We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +1 6474932992 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Cyber Resilience is an organisation's ability to prepare for, respond to, and recover from cyber threats while continuing to operate effectively. It's like a shield that not only deflects cyberattacks but also strengthens the organisation's defences and response mechanisms.
Read this blog to delve deeper into What is Cyber Resilience and why it's crucial in today's digital world. We will also discuss how organisations can enhance their Cyber Resilience posture. So, let's explore the world of Cyber Resilience together!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Cyber Resilience
2) How Does Cyber Resilience Work?
3) The Importance of Cyber Resilience
4) What are the goals of Cyber Resilience?
5) Building Cyber Resilience
6) How do you achieve Cyber Resilience?
7) Challenges in Achieving Cyber Resilience
8) The four categories of Cyber Resilience
9) The benefits of Cyber Resilience
10) Components of Cyber Resilience
11) Conclusion
Understanding Cyber Resilience
Cyber Resilience has emerged as a critical pillar of modern Cybersecurity strategies. Unlike traditional approaches that focus primarily on preventing cyberattacks, Cyber Resilience acknowledges the inevitability of breaches and disruptions while emphasising an organisation's ability to withstand, respond to, and recover from such incidents.
It encompasses a comprehensive set of strategies, practices, and technologies that collectively fortify an organisation's ability to endure, adapt, and thrive in the face of ever-evolving cyber threats. It acknowledges that the digital landscape is inherently risky and aims to mitigate the impact of incidents rather than solely preventing them.
Cybersecurity and Cyber Resilience are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct yet complementary concepts. Cybersecurity predominantly concentrates on establishing protective measures to prevent unauthorised access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. It encompasses tools like firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems.
On the other hand, Cyber Resilience transcends the boundaries of prevention to encompass the full spectrum of incident response and recovery. It assumes that breaches are unfortunate and focuses on minimising the damage, reducing downtime, and ensuring that the organisation can continue its operations as smoothly as possible.
How Does Cyber Resilience Work?
Cyber resilience is a multifaceted approach that extends beyond traditional cybersecurity measures, focusing on ensuring an organisation can maintain its operations despite facing cyber threats. It begins with risk management, which involves identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities within the organisation's systems. Once identified, these threats are evaluated based on their potential impact and likelihood, allowing for prioritisation. Mitigation measures such as patch management, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems are then implemented to reduce these risks effectively.
Another critical component is the implementation of proactive defenses. This involves using threat intelligence to anticipate and prepare for potential attacks. Continuous monitoring of networks and systems is essential to detect unusual activities or breaches early on. Additionally, educating employees about cybersecurity best practices and potential threats, such as phishing, forms a significant part of this proactive stance, ensuring everyone in the organisation is vigilant and informed.
The Importance of Cyber Resilience
The digital revolution has ushered in remarkable advancements. It transformed how we communicate, conduct business, and interact with the world. However, this transformation has also introduced several challenges, particularly in Cybersecurity. There is an increase in data breaches, cyber-attacks, and other threats day by day. This lets individuals and entities constantly battle to safeguard sensitive information.
There is an urgent need for improved Cybersecurity measures to protect businesses from these emerging threats. Therefore, governments and regulatory bodies have turned their attention to legislation promoting Cybersecurity and Cyber Resilience. The Cyber Resilience Act represents a crucial milestone in this journey towards achieving a more secure digital landscape.
The growing threat of cyberattacks casts a long shadow over individuals, businesses, and governments. The internet has undoubtedly brought unparalleled connectivity, innovation, and progress opportunities. However, it has also exposed us to a new world of vulnerabilities that malicious actors are all too eager to exploit.
Cyberattacks have progressed from isolated, simplistic disruptions to sophisticated, well-coordinated global campaigns. The era of hackers seeking thrills or notoriety has given way to more complex and strategic threats.
Today, cybercriminals have adopted a professional and profit-driven mindset, often working as part of more extensive criminal networks or state-sponsored entities.
Our increasing dependence on technology has expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. Internet of Things (IoT) devices, often designed conveniently rather than securely, can serve as network entry points. While offering immense benefits, Cloud Computing also introduces potential vulnerabilities if they are not properly secured.
Learn everything about Cyber Resilience with our RESILIA® Foundation – Register today!
What are the Goals of Cyber Resilience?
The primary objectives of a Cyber Resilience plan are to:
1) Maintain Cybersecurity Preparedness: It ensures a high level of cybersecurity readiness to prevent or minimise disruptions to business functions. This includes ongoing security monitoring to detect and address attacks that bypass initial defences.
