We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +1800812339 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In the digital era, in which data carries the number one spot for businesses, the importance of information management and control has never been so self-evident. Information Governance (IG) is a holistic approach that involves policies, procedures, and technologies to control and secure information assets during their lifecycle. The purpose of this blog is to offer a practical and detailed information on Information Governance, its meaning, its legal and technical frameworks, its essential elements, its model and its fundamentals, along with its advantages, challenges and the role it plays in today's organisational setting.
Table of Contents
1) What is Information Governance?
2) Why is Information Governance important?
3) Framework for Information Governance
4) Essential Elements of Information Governance
5) Models of Information Governance
6) Fundamentals of Information Governance
7) Advantages of Information Governance
8) Challenges in Information Governance
9) Conclusion
What is Information Governance?
Information Governance (IG) is a strategic system of information asset management to guarantee their worthiness for use, safety, reliability and compliance with the relevant policies and regulations. It entails a comprehensive philosophy that allows organisations to manage information throughout their lifecycle, starting from creation up to its disposal. The key activities of IG are identifying the procedures and positions and defining responsibilities to process the information and keep it reliable regardless of its classification or locality.
Why is Information Governance important?
Organisations that operate currently in the environment of digital space, in which data are generated at an unimaginable rate face multiple information-related challenge. These challenges involve the ensuring of data security, the compliance with internal regulatory requirements, the managing of data proliferation, and the adopting and completion of the data as the source of decision-making. Information Governance addresses such concerns by offering a well-situated structure within which information assets can be managed and risks mitigated while the values of data can be optimally extracted.
Framework for Information Governance
The Information Governance Framework represents the foundation on which organisations manage and protect the digital assets from the within. It has several key elements that work together to making up the way in which the structure, processes and the principal of Information Governance are enforced in the organisation. Let's delve deeper into each component to understand its significance within the framework:
1) Definition and scope: Outline the scope of Information Governance, such as the covered types of information, compliance with applicable regulations, and organisational objectives.
2) Assignment of roles and responsibilities: Ensure that people or groups having authority over information assets are clearly regulated and they are assigned and responsible for the work.
3) Establishment of information policies and procedures: Frame a comprehensive policy and procedure which will tackle the generation, arrangement, and management of the information. Also, its access and disposal will be included.
4) Management of third-party relationships: Prescribe that the vendors and other partners adhere to the Information Governance regulations and procedures.
5) Ensuring business continuity, disaster recovery, and contingency plans: Create and implement telecommunication plans to ensure the provision of data and its integrity during disasters and disruptions.
6) Conducting audits and reviews: Conduct targeted audits and reviews of the Information Governance frameworks to identify areas for enhancements and in line with the set standards.
Essential elements of Information Governance
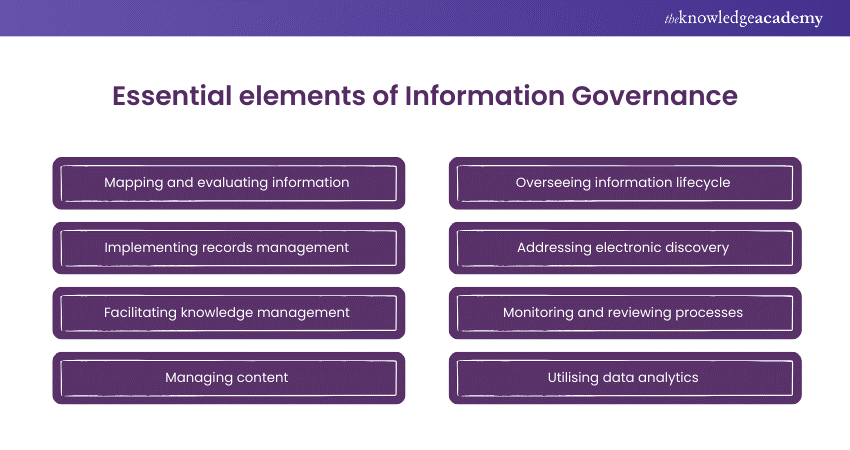
An Information Governance strategy comprises diverse measures, processes, and practices directed to controlling and protecting information resources via all stages of their lifecycle. All elements are key to the organisation's proper functioning, which indicates the effectiveness of the system to preserve the security, secrecy, accessibility, and compliance of information.
