We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +55 8000201623 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Ethereum 2.0, commonly referred to as Eth2, represents a pivotal evolution in Blockchain technology. As a substantial upgrade to the existing Ethereum Blockchain, Ethereum 2.0 aims to address issues related to scalability, security, and sustainability, thus fostering an environment conducive to the development of decentralised applications and smart contracts. The curiosity surrounding Ethereum 2.0 has been growing, given its potential to significantly influence the future of Decentralised Finance (DeFi) and numerous other sectors within the Blockchain space.
According to Forbes, Ethereum is one of the two most popular Cryptocurrencies, contributing 60% of the global Crypto market. With Ethereum 2.0, several transformative features and modifications are introduced, including transitioning from a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) model and incorporating shard chains to enhance the network’s transaction capacity. This blog what is Ethereum 2.0, and uncover how this change is set to redefine how developers create on the Blockchain and how users engage with decentralised platforms and services.
Table of Contents
1) What is Ethereum 2.0?
2) Transition process of Ethereum 2.0
3) Critical features of Ethereum 2.0
4) How is Ethereum 2.0 different from Ethereum?
5) Benefits and challenges of Ethereum 2.0
6) Future for Ethereum 2.0
7) Conclusion
What is Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum 2.0, or Eth2, signifies a monumental upgrade to the existing Ethereum Blockchain, focusing on enhancing scalability, security, and sustainability. Designed to accommodate a growing ecosystem of decentralised applications and smart contracts, Eth2 addresses the limitations of its predecessor through transformative features and technological advancements.
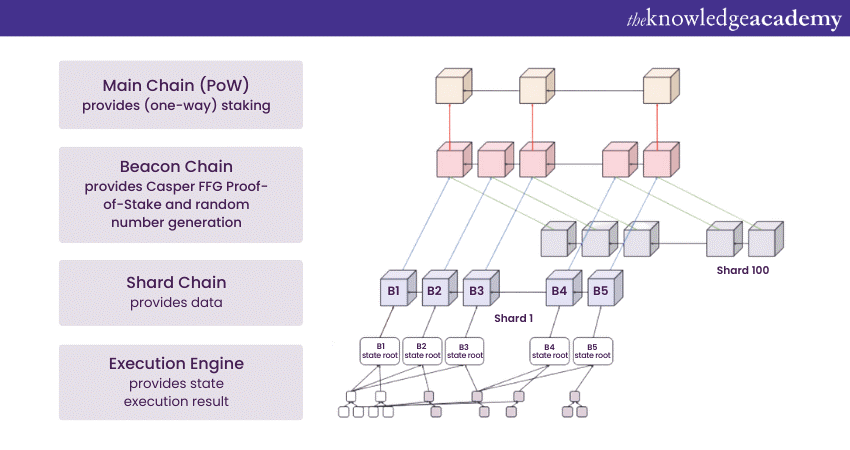
The upgrade introduces a shift from the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism to the more efficient Proof-of-Stake model. Additionally, Ethereum 2.0 incorporates shard chains and the Beacon Chain, playing pivotal roles in optimising transaction processing and network coordination. Together, these innovations aim to position Ethereum 2.0 as a more scalable, secure, and sustainable Blockchain network.

Transition process of Ethereum 2.0
The transition to Ethereum 2.0 was a meticulously planned multi-phase process designed to ensure a smooth evolution of the network. It commenced with Phase 0, focusing on the launch of the Beacon Chain, which laid the foundation for Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus. Subsequently, Phase 1 introduced shard chains, improving scalability by partitioning data processing. The final stage, Phase 2, saw the integration of state execution engines, enhancing the network's computational capacity. This phased approach allowed for incremental advancements, thorough testing, and adjustments, ensuring the integrity and functionality of the network were maintained throughout the transition to Ethereum 2.0.
This transition has allowed Ethereum to cut down its energy usage by 99%.
