We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In this hyper-competitive environment, organisations must constantly strive for efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction to gain and maintain their competitive edge. This is where Six Sigma Principles come into play, acting as a beacon of transformation.
It empowers businesses to overcome challenges and achieve unparalleled success by blending data-driven methodologies, problem-solving techniques, and continuous improvement. Read this blog to learn about the various Six Sigma Principles like customer focus, continuous improvement, etc. and how they can benefit your business.
Table of Contents
1) An Introduction to Six Sigma
2) What are Six Sigma Principles?
a) Customer Focus
b) Data-Driven Decision Making
c) Process Focus
d) Continuous Improvement
e) Employee Involvement and Engagement
f) Management Commitment
3) How Six Sigma Principles can benefit your business?
4) Conclusion
An Introduction to Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology and set of tools widely used in business and process improvement. It aims to minimise defects, reduce variations, and enhance overall performance by identifying and eliminating the root causes of problems.
By applying statistical analysis and rigorous problem-solving techniques, it helps organisations achieve high levels of quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Since it has become a popular framework, companies worldwide have adopted it to achieve operational excellence and deliver exceptional results.

What are Six Sigma Principles?
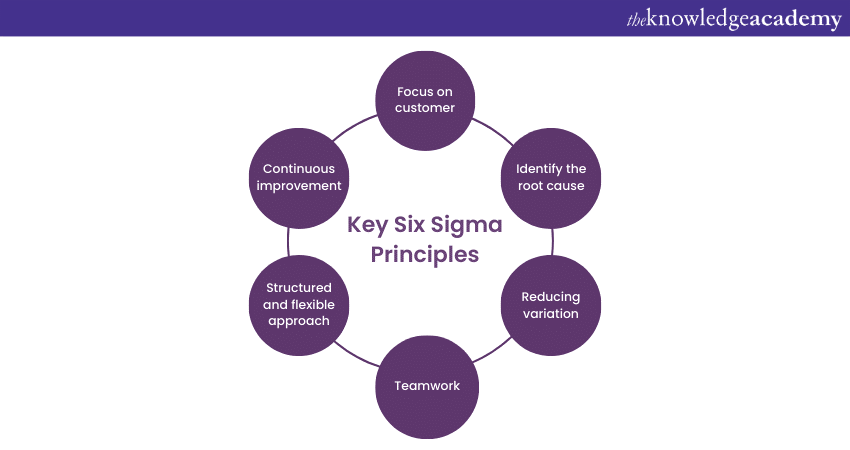
Six Sigma Principles form the foundation of this methodology. They guide organisations to achieve process improvement and excellence. Let's explore the key principles of Six Sigma:
Customer focus
Customer focus is one of the fundamental principles of Six Sigma. It emphasises the importance of understanding and meeting customer needs and expectations. Organisations can drive customer satisfaction and loyalty by putting customers at the forefront, leading to improved business performance. Here are key points highlighting its significance in customer focus:
a) Understanding customer requirements: It encourages organisations to thoroughly understand customer requirements, including their preferences, expectations, and pain points. This understanding forms the basis for process improvement and product/service development.
b) Voice of the Customer (VOC): It is a critical component of Six Sigma. It involves collecting and analysing customer feedback directly to understand their needs and expectations. VOC data guides decision-making and helps prioritise improvement efforts.
c) Customer satisfaction measurement: It emphasises measuring customer satisfaction using metrics such as customer surveys, feedback mechanisms, and Net Promoter Score (NPS). These measurements provide organisations with a clear understanding of their performance from the customer's perspective.
d) Customer-driven metrics: It encourages using customer-driven metrics to evaluate process performance. Metrics like customer defect rate, on-time delivery, and customer complaints indicate how well processes meet customer requirements.
e) Quality Function Deployment (QFD): It is a tool that helps organisations translate customer requirements into specific product or process characteristics. It ensures that customer needs are effectively incorporated into the design of its principles and development stages.
f) Continuous improvement for customer satisfaction: Six Sigma advocates for continuous improvement efforts to enhance customer satisfaction. Organisations can regularly evaluate and improve processes, address customer pain points, reduce defects, and deliver better products and services.
g) Customer-centric culture: It promotes a customer-centric culture within organisations. It encourages all employees to understand and embrace the importance of meeting customer needs. This cultural shift fosters an organisation-wide commitment to customer satisfaction.