1) Mapping and evaluating information: Categorise and tag information assets based on their importance, confidentiality and the significance that they have for the organisation.
2) Implementing records management: Develop filing mechanisms which will catalog record managerial activities from creation to disposition.
3) Facilitating knowledge management: Institute a channel of knowledge sharing and collaboration within the organisation through effective data management and dissemination of information.
4) Managing content: Prepare ways to manage digital content which may include records, emails and multimedia materials to retain accessibility and security.
5) Overseeing information lifecycle: Manage the whole life of information with the procedures, such as creation, storage, retrieval, and disposal, compliantly and in an orderly manner.
6) Addressing electronic discovery: Come up with methods and instruments for tracking, saving, and retrieving electronic information in connection with due-process and compliance issues.
7) Monitoring and reviewing processes: Continuously monitor and analyse the Information Governance processes to detect and address compliance issues, security breaches, and inefficiencies of various kinds.
8) Utilising data analytics: Utilise the data analytics tools and techniques to gain depth knowledge of information usage patterns, identify risks, and enhance the quality of decision-making processes.
Models of Information Governance
Several models of Information Governance exist, from a centralised style to a decentralised style and more. These models may lay down differences regarding the power to decide the issues at hand, allocation of resources, and the organisational structure. Common models for this purpose are the Federative model, wherein responsibility for Information Governance is distributed between various departments or business units and Centralised model, where a single entity governs all aspects of Information Governance.
Fundamentals of Information Governance
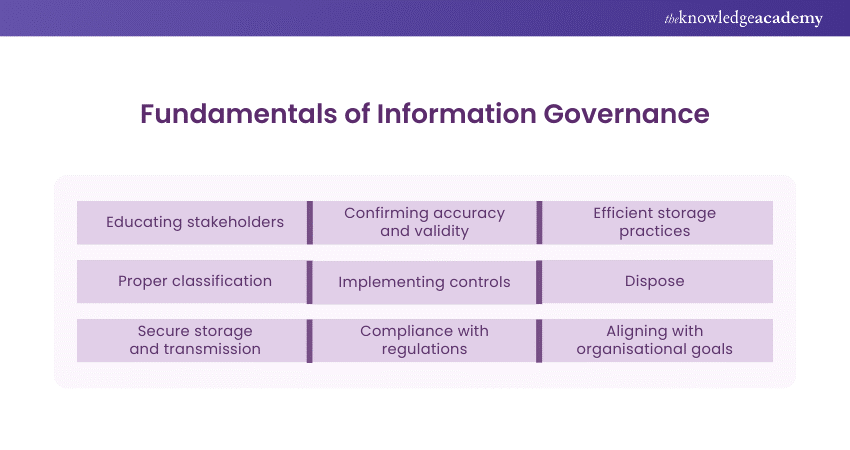
The digital world of today requires the exemplary management of Information Governance (IG). The fundamentals supply a systematic method, which ensures a faithful, secure, and self-consistent data storage. These fundamentals are pivotal as they allow the organisations to take a proactive approach to the handling of the information and its security. Lets look at some of the Fundamentals of Information Governance:
1) Educating stakeholders: Raise awareness among employees on the implementation of Information Governance and their position in maintaining information safety and rules.
2) Confirming accuracy and validity: Make sure that the information is accurate, reliable, and up to date by the verification processes and quality controls.
3) Efficient storage practices: Bring out the best from the storage infrastructure and practices through controlling costs and providing optimal performance and scalability.
4) Proper classification: Cluster assets related to information according to their consent, the importance, and the regulatory compliance for creating adequate protection and management.
5) Implementing controls: Apply access controls, encryption and other security based measures to avoid leakage of information to unauthorised parties for disclosure or modification.
6) Dispose: Include methodologies of secure disposal of whatever has expired or no more required in accordance with the law and its regulatory requirements.
7) Secure storage and transmission: Ensure that information is secured during storing, transmission, and processing to effectively avert unauthorised access or interception.
8) Compliance with regulations: Maintain compliance with existing legislation, regulations, and industry standards regarding information protection, data privacy, and disclosure issues.
