We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +1 6474932992 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Curious about how data protection impacts your daily life? Let’s discuss the GDPR Principles that guide the handling of personal data. How do these principles ensure data is processed legally, fairly, and transparently? What steps can we take to keep data secure and used only for its intended purpose?
By following these guidelines, how can we protect our privacy and build trust in the digital world? Join us as we explore insights to help you navigate the complexities of data protection with ease and confidence. Ready to learn more? Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
1) What is GDPR?
2) The Seven GDPR Principles
a) Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
b) Purpose Limitation
c) Data Minimisation
d) Accuracy
e) Storage Limitation
f) Integrity and Confidentiality
g) Accountability
3) What is the Significance of GDPR Principles?
4) Conclusion
What is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a broad data protection law that came into effect on 25 May 2018. It applies to any organisation within the European Union (EU). It also covers organisations outside the EU that offer goods or services to EU residents. The GDPR aims to protect individuals' personal data, giving them greater control over how their information is collected, used, and stored.
A GDPR Guide can help businesses navigate compliance requirements effectively. It also imposes strict penalties for non-compliance, encouraging organisations to prioritise data protection. By doing so, the GDPR helps build trust between consumers and businesses.
The Seven GDPR Principles
The seven Principles of the GDPR are fundamental guidelines for protecting personal data. Let's explore each in detail:
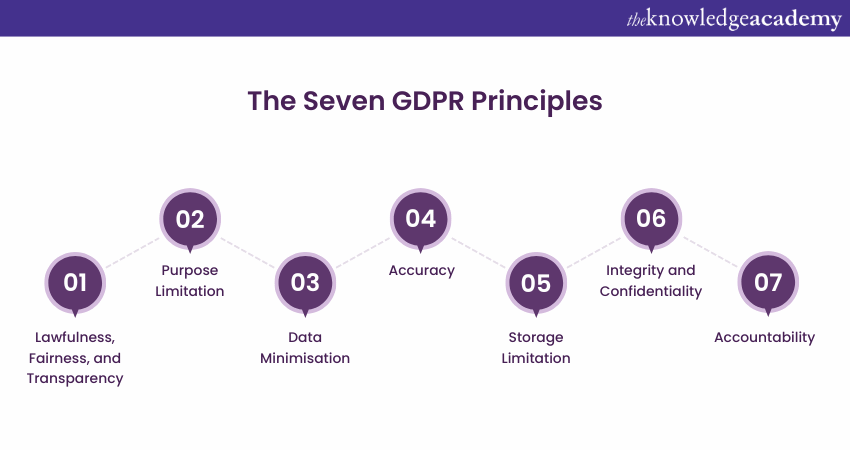
1) Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
Data must be processed in a lawful manner, aligning with the GDPR Structure and adhering to all relevant legal requirements. It should be handled fairly, ensuring that individuals are not misled or deceived about how their data is used. Transparency is crucial, meaning organisations must be open about their data processing activities. Individuals should be informed about who is collecting their data, the reasons for its collection, and how long it will be retained.
Clear communication helps build trust and ensures compliance with legal standards. This principle ensures that data processing is conducted ethically and openly.
2) Purpose Limitation
Data should be collected for legitimate purposes. It should not be used in ways that are incompatible with those initial purposes. For instance, if data is collected for a customer survey, it should not be repurposed for marketing without additional consent. This principle ensures that data is not misused or exploited for unintended purposes.
Organisations must clearly define the purpose of data collection and communicate this to individuals. For example, when processing a Subject Access Request, any change in the purpose of data use requires further consent from the data subjects.
3) Data Minimisation
Only the data necessary for the intended purpose should be collected. This means avoiding the collection of excessive or irrelevant information. By minimising the amount of data collected, organisations minimise the risk of data breaches and simplify data management.
It also ensures that individuals’ privacy is respected by not gathering more information than needed. Regular reviews of the data held can help ensure that only necessary data is retained. This principle promotes efficiency and security in data handling.
4) Accuracy
Data must be accurate and kept up to date. Inaccurate data should be corrected or deleted promptly to ensure reliability. Regular checks and updates help maintain the quality of the data. Individuals have the right to request corrections to their data, ensuring that their information is accurate.
Accurate data is essential for making reliable decisions and maintaining trust with individuals. This principle emphasises the importance of data quality and integrity.
5) Storage Limitation
Data should not be kept longer than necessary for the purposes for which it was collected. Once it is no longer needed, it should be securely deleted or anonymised. This reduces the risk of GDPR Data Breaches and misuse. Organisations should have clear policies on data retention and audit their data to ensure compliance.
Proper data disposal methods are crucial for maintaining security and privacy. This principle ensures that data is not retained indefinitely without justification.
6) Integrity and Confidentiality