By prioritising customer focus in their Six Sigma initiatives, organisations can create a strong foundation for continuous improvement, drive customer loyalty, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Supercharge your business performance with our comprehensive Six Sigma Green Belt Training - Signup today!
Data-driven decision making

Data-driven decision-making is a crucial principle in Six Sigma that emphasises using accurate and reliable data to drive effective decision-making and process improvement. By relying on data rather than assumptions or personal opinions, organisations can make informed choices that lead to better outcomes. Here are key points highlighting the significance of data-driven decision-making in Six Sigma:
a) Data collection and analysis: Six Sigma encourages organisations to collect relevant data from various sources and analyse it using statistical tools and techniques. This ensures a thorough understanding of the current state of processes and helps identify areas for improvement.
b) Identifying root causes: Organisations can identify the root causes of problems and defects by analysing data. This enables them to implement targeted solutions that address the underlying issues rather than merely treating symptoms.
c) Process performance measurement: Data-driven decision-making involves measuring process performance using key metrics and indicators. This gives organisations objective insights into their processes' performance and helps track progress over time.
d) Statistical analysis and tools: Six Sigma employs statistical analysis tools such as control charts, process capability analysis, hypothesis testing, and regression analysis. These tools enable organisations to make data-driven decisions based on evidence and statistical significance.
e) Risk assessment and mitigation: Data-driven decision-making allows organisations to assess risks associated with process changes or improvements. By considering the data, organisations can evaluate the potential impact and make informed decisions to mitigate risks effectively.
f) Data visualisation: Techniques such as charts, graphs, and dashboards help communicate complex data clearly and concisely. Visually representing the data aids decision-makers in understanding trends, patterns, and insights derived from the data.
g) Benchmarking and best practices: Data-driven decision-making in Six Sigma involves benchmarking against industry standards and best practices. Organisations can find areas to improve and adopt proven practices by comparing performance metrics with industry benchmarks.
h) Data-driven problem solving: It utilises structured problem-solving methodologies, such as Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control (DMAIC), which relies on data analysis to identify and solve problems systematically.
i) Data governance and quality: It emphasises the importance of data governance and ensures data quality. This involves establishing data collection processes, validation methods, and management practices to maintain the integrity and reliability of the data used for decision-making.
By embracing data-driven decision-making in it initiatives, organisations can make objective choices, minimise the guesswork, and drive continuous improvement based on evidence and analysis.
Elevate your problem-solving prowess and achieve operational excellence through our DMAIC Training – Signup now!
Process focus
Process focus is an essential principle of Six Sigma that emphasises the importance of understanding and optimising the entire process flow rather than focusing solely on individual tasks. Adopting a process-centric approach can significantly improve efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. Here are key points highlighting the significance of process focus in Six Sigma:
a) Holistic process understanding: Six Sigma encourages organisations to comprehensively understand the end-to-end processes involved in delivering products or services. This includes mapping the process steps, inputs, outputs, and dependencies.
b) Identifying process variation: Process focus involves identifying and analysing process variation, which can lead to defects, inefficiencies, and customer dissatisfaction. By measuring and analysing process performance, organisations can identify areas of variation that require improvement.
c) Process mapping and visualisation: Six Sigma utilises process mapping techniques, such as flowcharts and value stream mapping, to visualise and understand the process flow. This enables organisations to identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for improvement.
d) Process standardisation: Standardising the processes is an essential aspect of process focus. By defining standardised procedures, organisations can minimise variation and ensure consistency in output quality.
