We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +55 8000201623 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
One machine emulating many - That's the essence of Virtualisation. This technology turbocharges the modern digital landscape by creating virtual versions of physical resources such as servers, storage, and networks. This helps maximise efficiency, scalability, and cost savings. This blog explores What is Virtualisation, covering everything from server virtualisation to GPU virtualisation. So read on and learn how it's reshaping the relationship between business and technology.
Table of Contents
1) What is Virtualisation?
2) How Virtualisation Works
3) Types of Virtualisation
4) Why Use Virtualisation?
5) Is Virtualisation Safe for PC?
6) Conclusion
What is Virtualisation?
Virtualisation, one of the fundamental cloud computing terms, is a revolutionary technology that transforms the traditional approach to computing by abstracting physical resources and creating virtual instances. At its core, Virtualisation involves the emulation of hardware, allowing multiple virtual environments to coexist on a single physical system. This innovative concept spans various domains, including servers, storage, desktops, and networks.
In server Virtualisation, a physical server is partitioned into multiple virtual machines, each operating independently with its own operating system and applications. This optimisation of server resources enhances efficiency and reduces hardware costs. Desktop Virtualisation extends this principle to end-user computing, providing flexibility and centralised management.
Storage Virtualisation abstracts physical storage devices, simplifying management and improving data mobility. Network Virtualisation, on the other hand, decouples networking components, enabling the creation of independent virtual networks for enhanced scalability and simplified administration.
How Virtualisation Works
Virtualisation is a transformative technology that operates on the fundamental principle of abstracting physical resources to create virtual instances, allowing for more efficient and flexible computing. At the heart of Virtualisation are Cloud instances or Virtual Machines (VMs) and hypervisors, both playing pivotal roles in reshaping the traditional concept of computing:
Cloud Instances or Virtual Machines
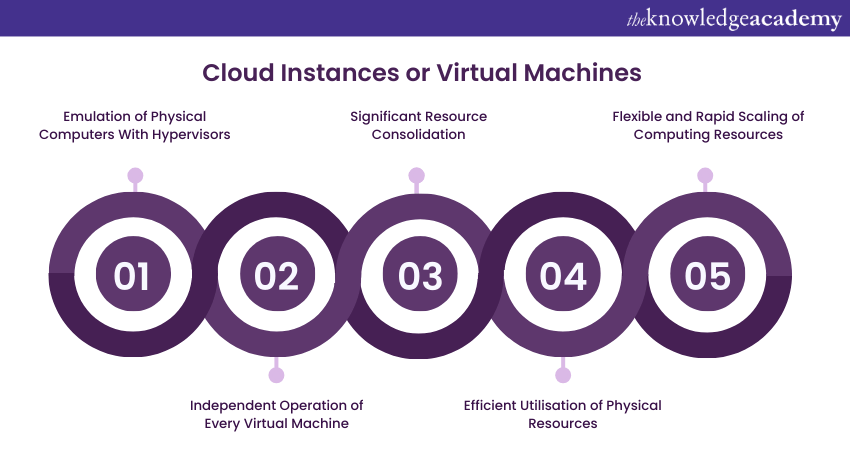
Cloud instances, also known as virtual machines, are the cornerstone of Virtualisation. A virtual machine emulates a complete physical computer, including the Operating System, applications, and associated hardware. This emulation is achieved through the use of hypervisors, which act as a layer between the physical hardware and the virtual machines.
Each virtual machine operates independently on a shared physical server, creating the illusion of multiple isolated systems coexisting on the same hardware. This allows for significant resource consolidation, as a single server can host numerous virtual machines, each running its own unique set of applications and services.
Cloud instances provide several key advantages:
a) Resource Optimisation: Virtualisation allows for the efficient utilisation of physical resources by running multiple virtual machines on a single server. Such consolidation results in improved resource efficiency and reduced hardware costs.
b) Isolation and Security: Each virtual machine operates in its very own isolated environment, ensuring that applications and processes within one VM do not interfere with those in another. This isolation enhances security and stability, minimising the risk of vulnerabilities spreading across different instances.
c) Flexibility and Scalability: Cloud instances can be quickly provisioned or de-provisioned based on demand. This flexibility enables organisations to scale their computing resources up or down rapidly, responding dynamically to changing workloads.
Hypervisors
At the core of Virtualisation is the hypervisor, known as a Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM). The hypervisor is designed to manage and allocate the physical attributes of a host machine to multiple virtual machines.