Data must be protected against unauthorised access, loss, or damage. Security measures such as access controls and regular security assessments should be in place. Employees should be trained on data protection practices to prevent breaches. In the event of a breach, it should be reported promptly and managed effectively.
Maintaining data integrity and confidentiality helps prevent harm to individuals and builds trust. This principle emphasises the importance of robust security measures.
7) Accountability
Organisations must take responsibility for their data processing activities and demonstrate compliance with GDPR Principles. This covers maintaining records of data processing activities and conducting regular audits and assessments. Organisations should appoint a Data Protection Officer if required by law.
Being accountable means being transparent about data practices and taking steps to ensure compliance with GDPR. Implementing a well-structured GDPR Privacy Policy Template can help organisations outline their data-handling practices clearly. It also involves responding to data subjects’ requests and concerns promptly. This principle builds trust and ensures that organisations are held responsible for their data-handling practices.
Learn how to perform a personal data audit with our Certified Data Protection Officer (CDPO) Course – Join today!
What is the Significance of GDPR Principles?
The GDPR Principles are crucial for ensuring that personal data is handled responsibly and securely. Here are some of the Benefits of GDPR:
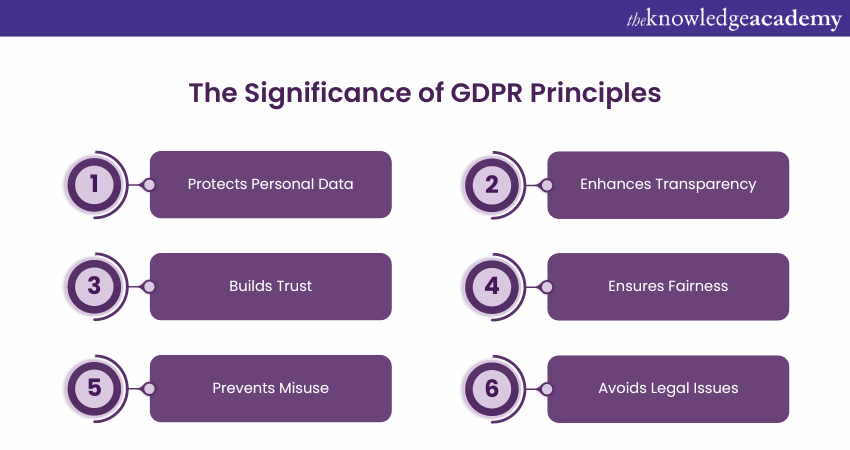
a) Protects Personal Data: GDPR Principles ensure that personal information is kept safe from misuse and unauthorised access. They help prevent data breaches and protect individuals' privacy.
b) Enhances Transparency: Organisations must clearly explain how they collect and use personal data. This openness helps individuals understand what happens with their information.
c) Builds Trust: By following GDPR Principles, organisations show they care about data privacy. This promotes trust between businesses and their customers.
d) Ensures Fairness: GDPR requires that personal data is handled fairly and legally. This means using data only for the purposes agreed upon and treating individuals’ information with respect.
e) Prevents Misuse: GDPR Principles limit the use of personal data to specific, stated purposes. This prevents organisations from using data in ways that were not originally intended.
f) Avoids Legal Issues: Following GDPR helps organisations avoid fines and legal problems. It ensures they are compliant with data protection laws and regulations.
Learn about the categorisation of personal data with our Personal Data Protection Bill Training – Join today!
Conclusion
The GDPR Principles are vital for protecting personal data and ensuring privacy in today’s digital world. They guide organisations in handling data fairly and transparently, helping to build trust with customers and avoid legal issues. By following these principles, businesses comply with the law and demonstrate their commitment to respecting individuals’ privacy. Adhering to GDPR ensures a secure and trustworthy environment for managing personal information and highlights the need for Data Protection Officer in the process.
Learn to reduce the risk of data breaches with our GDPR Awareness Training – Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does GDPR Manage International Data Transfers?

GDPR allows data transfers outside the EU only if the destination country has adequate data protection standards or if specific safeguards are in place. This ensures that personal data remains protected even when it moves across borders.
Does GDPR Specify Rules for Encrypting and Anonymising Personal Data?

GDPR doesn’t set specific rules for encryption or anonymisation but requires that personal data be protected. Using encryption and anonymisation is encouraged as they help secure data and comply with GDPR’s overall privacy requirements.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What are the related courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various GDPR Training, including Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation and Practitioner Training, Certified Data Protection Officer Course and Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Practitioner Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Who Does GDPR Apply To?
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to GDPR offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your knowledge on GDPR, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation and Practitioner
Certified EU General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) Foundation and Practitioner






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