e) Process improvement opportunities: Process focus helps organisations identify improvement opportunities within the process flow. This includes eliminating non-value-added steps, reducing waste, and streamlining activities to improve efficiency.
f) Process performance metrics: Six Sigma uses key metrics to measure and monitor process performance. Metrics such as cycle time, throughput, defect rate, and process capability provide insights into how well the process meets customer requirements.
g) Root cause analysis: Process focus involves analysing root causes to identify the underlying factors contributing to process inefficiencies or defects. By understanding how to do root cause analysis, organisations can implement targeted improvements and prevent future issues.
h) Process integration and collaboration: Process focus encourages cross-functional collaboration and integration across departments and teams. Organisations can eliminate silos and improve overall process effectiveness by aligning processes and fostering collaboration.
i) Continuous process improvement: Process focus is synonymous with continuous improvement. It emphasises the need for ongoing evaluation and enhancement of processes to achieve higher levels of performance and customer satisfaction.
By embracing process focus in Six Sigma initiatives, organisations can optimise their processes, reduce waste, improve quality, and deliver products or services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
Continuous improvement
One of the primary Six Sigma Principles is continuous improvement. It emphasises the ongoing effort to enhance processes, products, and services. It involves systematically identifying areas for improvement, making incremental changes, and striving for excellence. Here are key points highlighting its significance in continuous improvement:
a) The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle: It adopts the PDCA cycle for continuous improvement. This iterative approach involves planning the improvement, implementing it, checking the results, and acting upon lessons learned to drive further enhancements.
b) Decision making: Continuous improvement in Six Sigma relies on accurate data analysis to find areas of improvement and measure the effectiveness of changes. By making informed decisions based on data, organisations can target improvements effectively.
c) Process variation reduction: Continuous improvement minimises process variation by identifying and eliminating the root causes of defects, errors, and inefficiencies. This leads to improved quality and consistent outcomes.
d) Kaizen philosophy: Six Sigma embraces the Kaizen philosophy of making small and incremental changes. Instead of seeking drastic transformations, continuous improvement focuses on making small, manageable improvements that accumulate over time.
e) Cross-functional collaboration: Continuous improvement encourages collaboration among different departments and teams. Organisations can gain diverse perspectives and leverage collective knowledge for more effective improvements by involving stakeholders from various areas.
f) Employee engagement: Six Sigma's core principles recognise the importance of engaging employees in the continuous improvement process. Companies can tap into their expertise and creativity by empowering and involving employees to identify improvement opportunities and drive change.
g) Benchmarking and best practices: Continuous improvement involves benchmarking against industry standards and adopting best practices. Organisations can accelerate their improvement efforts by learning from successful organisations and incorporating proven methods.
h) Feedback and lessons: Continuous improvement promotes a culture of learning and feedback. Organisations encourage feedback from customers, employees, and other stakeholders and use it to identify improvement areas.
i) Sustaining improvement: Continuous improvement is not a one-time effort but an ongoing commitment. It requires organisations to establish systems for monitoring and sustaining improvements to ensure long-term benefits.
By embracing continuous improvement in its initiatives, organisations can drive innovation, enhance efficiency, and deliver products and services that regularly meet or exceed customer expectations.
Employee involvement and engagement
Employee involvement and engagement are vital in successfully implementing Six Sigma methodologies. When actively involved and engaged, employees become valuable contributors to process improvement initiatives. Here are key points highlighting it significance in employee involvement and engagement:
a) Ownership and accountability: Six Sigma encourages employees to own their work and processes. Employees who feel accountable for their tasks are more likely to strive for excellence and actively contribute to process improvement efforts.
b) Training and development: It emphasises the importance of providing employees with the required training and development opportunities that help improve their skills and knowledge. Well-trained employees are better equipped to identify improvement opportunities and implement changes effectively.
c) Cross-functional teams: Six Sigma promotes the formation of cross-functional teams that consist of employees from different departments or areas of expertise. Organisations can leverage collective knowledge and experience to drive innovative solutions by involving employees with diverse perspectives.