2) Sustain Essential Business Functions: Preserve the ability to continue critical business operations during a cyber incident.
3) Quickly Restore Critical Functions: Rapidly recover key business functions following a breach.
4) Adapt and Improve: Leverage intelligence from attacks to enhance the organisation's business processes and cyber capabilities, increasing overall resilience.
Building Cyber Resilience
Proactive identification of potential threats is at the core of Cyber Resilience. It constantly monitors network activities and digital environments to detect anomalies, vulnerabilities, and signs of compromise. Threat intelligence uses data from various sources to predict and counter emerging threats. This enable organisations to take pre-emptive actions.
Understanding an organisation's digital vulnerabilities and potential risks is paramount for effective Cyber Resilience. Detail risk assessments evaluate the organisation's assets, openness, and the potential impact of cyber incidents. This information helps in prioritising resources and efforts toward safeguarding critical assets.
1) Factors in Building Cyber Resilience
Now, let’s learn some of the factors that help in building Cyber Resilience. They include:
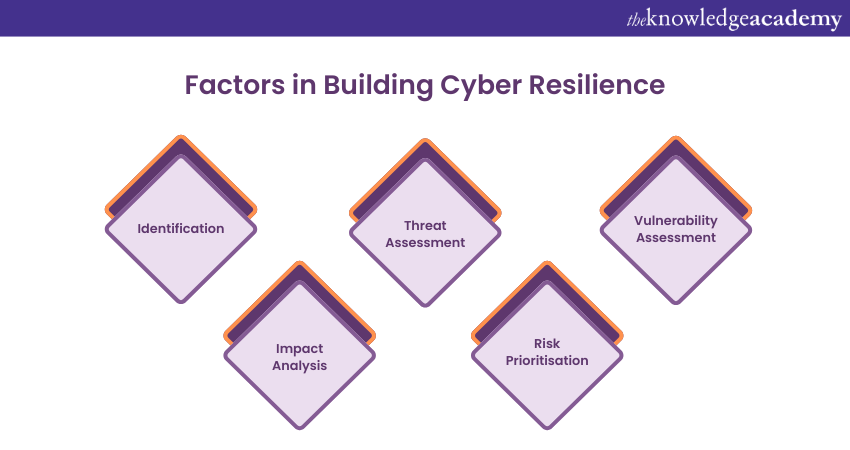
1) Identification: Identify assets, systems, and processes critical to the organisation's operations. This includes both digital and physical assets.
2) Threat Assessment: Analyse the potential threats that could target these critical assets. Understand the tactics, techniques, and procedures that cyber attackers might employ.
3) Vulnerability Assessment: Evaluate vulnerabilities in the organisation's systems and processes that attackers could exploit. This can involve vulnerability scanning and penetration testing.
4) Impact Analysis: Determine the potential impact of a successful cyberattack on the organisation's operations, finances, reputation, and compliance.
5) Risk Prioritisation: Assign a risk level to each identified vulnerability based on its likelihood and potential impact. This helps prioritise resources for mitigation efforts.
2) Methods to Protect Digital Infrastructure
Organisations must architect their digital infrastructure with adaptability to enhance Cyber Resilience. Adaptive security architecture focuses on creating multiple layers of defence that can adjust to emerging threats and attacks. The following methods can ensure a secured digital infrastructure:
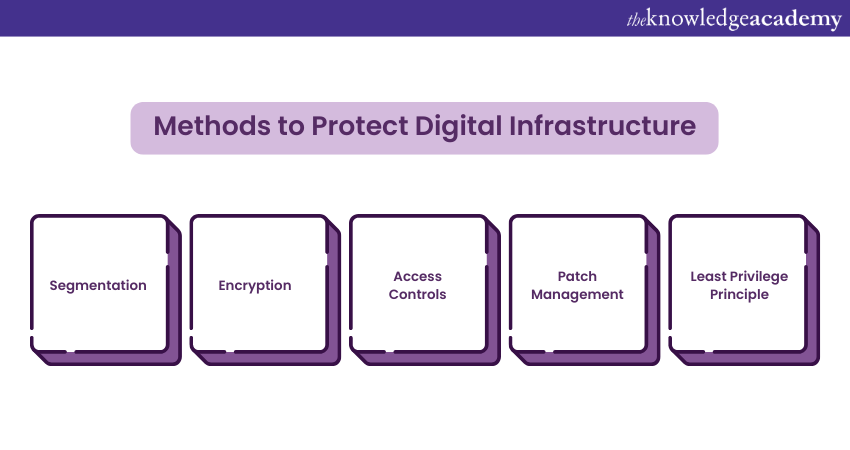
1) Segmentation: Divide the network into segments to restrict the lateral movement of attackers. This limits the potential damage if one part is breached.