Critical features of Ethereum 2.0
To better understand Ethereum 2.0, let us discuss the key elements of it:
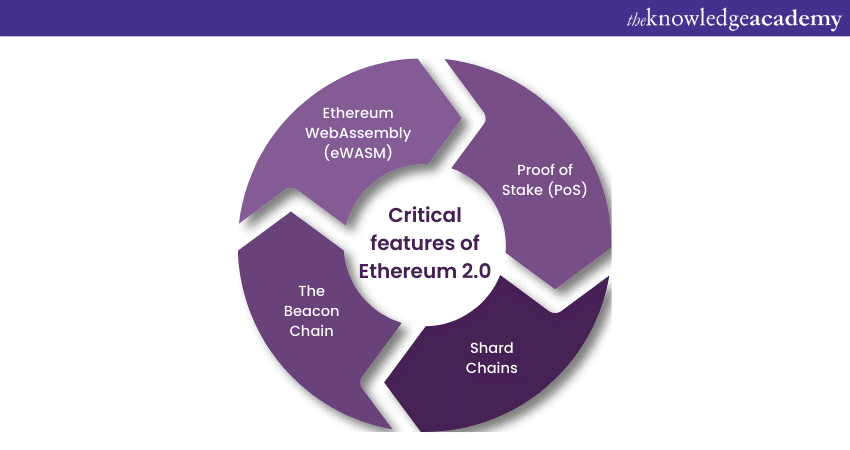
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a pivotal consensus mechanism in Ethereum 2.0, transitioning from the original Proof of Work (PoW) model. In PoS, validators, individuals who lock up (or "stake") their cryptocurrency to participate in block validation, replace miners. The system selects validators to create new blocks and confirm transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrency they stake, thereby significantly reducing the network's energy consumption and addressing sustainability issues inherent in PoW.
To become validators in Ethereum 2.0, participants must stake 32 ETH. Once staked, these validators are chosen randomly to propose blocks and attest to the validity of block proposals. They earn rewards for accurate validations and incur penalties for malicious actions or non-participation, ensuring alignment with the network’s best interest and enhancing security and integrity.
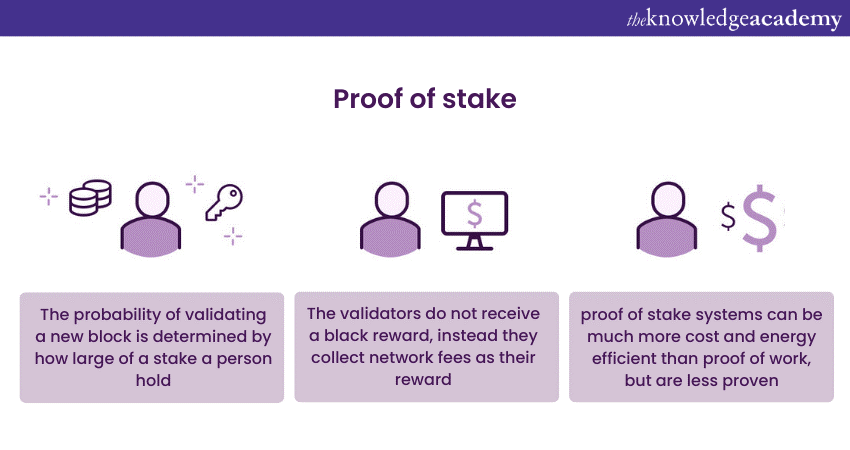
The introduction of PoS and the role of validators in Ethereum 2.0 are critical in addressing scalability, security, and environmental concerns. This new model aspires to secure a decentralised and more eco-friendly network, reinforcing Ethereum's standing as a prominent platform for decentralised applications and smart contracts, and paving the path for broader adoption.
Shard chains
Shard chains are a pivotal feature of Ethereum 2.0, designed to address the scalability issues faced by the original Ethereum Blockchain. In essence, shard chains are smaller, independent chains that run concurrently with the main chain, allowing the network to process multiple transactions and smart contracts simultaneously. This parallel processing significantly increases the network’s capacity and reduces transaction times, enabling Ethereum to handle more complex decentralised applications and meet the growing demand.