There are two types of hypervisors:
a) Type 1 Hypervisor (Bare-metal): This hypervisor operates directly on the hardware, eliminating the need for a host Operating System. With direct control over physical resources, it is typically more efficient than Type 2 hypervisors. Examples include Microsoft Hyper-V Server, KVM, and ESX vs. ESXi by VMware.
b) Type 2 Hypervisor (Hosted): This hypervisor runs on top of a host Operating System and relies on it for Resource Management. While not as performance-optimised as Type 1 hypervisors, Type 2 hypervisors are more user-friendly and easier to set up. Examples include VMware Workstation, Oracle VirtualBox, and Parallels.
The hypervisor creates and manages virtual machines by dividing the physical resources of the host machine into multiple isolated environments. It allocates Central Processing Unit (CPU), memory, storage, and network resources to each virtual machine, ensuring fair and efficient utilisation.
Learn how to implement serverless technology with AWS in our comprehensive Serverless Computing With Amazon Web Services Course – Sign up now!
Types of Virtualisation
Below are the 11 types of Virtualisation methods possible for users:
1) Server Virtualisation
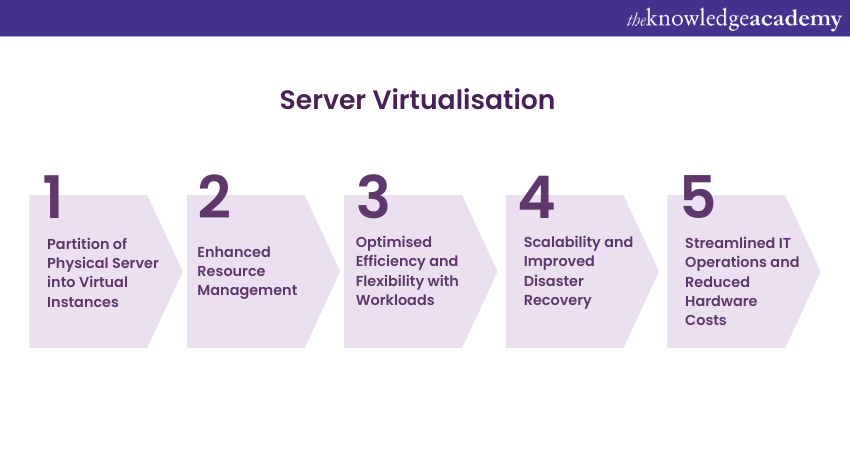
Server Virtualisation is a transformative IT practice where a physical server gets partitioned into several virtual instances, each operating independently with its own dedicated resources, Operating System, and applications. This technology, which is powered by hypervisors, enhances resource utilisation, reduces hardware costs, and simplifies management.
Additionally, server virtualisation allows businesses to host several virtual servers on one single physical machine, optimising efficiency and providing flexibility to adapt to varying workloads. This method helps revolutionise Data Centre Management, offering scalability, improved disaster recovery and streamlined IT operations. Popular platforms include VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, and KVM.
Master the concepts of Virtualisation and Hypervirtualisation through our Introduction To Virtualisation Technologies Course - Sign up now!
2) Network Virtualisation
Network Virtualisation is a revolutionary IT strategy that abstracts networking components, such as switches and routers, creating virtual networks independent of the physical infrastructure. This innovative approach enhances scalability and flexibility and simplifies Network Management.
By isolating and segmenting virtual networks, organisations achieve efficient resource utilisation while ensuring security and stability. Network Virtualisation facilitates dynamic allocation of network resources, streamlining configuration and enabling seamless adaptation to changing business needs.
Key technologies like VMware NSX and Cisco ACI empower businesses to optimise their network infrastructure for improved performance, security, and overall efficiency.
3) Storage Virtualisation
Storage Virtualisation is a groundbreaking technology that abstracts physical storage resources into a unified virtual layer. This method allows for the centralised management of diverse storage systems, offering improved data mobility, flexibility, and efficient allocation of storage space.
By decoupling logical storage from physical devices, storage Virtualisation simplifies Data Management, enhances scalability, and mitigates complexities associated with heterogeneous storage environments. This transformative approach optimises resource utilisation, streamlines data access, and facilitates seamless integration of storage systems across an enterprise. Popular solutions include EMC ViPR, IBM Spectrum Virtualise, and open-source options like Ceph.
4) Desktop Virtualisation
Desktop virtualisation is a transformative IT solution that extends virtualisation principles to end-user computing. It involves creating virtual desktop instances accessible from various devices. This approach enhances accessibility and security and centralises Desktop Management.
