We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +41 315281584 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Imagine having tons of valuable information at your fingertips but not knowing how to harness its power. That’s where Data Management steps in. It’s all about storing and safeguarding data to empower businesses to make smarter decisions and stay ahead of the competition.
In this blog, we discuss what Data Management is, how it works, the challenges involved, and best practices to ensure your organisation can unlock the full potential of its data. Ready to dive into the world of Data Management? Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
1) What is Data Management?
2) Different Types of Data Management
3) How Does Data Management Work?
4) The Importance of Data Management
5) Challenges of Data Management
6) Best Practices for Data Management
7) Conclusion
What is Data Management?
Data Management involves gathering, organising, protecting, and storing data so it can be used to make business decisions. As companies generate more data than ever, managing it well is crucial. Modern Data Management tools ensure that the data used for decisions is always accurate and current.
These tools help with preparing data, organising it, searching for it, and ensuring it follows rules and standards, making it easy for people to find and use the information they need.
Different Types of Data Management
Data Management involves various techniques to make handling data easier and more efficient. Here are some key types:
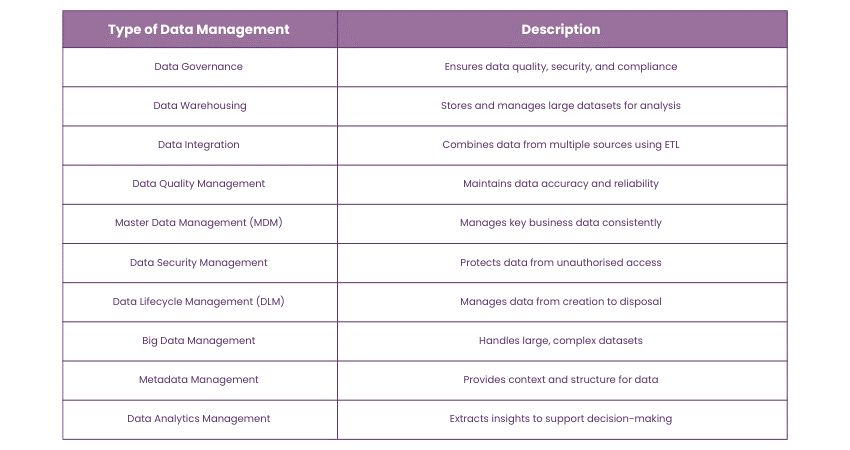
a) Data Governance: Sets rules and guidelines to ensure data is high-quality, consistent, secure, and follows regulations. It helps maintain data integrity and compliance.
b) Data Warehousing: Collects, stores, and manages large amounts of data from various sources for analysis and reporting. It is mainly used for historical data.
c) Data Integration: Combines data from different sources into a single, unified view. This often involves ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes to make data ready for analysis.
d) Data Quality Management: Ensures data is accurate, complete, reliable, and relevant. It maintains the integrity of data across the organisation.
e) Master Data Management (MDM): Manages key business data like customer or product information to provide a consistent reference across systems. It ensures data is accurate and uniform.
f) Data Security Management: Protects data from unauthorised access and cyber threats using encryption and access controls. It ensures data remains safe and secure.
g) Data Lifecycle Management (DLM): Manages data from creation to disposal, ensuring it is available and secure throughout its lifecycle. It includes storing, archiving, and deleting data as needed.
h) Big Data Management: Handles large and complex datasets that traditional tools can’t process. It uses technologies like Hadoop or NoSQL databases to manage big data.
i) Metadata Management: Manages data about data (metadata), providing context and information on data usage, source, and structure. It helps users understand and find data easily.
j) Data Analytics Management: Manages data to extract insights through analysis. It supports decision-making by providing valuable information from data.
How Does Data Management Work?
Here is how it works:
a) Collecting Data: Information is gathered from various sources such as databases, files, and online systems.
b) Storing Data: The collected data is stored in databases or data warehouses for easy access later.
c) Organising Data: Data is sorted, labelled, and structured to make it easier to find and use.
d) Cleaning Data: Errors, duplicates, and irrelevant information are removed to ensure the data is accurate and useful.
e) Securing Data: Encryption and access controls are implemented to protect data from unauthorised access.
f) Analysing Data: Managed data is analysed to uncover insights, trends, and patterns that aid in business decision-making.
Learn how to work with missing data with our Pandas for Data Analysis Training – Join today!
