We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +55 8000201623 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Have you ever wondered how a company manages and processes huge amounts of data in a consistent and organised manner? Well, the answer is Data Architecture. But What is Data Architecture? It is a set of standards and policies for managing, storing, and transporting data efficiently and effectively. It helps the organisation make data-driven decisions. To learn more about Data Architecture, including its importance, principles, and frameworks, read this blog.
Table of Contents
1) What is Data Architecture?
2) Importance of Data Architectures
3) Principles of Data Architecture
4) Frameworks for Data Architecture
5) Tools for Data Architecture Diagram
6) Difference between Data Architecture and Data Modelling
7) Conclusion
What is Data Architecture?
Data Architecture is defined as the framework, policies, and rules for managing, monitoring, and accessing data easily. It acts as a blueprint for data and how it is transferred through data storage systems. Data architecture design should ideally be based on organisational needs, and a standard design ensures that data is manageable and useful.
Data Architecture aims to minimise unessential redundant storage and enhance data quality through cleansing and deduplication. It also provides the foundation for data analytics. Data architectures sometimes use cloud platforms to control and process data.

Importance of Data Architectures
Data Architecture provides several key benefits to organisations. It helps businesses to enhance strategic planning and make operational decisions. Some of them are listed below:
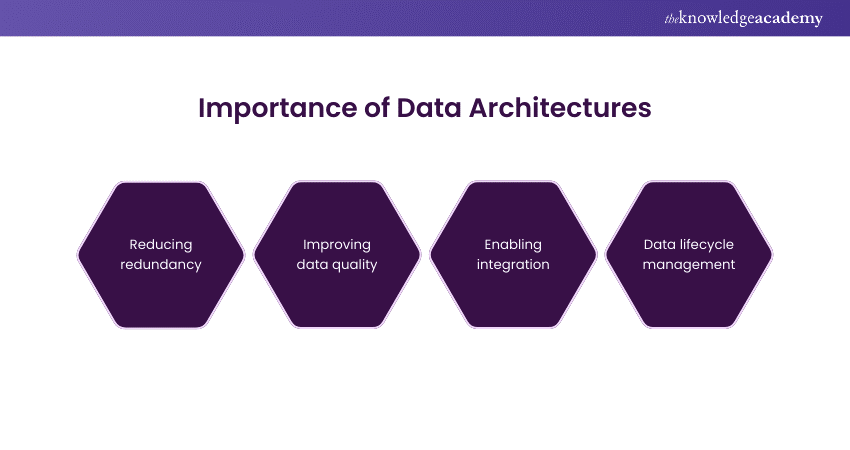
1) Reducing redundancy: A standard Data Architecture defines how the data is stored, hence minimising the chance of duplication. This helps to avoid inconsistency, data inaccuracies, and missed opportunities for data integration.
2) Improving data quality: Data architectures can fix issues of poorly managed data lakes, also known as “data swamps.” They assist in enforcing data governance and security standards, allowing the appropriate oversight into the data pipeline to operate as planned. To improve data quality and governance, data architectures check that data is stored predefined to improve data quality.
3) Enabling integration: Due to technical restrictions on data storage and organisational barriers, Data become siloed. Hence, data architectures should facilitate data integration across domains for different business functions to access each other’s data. This allows a better understanding of common metrics and decision-making.
4) Data lifecycle management: Data Architecture checks how data is managed over time. After some time has passed, data is bound to become less useful. Such data with low relevance can be moved to cheaper and slower storage types. However, it remains available for reports and audits.
Keen to set up acreer in the field of data analytics, Refer to our blog "Data analytics a good career"
Principles of Data Architecture
The Principles of Data Architecture are the rules and policies that govern the collection, management, use and integration of data in an organisation. It helps to form the foundation of a Data Architecture framework and make data strategies and data-driven decisions. These principles are discussed below:
1) Validating data at entry points: A standard Data Architecture design flags and fixes errors as soon as possible, improving the organisation's overall health. For that, use the Data Integration Platform that automatically validates your data at the entry point to protect against future damage.
2) Striving for consistency: The use of common vocabulary will reduce confusion among developers and non-developers, further helping them collaborate and work on the same project. Common vocabulary must be used to maintain control of data architecture, product catalogues, fiscal calendar dimensions, and others.
3) Documentation of everything: Documenting all data processes allows organisations to check how much data is collected, which datasets are aligned, and which applications need to be updated. This helps maintain data visibility across organisations.
4) Minimising data duplication and movement: Every time data is moved, it impacts cost, accuracy, and time. Data Architecture must include a framework to minimise the requirement for additional data movement. It helps cut costs, enhance data freshness, and optimise data agility. It sees data as a shared asset, allowing everyone to operate from a single data version.
5) Ensuring adequate user data access: Data Architecture must be designed to give users the proper interfaces to use data utilising designated tools.
6) Importance of security and access controls: Data architectures must have security access without compromising access controls on the raw data. With the coming of data security projects, it is easy to check unified data security.