Users can access their virtual desktops remotely, fostering flexibility and mobility. Citrix Alternatives in desktop virtualization streamline software updates, reduce hardware dependency, and enhance data security by keeping sensitive information centralized.
Technologies like VMware Horizon, Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops, and Microsoft Remote Desktop Services empower businesses to deliver a consistent desktop experience while optimising resource utilisation and simplifying IT Administration.
Understand system architecture with our Linux Fundamentals Course – Register now!
5) Data Virtualisation
Data Virtualisation is an innovative approach that integrates data from diverse sources, providing a unified view without physically moving or copying the data. Cisco Data Virtualisation and Denodo are exemplary solutions in this realm. Cisco's Data Virtualisation Suite offers real-time, unified data access across various platforms, simplifying Data Management and enhancing agility.
Denodo's data Virtualisation platform seamlessly connects disparate data sources, enabling businesses to access and analyse data in real time. These solutions exemplify how data Virtualisation optimises data access, accelerates analytics, and fosters a more agile and efficient data infrastructure.
6) Application Virtualisation
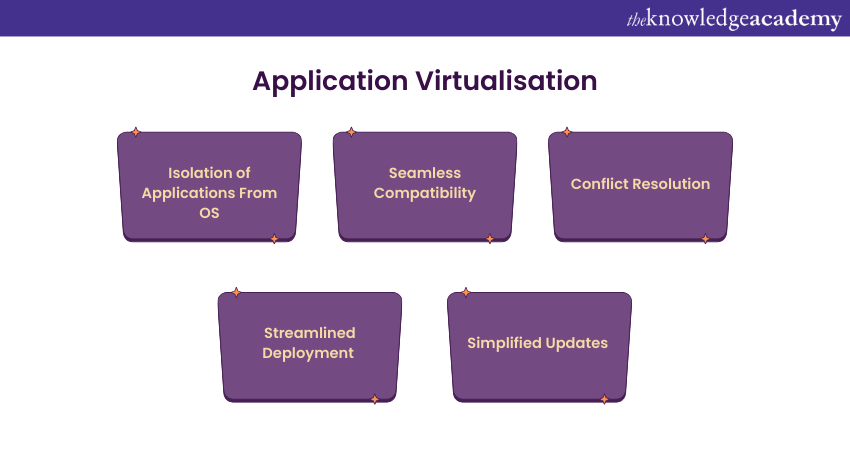
Application virtualisation is an advanced IT practice that isolates applications from the underlying Operating System (OS), enabling seamless compatibility and reducing conflicts. By running applications in isolated environments, this technology streamlines deployment, simplifies updates and enhances security.
Microsoft App-V, VMware ThinApp, and Citrix Cloud exemplifies application virtualization solutions with XenApp, as it encapsulates applications into virtual packages, eliminating compatibility issues and allowing for efficient delivery across diverse environments.
This approach revolutionises Software Management, ensuring consistent performance and flexibility while reducing the complexities associated with application deployment in varying computing environments.
7) Data Centre Virtualisation
Data centre Virtualisation combines physical resources like servers, storage, and networks into virtual systems. This allows businesses to manage and optimise resources more efficiently.
Technologies like VMware vCloud Suite and Microsoft Azure Stack exemplify data centre virtualisation solutions. They provide a unified platform for managing virtualised resources, ensuring seamless integration of various services. Data centre Virtualisation, streamlines operations, reduces hardware costs and facilitates dynamic scaling to meet evolving business demands, making it a cornerstone for modern, agile, and scalable IT environments.
Learn to allocate processors and memory to a Virtual Machine by signing up for our Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications Training now!
8) Linux Virtualisation
Linux Virtualisation refers to the practice of virtualising Linux-based Operating Systems on a single physical server. This approach allows for the simultaneous operation of multiple Linux instances, optimising resource utilisation and providing flexibility.

Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) stands out as a prominent open-source solution for Linux virtualisation, leveraging the Linux kernel's virtualisation capabilities. It offers efficient performance and scalability and supports various guest Operating Systems.
Linux Virtualisation enables organisations to harness the power of virtual machines while benefiting from the robust and open-source nature of the Linux Operating System, making it a preferred choice for many IT environments.
9) Cloud Virtualisation
Cloud Virtualisation forms the backbone of Cloud Computing, allowing for creating and managing of virtual resources in a Cloud environment. This approach includes virtualising servers, networks, and storage to deliver scalable, on-demand services.