The implementation of shard chains was integral to the phased rollout of Ethereum 2.0. By dividing the network into smaller, interconnected shards, the Ethereum Blockchain became more scalable and efficient, paving the way for a more diverse and robust ecosystem of applications, contracts, and services. This innovation in Ethereum 2.0 represented a significant step towards achieving a scalable, secure, and sustainable decentralised platform.
The Beacon Chain
Introduced in the initial phase of Ethereum 2.0, the Beacon Chain played a foundational role in establishing the network’s upgraded architecture. Serving as the heartbeat of Ethereum 2.0, it orchestrated the network’s activities and was integral in facilitating the shift from a Proof of Work (PoW) to a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. T The Beacon Chain manages validators, executes the consensus protocol, and ensures the security and liveliness of the system through attestations and cross-links.
Not only does it coordinate the activities of various shard chains, but it also maintains a record of the validator's stakes and manages the rewards and penalties. By laying the groundwork for the system’s shard chains and introducing PoS, the Beacon Chain was essential in propelling Ethereum towards improved scalability, security, and sustainability, underscoring its evolution in the Blockchain space.
Unlock the future of Blockchain with our Ethereum Developer Training Join today!
eWASM
eWASM, short for Ethereum WebAssembly, is a pivotal innovation in Ethereum 2.0, designed to replace the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). eWASM optimises smart contract execution, enabling them to run faster and more efficiently. It allows developers to code smart contracts in multiple languages, broadening the development scope. This innovation is not only instrumental in enhancing the performance and developer experience on the Ethereum network but also plays a crucial role in facilitating greater scalability and diversity of applications. Through the implementation of eWASM, Ethereum 2.0 aimed to foster a more inclusive, efficient, and versatile decentralised platform.
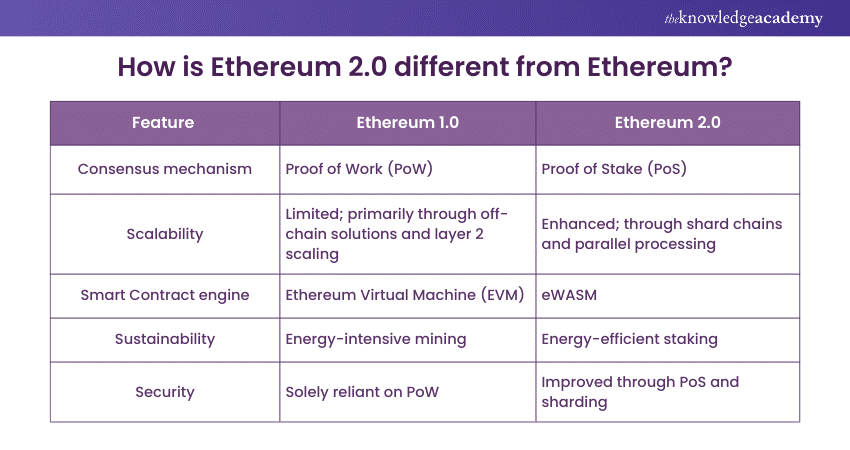
How is Ethereum 2.0 different from Ethereum?
Ethereum 2.0 represented a significant evolution from Ethereum 1.0, addressing key limitations of the earlier version. The shift from a Proof of Work to a Proof of Stake consensus mechanism marked a stride towards energy efficiency and sustainability. The introduction of shard chains and the Beacon Chain enhanced scalability, allowing for parallel transaction processing and increased network capacity. Additionally, eWASM replaced the Ethereum Virtual Machine, optimising smart contract execution and broadening development possibilities. Together, these innovations positioned Ethereum 2.0 as a more scalable, secure, and sustainable platform, ready to meet the growing demands of the decentralised application ecosystem.