d) Empowerment: It encourages organisations to empower employees by giving them the authority to make decisions and contribute ideas for process improvement. Empowered employees feel valued and motivated to actively participate in finding innovative solutions.
e) Communication and collaboration: Effective communication channels and collaborative environments foster employee involvement and engagement. It encourages open dialogue, sharing of ideas, and collaboration across all levels of the organisation to harness the collective intelligence of employees.
f) Recognition and rewards: Recognising and rewarding employees for their contributions to Six Sigma initiatives foster a sense of achievement and encourages continued engagement. This can include acknowledging their efforts, providing incentives, and celebrating successful outcomes.
g) Employee feedback: It values employee feedback as a valuable source of insights and improvement opportunities. Organisations should actively seek employee feedback regarding process challenges, bottlenecks, and potential solutions and incorporate their input into improvement initiatives.
h) Continuous learning culture: It promotes a culture of constant learning and improvement. Encouraging employees to expand their knowledge, share best practices, and learn from failures creates a culture that supports ongoing employee involvement and engagement.
i) Leadership support: Strong leadership support fosters employee involvement and engagement in Six Sigma. Leaders should actively champion the importance of employee contributions, provide resources and guidance, and create a supportive environment for continuous improvement.
By prioritising employee involvement and engagement in its initiatives, organisations can tap into the collective expertise of their workforce, drive innovation, and achieve sustainable process improvements.
Signup for our Six Sigma Yellow Belt Training and gain the expertise to streamline processes, improve quality, and drive success in any industry.
Management commitment
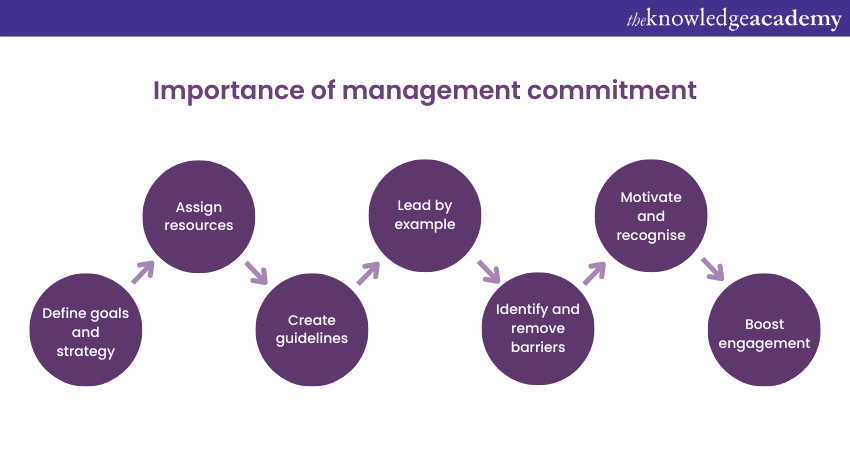
Management commitment is a key factor in successfully implementing its methodologies. When management is fully committed to Six Sigma Principles and practices, it sets the foundation for a culture of continuous improvement and drives the organisation towards achieving its goals. Here are key points highlighting the significance of management commitment in Six Sigma:
a) Setting clear goals and objectives: Management commitment begins with setting clear goals and objectives aligned with the organisation's vision and strategy. By defining and communicating the desired outcomes effectively, management provides a clear direction for implementing its initiatives.
b) Resource allocation: Management commitment involves allocating the necessary financial, technological, and human resources to support such projects. Adequate resource allocation demonstrates the organisation's dedication to achieving process improvement and enhances the chances of project success.
c) Establishing policies and procedures: Management commitment entails establishing policies and procedures that support Six Sigma Principles and practices. This includes defining standardised processes, providing data collection and analysis guidelines, and setting expectations for performance improvement.