9) Aligning with organisational goals: Develop Information Governance ideas to be in line with organisational targets and expectations to make most of the information assets possible and meet business goals.
Improve your CISA skills through our CISA Certified Information Systems Auditor
Advantages of Information Governance
With data being the driving force behind many businesses today, Information Governance is becoming a mission-critical function in organisations. To be a successful company, a business must understand the benefits it can provide if it wants to overcome digital barriers. The advantages of Information Governance solution are not limited to developing administrative procedures but extend to improving user experience, accessibility and collaboration too. This allows IG to match with the organisation’s objectives and to resolve regulatory concerns, thus creating data integrity, security, and efficiency. These are the advantages of Information Governance:
a) Establishment of governance policies: Built upon Information Governance the policies and procedures governing information management that promote consistency, transparency and accountability.
b) Enhanced accessibility and storage efficiency: Through its aid in organising and classifying information assets, Governance of information streamlines better access and promotes storage efficiency, enabling employees to locate and retrieve information faster and more conveniently.
c) Improved decision-making processes: Access to the right information is not only accurate, timely and relevant but it also helps to make better decisions so that an organisation can perform at optimal efficiency and effectiveness.
d) Reduced costs and enhanced collaboration: It achieves this goal by centralising the sources of information management and reducing duplication of efforts which leads to saving costs and quick collaboration and exchange of information.
e) Decreased litigation expenses: Proper knowledge handling and retaining data decreases the likelihood of litigation and e-discovery cost by quick accessing and retrieving data that are essential.
f) Elimination of data silos: Today Information Governance is an effective tool for organisations to give up the line of communication and lead the way to cross-functional cooperation by providing a single strategy for information keeping and sharing.
g) Increased profitability: Through the procedures of gaining and holding of value of information assets, and reducing the risks, Information Governance serves to the sustainability of the organisation.
h) Implementation of governance policies: Relating to Information Governance, the policies and procedures developed by an organisation are crucially important to show their compliance with legislature and industry standards, which in turn contributes to the positive reputation and trustworthiness of the organisation.
Challenges in Information Governance
Organisations encounter several obstacles when conducting Information Governance. Knowing these constraints is fundamental for creating up-to-date solutions to fight them. From legislation and non-operational requirements to exponential growth of data, companies face manifold challenges. These issues in the lifecycle management are further intensified thus necessitates highly functioning systems and capabilities. With the help of such examination, businesses can avail a chance of being proactive to develop the IG frameworks where data integrity, security, and compliance with the regulations are included. Here are some examples:
a) Addressing compliance and regulatory concerns: This issue is one of the greatest obstacles that Information Governance programs face when adapting to the dynamic constraints and industry regulations.
b) Navigating the landscape of big data and machine learning: The rise in big data and machines learning creates the challenges intervening in the management and safeguarding of the huge data while efficiency, ensuring privacy and security.
c) Effective lifecycle management: Information lifecycle consisting of generation, circulation and disposal necessitates considerable processes, advanced tools and sufficient means, which is ultimately hard enough to put them into place and keep up.
Conclusion
Information Governance is an inevitable component of today's data-reliant environment. Additionally, by adapting firmly grounded IG frameworks, organisations will be able to navigate complexities, to create appropriate risks management strategies and to maximise the return on their information assets` investment. We hope that this blog will help readers to understand What is Information Governance in detail. Via a proactive approach with organisational objectives as the guideline, Information Governance assists businesses to remain on top in the ever-changing digital world.
Improve your CISM skills through our CISM Certified Information Security Manager Course!
Frequently Asked Questions

The coverage of the IG includes the managing of all type of data, ensuring of rules compliance, the reducing of risks, technology infrastructure maintenance, the establishment of organisational policies, the education of stakeholders, the management of third-party relationships and the monitoring of organisations’ practices for constant improvement.

Information Governance (IG) is an activity that is developed based on assessment, policy creation, role assignment, technology use, and continuous improvement ensures a good data management and compliance.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various CISM Training, including Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) Training Course, Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO) course and Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) courses. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into CISM or CRISC: A Complete Comparision
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs covers a range of topics offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Improvement skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CISM Certified Information Security Manager
CISM Certified Information Security Manager
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