2) Encryption: Use encryption to safeguard data both at rest and in transit. This ensures that intercepted data remains unreadable without the corresponding decryption key.
3) Access Controls: Enforce stringent access controls to restrict access to sensitive systems and data. Enhance security by using multi-factor authentication.
4) Patch Management: Regularly update software and systems to address known vulnerabilities. Many cyber incidents occur due to outdated software.
5) Least Privilege Principle: Grant users the minimum access necessary for their roles.
3) Developing a Response Plan
An integral aspect of Cyber Resilience is the development of comprehensive incident response and recovery plans.
1) Developing a Response Plan: A well-defined response plan outlines roles, responsibilities, communication protocols, and containment strategies that minimise the damage of a cyber incident.
2) Business Continuity Measures: It ensure critical functions can continue even during an incident. In addition, it minimises disruption to operations and customer service.
4) Human Factors in Cyber Incidents
Humans remain critical in cyber incidents. They often inadvertently facilitate attacks through social engineering or lack of awareness. Regular training and programs that raise awareness can empower employees to recognise threats and adopt secure behaviours. The following methods describe the components of training:
1) Phishing awareness: Educate workers about the dangers of phishing and how to identify suspicious links and attachments.
2) Password hygiene: Promote solid and unique passwords and the practice of not sharing credentials.
3) Social engineering: Train employees to be cautious when sharing sensitive information, even with seemingly legitimate individuals.
4) Data handling: Teach employees proper data handling procedures to prevent accidental data leaks or breaches.
5) Reporting: Establish clear procedures for reporting potential security incidents or concerns to the IT or security team.
How do you Achieve Cyber Resilience?
Organisations can enhance their Cyber Resilience by taking several key steps:
1) Strengthening Security: Implement robust security measures to prevent unauthorised access. This includes using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA), and regularly updating software.
2) Detecting Attacks: Establish systems to quickly identify potential attacks, allowing for a swift response to minimise damage. This involves continuous monitoring for suspicious activities and training staff to recognise signs of an attack.
3) Responding to Attacks: Develop a comprehensive response plan to effectively address detected attacks. This plan should outline whom to contact and the specific steps to mitigate damage.
4) Recovering from Attacks: Ensure systems and data can be restored following an attack. This requires maintaining regular backups and having a clear recovery plan in place.
Challenges in Achieving Cyber Resilience
One of the foremost challenges in building Cyber Resilience is the rapid evolution of cyber threats. Hackers and malicious actors constantly refine their tactics. They use advanced technologies and exploit newly discovered vulnerabilities. This dynamic nature of cyber threats requires organisations to stay vigilant and adaptive. They often require them to predict the unpredictable.
1) How to Address Challenges in Achieving Cyber Resilience
The following ways can be adopted to address the challenges:
1) Threat Intelligence: Invest in robust threat intelligence mechanisms that monitor and analyse emerging threats. This provides timely information to guide defensive strategies.
2) Agile security measures: Implement agile security practices that swiftly respond to new threats and vulnerabilities. This ensures up-to-date defence mechanisms.
3) Collaborative information sharing: Engage in collaborative efforts with industry peers, governmental agencies, and Cybersecurity communities to share threat intelligence and mitigation strategies.
2) Resource Constraints in Cyber Resilience
Resource constraints pose a significant challenge for organisations striving to build Cyber Resilience. Effective Cybersecurity requires financial investments in advanced tools, skilled Cybersecurity personnel, and ongoing training initiatives. Small organisations and those operating on limited budgets especially often need help to allocate adequate resources to combat cyber threats effectively. Following are a few mitigation strategies they can use for:
1) Prioritisation: Identify and prioritise critical assets and vulnerabilities. Focus resources on areas that present the highest risk to the organisation.
2) Outsourcing: Consider outsourcing certain Cybersecurity functions, such as penetration testing or incident response, to specialised service providers.
3) Security Awareness: Cultivate a culture of Cybersecurity awareness among all staff members. Use cost-effective training programs to increase their ability to identify and respond to threats.