d) Leadership support: Effective leadership is crucial for fostering a culture of Six Sigma within the organisation. Management should lead by example, actively promoting Six Sigma Principles and demonstrating their commitment through their actions. This includes participating in improvement projects, supporting employee involvement, and recognising achievements.
e) Removing barriers: Management commitment involves identifying and removing barriers that hinder its successful implementation. This can include addressing resistance to change, providing training and support, and facilitating effective communication and collaboration across departments.
f) Promoting employee engagement: Management commitment includes actively involving employees in its initiatives. By engaging employees in problem-solving and improvement efforts, management encourages participation, harnesses their expertise, and fosters a sense of ownership and accountability.
g) Performance measurement and feedback: Establishing performance metrics and feedback mechanisms to monitor the progress of Six Sigma projects is essential to show the management's commitment. By regularly reviewing performance and providing constructive feedback, management makes sure that projects stay on track and can make informed decisions for continuous improvement.
h) Recognition and rewards: Management commitment involves recognising and rewarding individuals and teams for their contributions to Six Sigma projects. Celebrating achievements and providing incentives motivates employees, reinforces its importance, and encourages further engagement.
i) Continuous improvement culture: Management commitment establishes a culture of constant improvement throughout the organisation. By embracing continuous learning, innovation, and excellence, management sets the tone for employees to participate in Six Sigma initiatives actively.
By demonstrating unwavering commitment to it, management establishes a strong foundation for successfully implementing process improvement initiatives, fosters employee engagement, and drives the organisation towards achieving sustainable results.
Unlock the power of data-driven decision-making and process improvement. Join our Six Sigma Black Belt course. and become a certified expert in Six Sigma methodologies.
How Six Sigma Principles can benefit your business?
Six Sigma Principles offer significant advantages to businesses in various industries. By embracing and implementing these methodologies, organisations can achieve operational efficiency, improved product quality, and increased customer satisfaction. Here's how it benefits your business:
a) Process improvement: Six Sigma eliminates inefficiencies, defects, and variations, resulting in smoother flow, increased productivity, and streamlined operations.
b) Data-driven decision-making: It uses statistical analysis and data to make informed decisions, ensuring that improvement efforts are targeted and effective.
c) Customer satisfaction: By aligning processes with customer needs and expectations, it helps deliver products and services that exceed customer satisfaction, enhancing loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
d) Reduced defects and errors: Six Sigma focuses on minimising defects and errors, leading to improved product quality, fewer customer complaints, and a stronger reputation for delivering reliable solutions.
e) Cost reduction: Through waste reduction and process optimisation, it helps identify and eliminate unnecessary costs, resulting in improved profitability and competitive pricing.
f) Employee engagement: Six Sigma empowers and motivates employees by involving them in improvement projects, fostering a culture of ownership, engagement, and continuous learning.
g) Strategic alignment: Six Sigma ensures that improvement initiatives are aligned with strategic goals, helping organisations prioritise efforts and achieve targeted improvements in critical areas.
h) Continuous improvement: It instils a mindset of continuous learning, innovation, and improvement, enabling businesses to adapt to evolving market demands and stay ahead of the competition.
i) Competitive advantage: By differentiating businesses through superior quality, customer satisfaction, and process efficiency, it provides a competitive edge, attracting customers and enhancing the overall brand reputation.
By embracing Six Sigma, businesses can achieve operational excellence, drive customer satisfaction, and foster sustainable growth in today's dynamic business landscape.
Want to become the driving force behind organisational success? Sign up for our Six Sigma Black Belt Upgrade course and unlock the power of data-driven decision-making.
Conclusion
Six Sigma Principles offer systematic and data-driven process improvement, enhancing efficiency, improving quality, and increasing customer satisfaction. By reducing defects, engaging employees, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, businesses gain a competitive advantage and drive sustainable growth.
Take the first step towards operational excellence with our Six Sigma Certification Training Courses – Signup now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Six Sigma Green Belt
Six Sigma Green Belt
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


