We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +41 315281584 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Financial modelling is essential for business success, providing numerous benefits such as supporting informed decision-making, future planning, and evaluating the viability of different strategies. It enables organisations to assess investment opportunities by creating mathematical models based on historical data. These models predict future outcomes of business decisions and guide strategic planning. As business operations become more complex, Uncovering How to Build a Financial Model is increasingly crucial for driving success and achieving financial goals.
Financial Modelling leverages statistical frameworks based on past and present financial parameters to make accurate and timely forecasts on the performance of a business, investment or project. This blog explores How to Build a Financial Model by shedding light on its most significant steps. Continue reading below to examine more.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Financial Model?
2) Why make a Financial Model?
3) How to Build a Financial Model?
a) Understand Your Company
b) Understand the Dynamics of the Industry
c) Begin with the Audited Numbers
d) Identify the assumptions
e) Project the Income Statement
f) Develop the Supplementary Schedules
4) Benefits of Building a Financial Model
5) Conclusion
What is a Financial Model?
A Financial Model is an important tool that helps you analyse the past, present, and future performance of a business, project, or investment. It can help you make informed decisions, plan, and evaluate different scenarios.
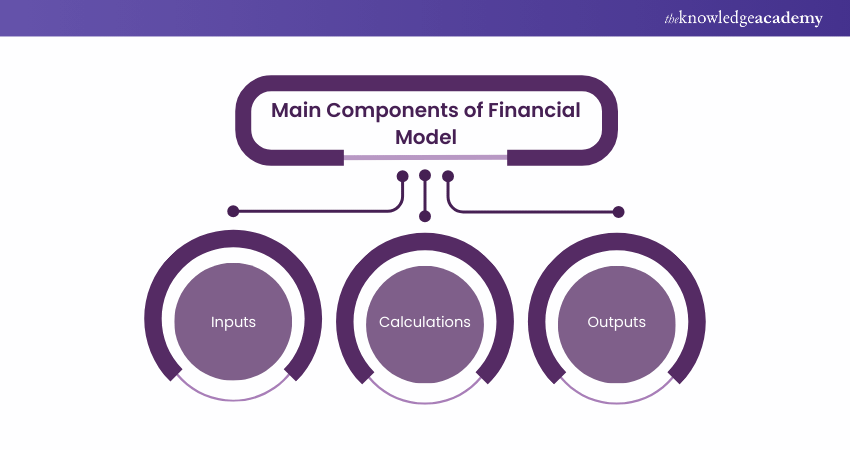
A Financial Model typically consists of three main components:
a) Inputs: These are the data, assumptions, and parameters you use to build your model. They can include historical financial statements, market research, industry benchmarks, growth rates, cost drivers, discount rates, etc.
b) Calculations: These are the formulas and functions that you use to process the inputs and generate the outputs. They can include income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, depreciation, amortisation, working capital, capital expenditures, etc.
c) Outputs: These are the results and outcomes you obtain from your model. They can include financial ratios, charts, graphs, summaries, scenarios, sensitivity analyses, etc.
Why Make a Financial Model?
Depending on your role and situation, a Financial Model can help you achieve various purposes and benefits. Some of the common reasons and advantages of making a Financial Model are:
a) Planning and Forecasting: A Financial Model can help you plan and forecast your financial performance and position for the future. It can help you achieve goals, allocate resources efficiently, and anticipate potential challenges and opportunities.
b) Decision-making and Evaluation: A Financial Model can help you make better and more informed decisions and evaluations. It can help you compare and contrast different options, assess the feasibility and viability of your business or project, and measure the return and risk of your investment.
c) Communication and Presentation: A Financial Model can help you communicate and present your financial information and analysis to various stakeholders, such as Investors, lenders, partners, customers, employees, etc. It can help you demonstrate your credibility, professionalism, and competence and persuade and convince your audience to support your business or project.
Transform your financial strategy: Secure your spot in our expert-led Financial Management Course!
How to Build a Financial Model?
Building a Financial Model is a multifaceted process that requires a deep understanding of your company and industry and a systematic approach to analysing financial data. Here is the step-by-step process to build a Financial Model:
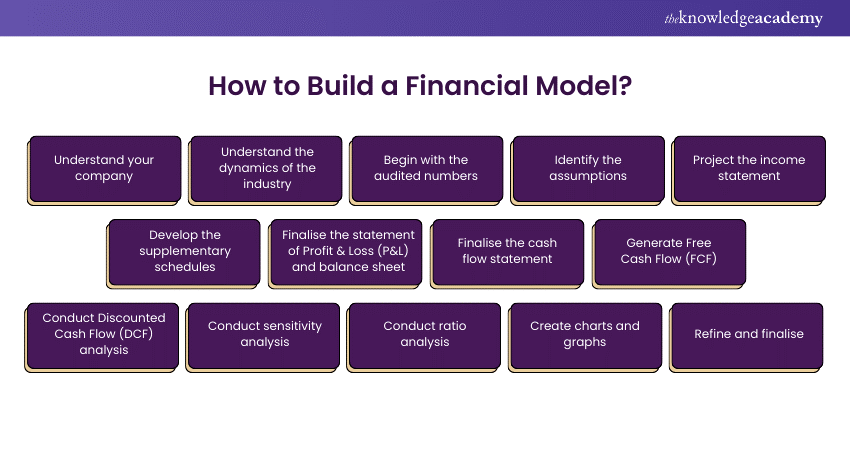
Understand Your Company
The initial step in building a Financial Model is to thoroughly understand your company's operations, revenue streams, cost structures, and growth prospects. It involves delving into the company's business model, competitive positioning, and strategic objectives. A deep understanding of these elements is important as they form the foundation of your financial projections. Consider factors like product lines, market share, customer segments, and operational efficiency to get a clear picture of your company's business dynamics.