Equip your organisation with the power of Cyber Resilience. Explore our RESILIA® Training and navigate the complex landscape of cyber threats with confidence.
The four categories of Cyber Resilience
There is a four-part approach to Cyber Resilience. They are:
1) Manage and Protect
This category involves implementing risk-appropriate information security measures that rely on people, processes, and technology to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets, business processes, and infrastructure. It also includes safeguarding information and systems from cyber-attacks, system failures, and unauthorised access.
Key areas may include:
1) Asset management
2) Information security (InfoSec) policies
3) Physical and environmental security
4) Identity and access control
5) Malware protection
6) Configuration and patch management
7) Encryption
8) System Security
9) Network and communications security
10) Security competence and training
11) Staff awareness training
12) Comprehensive risk management program
13) Supply chain risk management
2) Identify and Detect
This category focuses on the continuous monitoring of networks and information systems to detect anomalies and potential cybersecurity incidents before they cause substantial damage.
Key areas may include:
1) Threat and vulnerability intelligence
2) Security monitoring
3) Respond and Recover
An incident response management program and business continuity measures ensure that operations continue during a cyber-attack and that the organisation can return to normal as quickly as possible.
Key areas may include:
1) Incident response management
2) ICT continuity management
3) Business continuity management
4) Govern and Assure
This category ensures that the Cyber Resilience program is overseen by top-level management and integrated into everyday business operations. Over time, it should increasingly align with the organisation's broader business objectives.
Key areas may include:
1) Formal information security management program
2) Continual improvement process
3) Board-level commitment and involvement
4) Governance structure and processes
5) Internal audit
6) External certification/validation
The benefits of Cyber Resilience
Being cyber resilient helps you:
1) Minimise financial losses
2) Comply with legal and regulatory requirements
3) Enhance your security culture and internal processes
4) Safeguard your brand and reputation
Components of Cyber Resilience
Cyber Resilience has four components. They are:
1) Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is fundamental to a Cyber Resilience strategy. It involves teams and robust tools that protect an organisation's IT ecosystem—network, hardware, and data—by monitoring, detecting, defending against, and responding to malicious attacks and intrusions. Cybersecurity policies and solutions are also crucial for keeping workers secure, regardless of their location.
2) Risk Management
Risk management identifies potential risks that could impact an organisation's IT ecosystem, such as hacking, data breaches, and IT espionage. It also considers risks from human error, hardware failure, natural disasters, and power outages.
3) Business Continuity
Business continuity is the capability to maintain operational viability and continue delivering services after a short-term disruption. Cyber Resilience plays a critical role in supporting business continuity. Several businesses are re-evaluating their business continuity plan by identifying limitations and developing more detailed business resilience strategies.
4) Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery encompasses procedures, tools, and policies that an organisation can deploy to restore mission-critical functions after a catastrophic event, such as a cyber-attack, prolonged power outage, or natural disaster.
Conclusion
Cyber Resilience is a cornerstone of modern defence strategies in a digital frontier. It is a perspective that embraces adaptability, preparedness, and continuous improvement. As technology advances, threats become more sophisticated. Therefore, Cyber Resilience is important to withstand, adapt to, and recover from the challenges from digital world. We hope you have now understood What is Cyber Resilience and how can it change the modern business.
Understand how to enhance your organisation's Cyber Resilience today by signing up for our RESILIA® Practitioner Course.
Frequently Asked Questions

The four pillars of Cyber Resilience are:
1) Manage and Protect: Implement security measures to safeguard information assets.
2) Identify and Detect: Continuously monitor systems to detect threats.
3) Respond and Recover: Develop plans to handle and recover from incidents.
4) Govern and Assure: Ensure top-level oversight and alignment with business goals.

The seven steps to Cyber Resilience are:
1) Assess Risk: Identify potential cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
2) Develop Strategy: Create a comprehensive Cyber Resilience plan.
3) Implement Controls: Deploy security measures and protocols.
4) Monitor Continuously: Keep an eye on systems for any signs of threats.
5) Respond Quickly: Have an incident response plan in place.
6) Recover Swiftly: Ensure rapid recovery and business continuity.
7) Review Regularly: Continuously improve and update the resilience plan.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various RESILIA® Training, including RESILIA® Foundation, RESILIA® Practitioner and RESILIA® Foundation and Practitioner Courses. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is Cyber Resilience?
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to RESILIA® Training, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cybersecurity skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 RESILIA® Foundation and Practitioner
RESILIA® Foundation and Practitioner
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 26th May 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