The Importance of Data Management
Here are the key advantages of it:
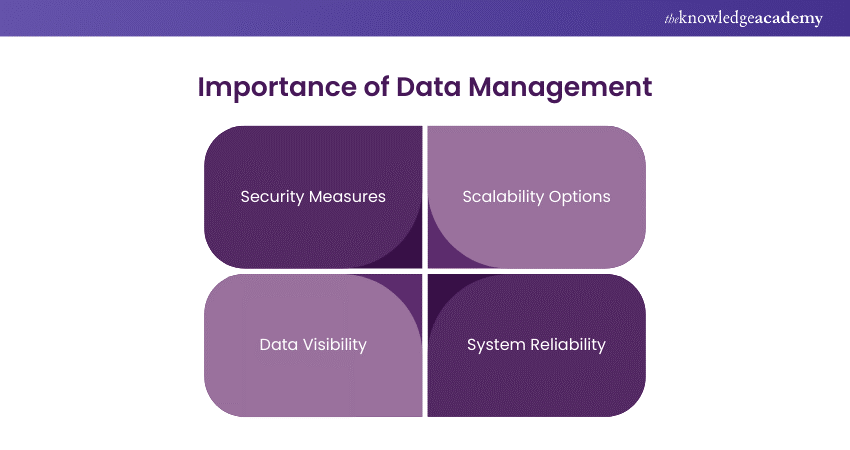
Security Measures
Data Management protects against data loss, theft, and breaches through authentication and encryption. Strong security measures ensure that important company information is backed up and can be retrieved if the primary source is unavailable. This is especially important for managing personally identifiable information in compliance with consumer protection laws.
Scalability Options
It allows organisations to scale their data and usage efficiently with repeatable processes. This prevents unnecessary duplication of efforts, such as redoing research or running costly queries multiple times, saving time and resources.
Data Visibility
It enhances the visibility of your organisation’s data assets, making it easier for employees to quickly find the data they need. This increased visibility helps your company stay organised and boosts productivity.
System Reliability
By establishing clear processes and policies, Data Management reduces errors and builds trust in the data used for decision-making. Reliable, up-to-date data enables companies to respond swiftly to market changes and customer needs.
Challenges of Data Management
Some of the disadvantages include:
Evolving Roles in Analytics
With more reliance on data-driven decisions, more people need to access and analyse data. If data analysis is outside their skill set, understanding complex data structures and naming conventions can be difficult. If converting data is too time-consuming, the analysis won’t happen, and the data’s potential value is lost.
Managing Growing Data Volumes
Every department has access to various types of data and needs to maximise its value. Traditional methods require IT to prepare and maintain data for each use case. As data accumulates, it becomes easy to lose track of what data exists, where it is, and how to use it.
Navigating Compliance Requirements
As compliance rules continue to evolve, it becomes nearly impossible to perfect the usage of data. Businesses require their people to be able to identify which data to use and how to handle Personally Identifiable Information (PII) to comply with privacy regulations.
Best Practices for Data Management
Here are some best practices for Data Management:
Emphasise Data Quality
Implement processes to improve data quality. Regularly check for accuracy to prevent outdated or incorrect data, and train team members on proper data entry and use automation to ensure data is correct from the start.
Make Data Security a Priority
Make sure data is accessible within the organisation but protected from outsiders. Train your team on data handling, meeting compliance requirements, and having a plan for potential breaches. The Data Management software can help keep your data secure.
Align Data Management with Business Goals
tart by defining your organisation’s goals. This helps determine how you collect, store, manage, clean, and analyse data, ensuring you only keep data relevant for decision-making and avoid clutter.
Ensure Data Access for Key Personnel
Ensure that the right people can access the data they need. Set up different levels of permissions to balance convenience and security, so employees can efficiently do their jobs without risking data security.
Learn powerful data analysis techniques with our Data Science with R Training – Join today!
Conclusion
We hope you have understood the importance of effective Data Management. It involves collecting, storing, organising, cleaning, securing, and analysing data to ensure it is accurate. By following best practices, organisations can make better decisions and improve efficiency. Overcoming challenges like increased data volumes and compliance requirements is essential for maximising the value of data.
Learn about data warehousing with our Data Mining Training – Sign up today!
Frequently Asked Questions

The six stages of Data Management include: Collection, Storage, Processing, Analysis, Deployment and Archiving.

SAP Data Management is the process of employing SAP tools to gather, archive and analyse data. It also comprises SAP HANA, SAP Data Services as well as SAP Master Data Governance to meet quality and compliance.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Data Science Courses, including Data Mining Training, Data Science with R Training, and Pandas for Data Analysis Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Decision Tree Analysis.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Data Management, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Data Mining Training
Data Mining Training
Thu 27th Feb 2025
Thu 10th Apr 2025
Thu 26th Jun 2025
Thu 28th Aug 2025
Thu 23rd Oct 2025
Thu 4th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