Keen to undesratnd the significance of Dara analytics, refer to our blog on "Importance of data analytics"
Frameworks for Data Architecture
Organisations can use popular architecture frameworks to create and implement data architectures rather than working from scratch. The three frameworks are mentioned below:
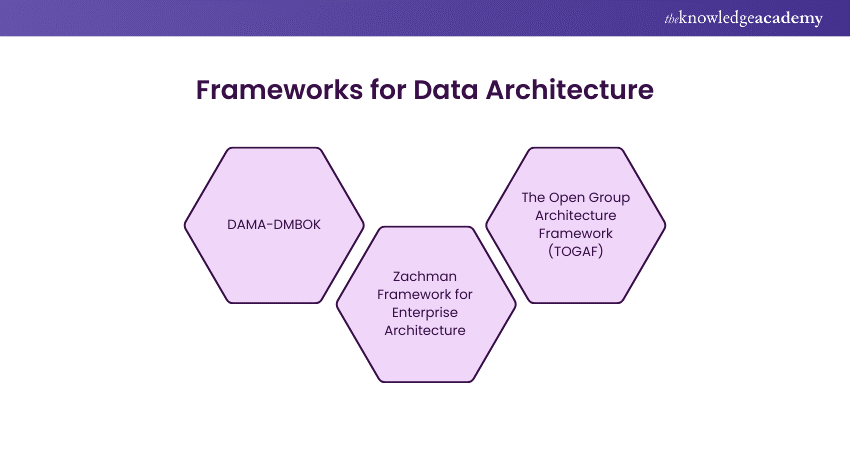
1) DAMA-DMBOK: The Data Management Body of Knowledge (DAMA-DMBOK) is a framework that addresses Data Architecture and data management principles. It covers the meaning of data management terminology, functions, deliverables and roles.
2) Zachman Framework for Enterprise Architecture: Zachman Framework was developed by John Zachman at IBM during the 1980s. This framework's 'data' column has multiple layers, such as architectural standards for the organisation, a semantic or conceptual/enterprise data model, an enterprise or logical data model, a physical data model, and actual databases.
3) The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF): TOGAF is the most popular enterprise architecture methodology for designing, planning, implementing, and managing data architecture. This framework defines the organisation's targets and aligns them with architectural goals.
Enhance your knowledge in in Architect roles with our Enterprise and Solution Architecture Course- sign up now!
Tools for Data Architecture Diagram
Data Architecture Diagram visually represents how and where data flows, is stored, and is consumed in an organisation. It provides a clear overview of how data is collected in the system. It further helps to plan how to change and streamline data storage resources. A standard Data Architecture Diagram covers the following:
1) Explain how data is processed
2) Disclose how and where data is stored
3) Reveal estimated data increment rate
4) Identifies components that contribute to future expansion
Software and cloud-based intelligent diagramming apps are utilised for Data Architecture Diagram. There are several tools available to develop an architecture model. Some of them are mentioned below:
a) Diagrams.net
b) Lucidchart
c) Gliffy
d) ER/Studio
Learn the concept of Business Change with our Business Change Course! join today!
Difference between Data Architecture and Data Modelling
Data modelling deals with specific data assets to develop a visual representation of data entities, attributes, and the relationships between different entities. It helps provide a complete view of the data requirements for applications and systems and further assists in designing the physical structures of the database. There are three phases of Data Modelling: conceptual model, logical model, and physical model.
Data Architecture covers the global view of the organisation's data. It is the practical implementation of data modelling. It develops a framework and policies for data management and utilisation. It has various components, such as databases, data warehouses, data lakes, and data pipelines.
However, both data modelling and Data Architecture complement each other. Data models are essential components in data architectures, and an established Data Architecture clarifies data modelling.
Keen to widen your knowledge in the field of data, then refer to our blog on "Data Lake vs Data Warehouse"
Conclusion
Data Architecture is integral for any organisation to use its data assets to their greatest potential. It sets a framework for managing and utilising data properly and ensures it is collected, stored, and used properly. Abiding by its good practices and standards allows companies to gain a competitive edge in the market.
Gain in-depth knowledge of the objectives of governance with our Architecture Concepts Course!
Frequently Asked Questions

Data Architecture Diagram visually represents how and where data flows, is stored, and is consumed in an organisation. It provides a clear overview of how data is collected in the system.

ETL stands for extract-transform-load. It is a process that involves moving data from one or more sources to a data warehouse, a data lake, or a database.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Architecture Concepts and Domains Course including Business Analysis Course, Enterprise and Solution Architecture Course, Project Management Course and Agile Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into BCS Code of Conduct
Our Business Analysis Blogs covers a range of topics related to Scrum, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Improvement skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 BCS Foundation Certificate in Architecture Concepts and Domains
BCS Foundation Certificate in Architecture Concepts and Domains
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 26th May 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