Benefits and challenges of Ethereum 2.0
Let’s look at the benefits and challenges of Ethereum 2.0:
Benefits of Ethereum 2.0:
Here are few benefits of Ethereum 2.0:
a) Enhanced Scalability: Shard chains allow for parallel transaction processing, significantly increasing network capacity.
b) Increased Security: The Proof of Stake mechanism improves network security and reduces the risk of attacks.
c) Improved Sustainability: Ethereum 2.0 consumes significantly less energy compared to its predecessor, addressing environmental concerns.
d) Efficient Smart Contract Execution: The introduction of eWASM enables faster and more versatile smart contract development and execution.
Challenges of Ethereum 2.0:
Discussed below are some of the challenges of Ethereum 2.0:
a) Complex Transition: Moving from Ethereum 1.0 to 2.0 required careful planning and execution to ensure the security of the network and user assets.
b) Testing and Validation: The introduction of new features and mechanisms necessitated extensive testing, posing potential risks of unforeseen vulnerabilities.
c) Adoption and Integration: The changes introduced in Ethereum 2.0 required adaptation and integration by developers and users, potentially impacting the existing ecosystem.
Ethereum 2.0's potential impact
Ethereum 2.0 is the next phase of the decentralised revolution. It carries with it a series of implications that could reshape the Blockchain landscape:
Transformative potential of Ethereum 2.0:
a) DeFi growth: Ethereum 2.0 provides a robust environment for Decentralised Finance, enhancing services like lending, borrowing, and asset trading.
b) NFT market expansion: With improved transaction speeds and lower costs, the upgrade fosters growth in the Non-Fungible Token market.
Diverse use cases of Ethereum 2.0 across industries:
a) Supply chain management: Ethereum 2.0 enables secure and transparent solutions, ensuring authenticity and compliance in supply chains.
b) Healthcare: The platform can safeguard patient data and facilitate consent management, revolutionising healthcare systems.
c) Digital voting: Ethereum 2.0 has the potential to enhance electoral systems by offering secure and transparent digital voting platforms.
Conclusion
Ethereum 2.0 marks a revolutionary stride in Blockchain technology, addressing scalability, security, and sustainability – the triad of challenges faced by its predecessor. With innovative features like shard chains, the Beacon Chain, and eWASM, Ethereum 2.0 has positioned itself as a versatile platform, primed to foster the development of diverse decentralised applications across industries. The transformative potential and broad spectrum of use cases, ranging from DeFi to supply chain management and healthcare, signify Ethereum 2.0’s capability to drive unprecedented innovation. Despite facing challenges and misconceptions, the upgrade has garnered widespread support from the community and developers, underscoring the optimism surrounding its future. As we reflect on the advancements and possibilities brought forth by Ethereum 2.0, it's evident that this upgrade is not just a technological enhancement but a cornerstone for the future of decentralised digital ecosystems.
Enhance your knowledge of Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency with our Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Course. join now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Ethereum 2.0 is an upgrade to Ethereum 1.0 that aims to improve scalability and security of the network. The main differences are:
Ethereum 2.0 will use Proof of Stake (PoS) instead of Proof of Work (PoW) as the consensus mechanism, which will reduce energy consumption and increase security.
Ethereum 2.0 will introduce shard chains, which will enable parallel processing and increase the throughput of the network, allowing more transactions and smart contracts to be executed simultaneously.

Staking rewards and penalties are mechanisms to incentive validators to participate in Ethereum 2.0’s PoS system. Validators can earn rewards for proposing and attesting blocks, as well as reporting malicious behaviour. Validators can also face penalties for going offline or acting dishonestly. Severe violations can result in slashing, which means losing a portion of the staked ETH.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Blockchain Training, including Ethereum Developer Training, Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into various Blockchain Developer Skills.
Our Advanced Technology Blogs cover a range of topics related to Ethereum Developer Training , offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Advanced Technology skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Programming & DevOps Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Blockchain Training Course
Blockchain Training Course
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 27th Mar 2025
Thu 15th May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 25th Sep 2025
Thu 13th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


