We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +1 6474932992 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Manual Handling involves tasks like lifting, carrying, and pushing. But did you know that these tasks come with inherent risks to employee health and safety? To mitigate these risks, understanding Manual Handling Risk Assessment can play a pivotal role.
According to hse.gov.uk, more than 37% of people suffered from musculoskeletal disorders, in the United Kingdom during the years 2021 and 2022. Hence, you can understand the importance of these assessments so that future workplace accidents can be prohibited. In this blog, you will learn about Manual Handling Risk Assessments, the step-by-step process for these assessments, examples and more! Read further to know more!
Table of Contents
1) What are Manual Handling Risk Assessments?
2) Importance of Manual Handling Risk Assessments
3) Conducting Manual Handling Risk Assessments: A step-by-step guide
a) Identifying hazards
b) Assessing risks
c) Implementing control measures
d) Monitoring and reviewing
4) Examples of Manual Handling Risk Assessments
5) Conclusion
What are Manual Handling Risk Assessments?
Manual Handling Risk Assessment is a systematic evaluation of tasks involving the manual lifting, moving, or manipulation of objects. Its primary goal is to identify potential hazards and minimise the risk of injury to employees.
The assessments analyse various factors, including the weight of objects, the frequency of tasks, the posture required, and the working environment. By thoroughly assessing these elements, employers can pinpoint potential risks that may lead to musculoskeletal disorders or other injuries.
The assessments provide a structured approach to ensure that Manual Handling activities are conducted safely. They involve identifying hazards, assessing the level of risk, and implementing control measures to mitigate those risks. These assessments are a key requirement under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations. Thus, Manual Handling Risk Assessments are crucial for maintaining a safe and healthy work environment, eliminating workplace injuries, and complying with legal regulations.
Empower your workforce with essential skills for safe Manual Handling. Register now for our Manual Handling at Work Training.
Importance of Manual Handling Risk Assessments
Manual Handling Risk Assessments are essential as they proactively identify potential Manual Handling Hazards and dangers associated with tasks involving lifting, carrying, and moving objects. By recognising these risks, employers can implement preventive measures that decrease the chances of injuries and musculoskeletal disorders.
This not only safeguards the well-being of employees but also enhances workplace productivity, reduces absenteeism, and minimises financial implications from workplace accidents. Furthermore, these assessments demonstrate a commitment to employee safety and ensure Compliance with legal regulations. As a result, they help foster a culture of health and well-being within the organisation.
Learn how to prioritise workplace safety with our Health & Safety in the Workplace Course.
Conducting Manual Handling Risk Assessments: A step-by-step guide
After learning about Manual Handling Assessments, it's time to understand the step-by-step procedure of conducting these assessments. So, read on more to find out:
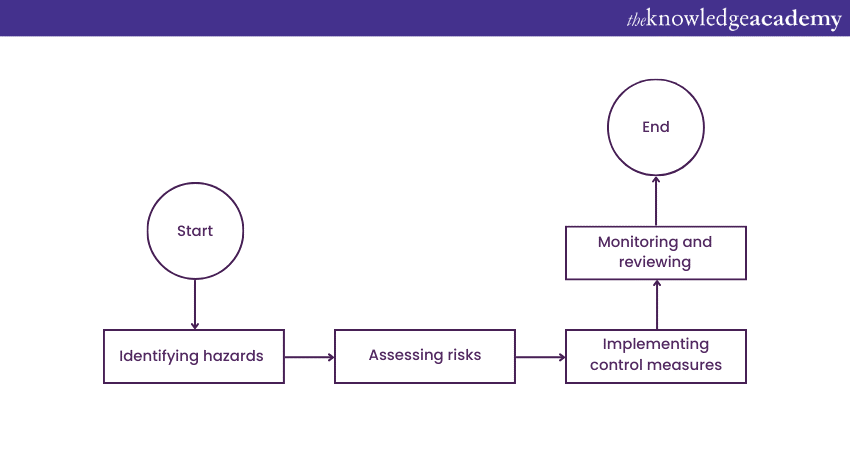
Identifying hazards
Begin by identifying all Manual Handling tasks within the workplace. These tasks may involve lifting, pushing, pulling, and carrying objects. Once identified, closely examine each task to identify potential hazards that could lead to injuries. Consider factors such as the weight of the load, the frequency of the task, and the posture required to perform it.
Assessing risks
After identifying hazards, assess the level of risk associated with each task. Consider the likelihood of an injury occurring and the potential severity of the injury. This assessment helps prioritise tasks that pose higher risks and require immediate attention. Common risk factors include the following:
a) Heavy loads
b) Awkward postures
c) Repetitive motions
d) Lack of proper training
Implementing control measures
Based on the Risk Assessment, devise and implement control measures to minimise or eliminate identified risks. These measures should focus on making the task safer for employees to perform. Control measures could include the following:
1) Providing lifting equipment: Utilise lifting aids such as trolleys, forklifts, or hoists to reduce the need for manual lifting.
