged Switches
These basic switches expand LAN connections without user configuration. They are plug-and-play, using device MAC addresses to transmit data. While affordable, their limited capabilities make them unsuitable for many corporate applications.
9) Modular Switches
These switches allow for the addition of extension modules, providing flexibility as the network grows. They support app-specific expansions like wireless connections, firewalls, and network analysis. Typically, more expensive, they are used in large networks and often include Layer 3 routing capabilities.
10) Data Center Switches
Designed for high-performance environments, these switches offer features like high-speed performance, large port capacity, low latency, virtualisation support, security, and QoS. They are ideal for implementing Software-defined Networking (SDN) and providing virtualisation and programmability.
11) Switches With Optical Fibre Ports
These switches extend connectivity beyond the 100-meter limit of standard Ethernet cables using fibre-optic connections. They often include both RJ45 and small-form-factor pluggable fibre optic ports used to connect remote switches within or across buildings.
12) Keyboard, Video, and Mouse (KVM) Switch
These switches connect multiple computers to a single keyboard, mouse, or monitor, often used to control server groups. They support keyboard hotkeys for quick switching and can extend reach by several hundred feet for video transmissions.
Stay ahead of threats with our CCNP Security Training - join us and equip yourself with the latest skills!
What Problems do Switches Solve?
Network switches are essential components in modern networking, addressing several key issues to ensure efficient and reliable communication. Here are seven detailed pointers on the problems they solve:
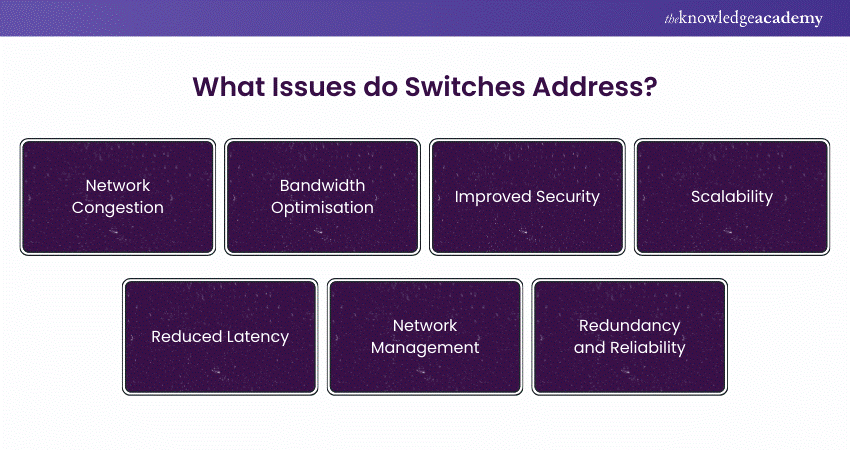
a) Switches segment a network into multiple collision domains, sending data packets only to their intended devices, not broadcasting to all.
b) Each device gets its own bandwidth, preventing competition and improving data transfer efficiency and overall network performance.
c) VLANs in switches segment network traffic, isolating sensitive data and restricting access to specific network parts.
d) Switches allow easy network expansion as the number of devices grows, without significantly impacting performance.
e) Direct paths for data packets minimise hops, reducing latency and improving transmission speed.
f) Managed switches offer QoS for prioritising critical traffic and SNMP for monitoring and managing network performance.
g) Configurable for redundancy, switches ensure network reliability and uptime by taking over if one switch fails.
Join our Cisco IOS Network Security Training and master the techniques to safeguard your network - sign up now!
How to set up a Network Switch?
Depending on the network type, different switches can be used. For a small office LAN or a home network, a switch is typically connected to one of the router’s ports. This setup expands the number of wired internet-connected devices, such as desktops, laptops, and printers. Here are the typical steps to set up a network switch:
a) Purchase the Switch: Choose a switch based on the network’s needs and requirements.
b) Connect to the Router: Use a straight-through cable to connect a port on the switch to the router. Most switches have uplink ports for this purpose, but if an uplink port is unavailable, any port can be used.
c) Configure IP Addresses: Once the switch is physically connected to the router, configure the IP addresses of the connected devices.
Gain expertise in Cloud Security with our comprehensive Cisco Umbrella Training - sign up now!
Network Switch vs Router
Network switches and routers are often confused, but they serve different functions and operate on different OSI model layers. Here are the key differences:
|
Aspect |
Router |
Network Switch |
|
Layer of Operation |
Operates at Layer 3 (Network Layer) of the OSI model |
Functions at Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) of the OSI model |
|
Function |
Moves data between two or more computer networks |
Connects multiple devices within a single LAN, facilitating resource sharing |
|
Address Examination |
Examines the IP addresses of packets to determine their route and destination |
Uses the MAC addresses of devices to transfer data to the correct destination |
|
Data Units |
Works with data packets |
Handles data frames at the data-link layer |
|
Complexity |
More sophisticated, using routing algorithms to direct data across large networks |
Less sophisticated, does not use routing algorithms |
|
Network Type |
Can operate within both wired and Wi-Fi networks |
Limited to wired network connections |
|
Additional Service |
Offers services like Network Address Translation (NAT), NetFlow, and Quality of Service (QoS) |
Does not provide services like NAT, NetFlow, and QoS |
Conclusion
Understanding What is a Switch in Networking, and its pivotal role can transform your approach to Network Management. Be it optimising a small home network or managing a large enterprise system, switches are the backbone of efficient data flow and robust connectivity. We hope this blog helped you unlock the full potential of your network infrastructure.
Master the art of network design with our Cisco Certified Design Associate Training - join us and start your journey today!
Frequently Asked Questions

A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) acts as a logical subdivision of a physical network, allowing network administrators to segregate traffic. Switches support VLANs by enabling devices in different VLANs to communicate as if they were on separate physical networks, improving network efficiency and security.

Yes, a switch can be used to expand the number of devices in your network by providing additional ports. This allows more devices to connect and communicate within the same network, enhancing connectivity and resource sharing.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cisco Trainings, including the Cisco IOS Network Security Training, Cisco Certified Design Associate Training, and Cisco Umbrella Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Cisco Switch.
Our IT Infrastructure & Networking Blogs cover a range of topics related to Networking Switch, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Infrastructure & Networking skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CCNP Security Training
CCNP Security Training
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