Leading Cloud providers like Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud Platform heavily rely on Cloud Virtualisation. It allows users to provision and de-provision resources dynamically, optimising cost and ensuring flexibility.
Cloud Virtualisation accelerates innovation by providing a scalable infrastructure for deploying applications and services, making it a fundamental technology in the era of modern computing and digital transformation.
10) CPU Virtualisation
CPU Virtualisation involves creating virtual instances of a computer's central processing unit (CPU), allowing multiple virtual machines to share the same physical CPU while operating independently. Hypervisors like VMware ESXi, KVM, and Hyper-V implement CPU Virtualisation to maximise the utilisation of computing resources.
This technology enables efficient allocation of CPU resources, leading to enhanced server performance and improved resource utilisation. CPU Virtualisation is fundamental to creating and managing virtual machines, providing the foundation for diverse applications, from server consolidation to running multiple Operating Systems on a single physical server.
11) GPU Virtualisation
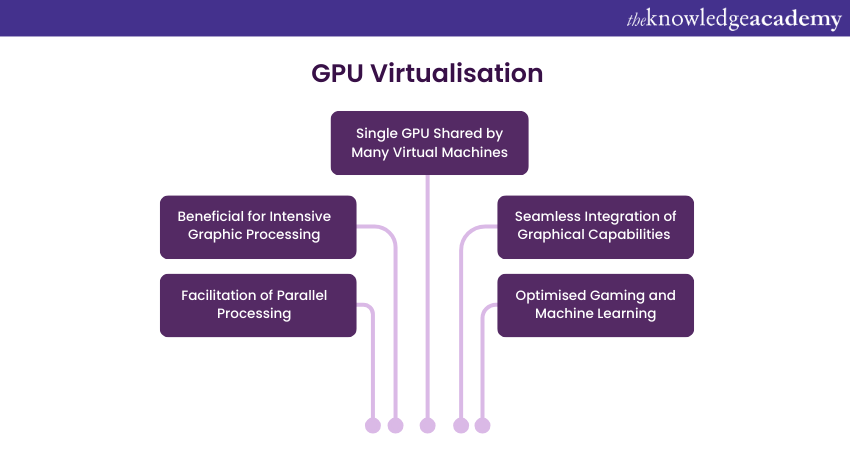
GPU Virtualisation extends Virtualisation principles to graphics processing units (GPUs), allowing multiple virtual machines to share a single physical GPU. This technology is crucial for applications demanding intensive graphical processing, such as virtual desktops and high-performance computing.
Solutions like NVIDIA GRID and AMD MxGPU offer GPU Virtualisation, optimising resource utilisation and enabling seamless integration of graphical capabilities in virtualised environments.
This approach enhances graphics performance, facilitates parallel processing, and is integral for industries requiring advanced visualisation, such as gaming, CAD, and machine learning. GPU virtualisation ensures the efficient utilisation of graphical resources across diverse computing scenarios.
Why use Virtualisation?
Virtualisation can be used for the following reasons:
1) Improved scalability
2) Better security
3) Simplified administration
4) Easier system migration
5) Faster deployment
6) Remote work support
7) Dynamic load balancing
Is Virtualisation Safe for PC?
Despite its benefits, virtualisation is not without some challenges. The challenges include:
1) Security breach in a hybrid network
2) Legacy application support
3) Data loss
4) Ransomware and malware
5) VM sprawl
Conclusion
We hope this blog has helped you comprehend What is Virtualisation and how it can benefit your IT infrastructure. If you’re looking to dive deeper into virtualization technologies, preparing for Virtual Reality Interview Questions can give you a competitive edge in the tech industry. Virtualisation allows you to run multiple virtual systems on a single physical machine, improving efficiency. By exploring its types, you can make better decisions on when to implement it. With the right approach, Virtualisation can optimise your resource management and streamline operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does VDI Mean?

Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) is an IT infrastructure that allows access to enterprise computer systems from almost any device, such as a smartphone, computer, or tablet.
What is an Example of Desktop Virtualisation?

Technologies such as Citrix Virtual Apps VMware Horizon, and Desktops, and Microsoft Remote Desktop Services offer Desktop Virtualisation
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Advanced Technologies Courses, including the Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies Course, Virtual Reality (VR) Training, and 5G Wireless Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Top 10 Benefits of Virtualisation for Organisations.
Our Advanced Technology Blogs cover a range of topics related to Virtualisation, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Virtualisation knowledge, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies
Introduction to Virtualisation Technologies
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