2) Rearranging workspace layouts: Optimise the workspace to reduce awkward postures and create Ergonomic work environments.
3) Training and education: Provide employees with proper training on lifting techniques, posture, and the use of equipment.
4) Reducing load weight: Minimise the weight of objects being lifted or carried to decrease the risk of strain.
Monitoring and reviewing
Manual handling risk assessments should not be static documents. You should regularly monitor and review the effectiveness of the implemented control measures. If new tasks are introduced or changes occur in the workplace, assess their impact on these risks and adjust the control measures accordingly, following the Manual Handling Hierarchy to ensure all steps are properly addressed.
Elevate your workplace's safety standards. Register now for our Health and Safety in the Workplace Training.
Examples of Manual Handling Risk Assessments
Let's explore a few practical examples of Manual Handling Risk Assessments to illustrate the process further:
1) Example 1: Lifting heavy boxes in a warehouse
a) Identifying hazards: Heavyweights, repetitive lifting, awkward postures.
b) Assessing risks: Likelihood of musculoskeletal injuries due to frequent lifting of heavy boxes.
c) Implementing control measures: Provide Manual Handling training, encourage team lifting for heavy loads, and use lifting equipment such as pallet jacks or trolleys.
d) Monitoring and review: Regularly assess employee feedback, monitor injury rates, and ensure compliance with control measures.
2) Example 2: Carrying patients in a healthcare setting
a) Identifying hazards: Patient weight, awkward postures, lack of assistance.
b) Assessing risks: Risk of back injuries, sprains, and strains among healthcare workers due to improper patient handling.
c) Implementing control measures: Provide training in safe patient Manual Handling Techniques, use patient hoists and transfer aids, and encourage teamwork for patient mobility.
d) Monitoring and review: Regularly assess employee compliance with proper techniques, review injury reports, and update control measures based on feedback.
3) Example 3: Pushing carts in a retail environment
a) Identifying hazards: Retail employees often push heavy carts loaded with products for restocking shelves or transporting items. Hazards include uneven flooring, heavy loads, and poor Ergonomic design of carts.
b) Assessing risks: Pushing heavy carts on uneven surfaces can lead to slips, trips, and strains. The weight of the cart combined with poor Ergonomic design can contribute to musculoskeletal issues.
c) Implementing control measures: Ensure clear pathways and even floors. Providing carts with Ergonomic handles and wheels can reduce strain on employees. Additionally, training employees in proper pushing techniques can prevent injuries.
4) Example 4: Moving tools and equipment on a construction site
a) Identifying hazards: Construction workers frequently move tools, equipment, and materials across a site. Hazards include lifting heavy Manual Handling Equipment, working in confined spaces, and potential collisions with moving vehicles.
b) Assessing risks: Moving heavy equipment without proper lifting techniques can lead to back injuries. Working in confined spaces increases the risk of awkward postures and strains. Collisions with vehicles pose a danger to workers' safety.
c) Implementing control measures: Employers can provide training on proper lifting techniques and safe material handling. Organising workspaces to allow for clear pathways and proper storage can prevent awkward postures. Implementing safety protocols for vehicle movement and ensuring proper signalling can reduce collision risks.
5) Example 5: Handling baggage at an airport
a) Identifying hazards: Airport personnel handle baggage, often lifting and loading heavy suitcases onto conveyors. Hazards include lifting heavy weights, repetitive motions, and inadequate lifting techniques.
b) Assessing risks: Lifting heavy suitcases without proper technique can lead to strains and injuries. The repetitive nature of handling baggage increases the likelihood of musculoskeletal disorders.
c) Implementing control measures: Employers can offer training on correct lifting techniques and promote the use of lifting aids for heavier luggage. Regular rotation of tasks and breaks can help prevent strain from repetitive motions.
d) Example 6: Organising inventory in a warehouse
e) Identifying hazards: Warehouse workers engage in tasks like stacking and organising inventory. Hazards include overhead lifting, improper posture, and potential falls from heights.
f) Assessing risks: Overhead lifting can strain shoulders and upper back. Poor posture while stacking items can contribute to back injuries. Working at heights without proper safety measures poses a risk of falls.
g) Implementing control measures: Providing lifting equipment for overhead tasks and emphasising proper posture can prevent injuries. Using safety measures such as harnesses and guardrails when working at heights can reduce the risk of falls.
These examples highlight the diversity of Manual Handling tasks across various industries and workplaces. Conducting thorough Manual Handling Risk Assessments and implementing appropriate control measures are essential to creating safer work environments and preventing injuries.
Conclusion
By thoroughly identifying hazards, evaluating risks, and implementing appropriate control measures, employers can safeguard the well-being of their employees. From lifting heavy boxes in a warehouse or carrying patients in a healthcare setting, a proactive approach to Manual Handling Risk Assessments translates to safer work practices, reduced injuries, and improved quality of work life for employees.
Equip your supervisors with leadership skills that foster a safe workplace with our Supervisor Leadership Skills for A Safe Workplace Course.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 First Aid at Work
First Aid at Work
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 6th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 26th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