Understand the Dynamics of the Industry
Next, analyse the industry in which your company operates. It includes understanding the market size, growth rates, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and economic factors influencing the industry. Pay attention to trends, threats, opportunities, and the overall market outlook. This step is vital because the industry dynamics can significantly impact your company's performance. For instance, a rapidly growing industry might offer opportunities for expansion, while a saturated market might pose challenges in maintaining market share.
Begin with the Audited Numbers
Your Financial Model should be grounded in reality, which means starting with audited historical financial statements. These include the balance sheet, cash flow statement and income statement. This step ensures the accuracy of the base figures used in the model and lends credibility to your projections. Historical financial data provides insights into trends, operational efficiency, and financial health, forming a basis for forecasting future performance. Carefully analyse past revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, and cash flows to establish a reliable starting point.
Identify the Assumptions
Building a Financial Model requires making assumptions about the future. These assumptions might include expected growth rates, inflation rates, market conditions, and internal company changes. Clearly identifying and documenting these assumptions is crucial as they significantly impact the projections. Assumptions should be realistic, based on available data and industry trends. It's also important to differentiate between optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely scenarios. This step ensures that the model is flexible and can be adjusted as more information becomes available or if circumstances change.
Project the Income Statement
After identifying the assumptions, the next step is to project the income statement for future periods. It involves forecasting revenues, costs of goods sold, operating expenses, and eventually net income. Revenue projections should be based on factors like market trends, sales pipelines, and historical growth rates. Similarly, estimate expenses based on historical trends and expected changes in the business. The projected income statement provides an overview of the company's expected profitability and is a key component of the Financial Model, as it highlights potential growth and profitability trends.
Develop the Supplementary Schedules
In this step, create supplementary schedules for elements like depreciation, amortisation, capital expenditures, debt, and equity. These schedules provide detailed information that feeds into the main financial statements. For example, a depreciation schedule shows how fixed asset value decreases over time, impacting both the balance sheet and income statement. Similarly, a debt schedule outlines future repayments, affecting cash flows and interest expenses. These schedules are crucial for comprehensively understanding the company's future financial position.
Finalise the Statement of Profit & Loss (P&L) and Balance Sheet
Once the income statement projections and supplementary schedules are in place, integrate them to finalise the P&L statement and balance sheet. The P&L statement shows the company's projected profitability, while the balance sheet provides a snapshot of its financial position at different times. It involves ensuring that all the components of the financial statements are aligned and accurately reflect the company's financial performance and position. It's important to ensure the balance sheet balances, with assets equalling liabilities plus equity.
Finalise the Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement is an important component of the Financial Model. It shows how the balance sheet and income statement changes impact the company's cash position. This statement is divided into cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities. Finalising the cash flow statement involves projecting how much cash the company will generate or use in each area. This step is vital for understanding the liquidity and solvency of the business. A positive cash flow indicates a healthy business capable of sustaining growth, paying dividends, or repaying debt, whereas a negative cash flow could signal potential financial difficulties.
Generate Free Cash Flow (FCF)
Free Cash Flow (FCF) is a crucial measure in financial analysis, denoting the cash produced by a company once it covers the expenses needed to maintain and operate its capital assets. It is calculated by deducting capital expenditures from the operating cash flow. FCF stands as a vital sign of a firm's financial stability and its capacity to create cash earnings. This metric is especially valuable for Investors, as it indicates the available cash for distribution among stakeholders or for reinvesting in the enterprise.
Conduct Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
DCF analysis is a method for valuing an investment by estimating its worth based on the anticipated future cash flows it will generate. This step involves discounting the projected free cash flows and a terminal value to their present value, using an appropriate discount rate (usually the weighted average cost of capital). DCF analysis is critical in Financial Modelling as it estimates the company's or a project's intrinsic value, aiding in investment decision-making and valuation exercises.
Elevate your career with top-tier Financial Modelling Skills – Sign up for our Financial Modelling Course!
Conduct sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis involves examining how different values of key variables impact the Financial Model's outcomes. This step is crucial for understanding the robustness of the model and the risks associated with the underlying assumptions. By altering key assumptions (like growth rates, cost margins, or discount rates) and observing the effects on the model’s outputs, you can identify which variables have the most significant impact and how changes in these variables affect the company's valuation or financial performance. This analysis helps in risk assessment and strategic planning.
Conduct Ratio Analysis
Ratio analysis compares various financial metrics to assess the company's performance and financial health. Key ratios include:
a) Profitability Ratios (like net profit margin).
b) Liquidity Ratios (like current ratio).
c) Leverage Ratios (like debt-to-equity ratio).
d) Efficiency Ratios (like inventory turnover).
Analysing these ratios over time and against industry benchmarks provides valuable insights into the company’s operational effectiveness, financial stability, and long-term viability. Ratio analysis is fundamental to financial analysis and helps stakeholders understand the financial implications of business decisions.
Create Charts and Graphs
Visual representation of financial data through charts and graphs makes the model more accessible and understandable. Graphs such as trend lines for sales, profit margins, cash flow projections, and debt levels help quickly grasp the financial story and trends. They also aid in presenting the model to stakeholders who may not be well-versed in financial analysis. Effective visualisation straightforwardly communicates complex data, facilitating better decision-making and helping to highlight key areas of interest or concern in the Financial Model.
Refinement and finalisation
The final step in building a Financial Model involves refining and finalising the document. It includes checking for errors, ensuring consistency in the numbers and assumptions, and formatting the model for clarity and ease of use. Create an index for easy navigation, especially in complex models. It's also important to document the sources of data and the rationale behind assumptions for transparency. Finally, review the model with key stakeholders, get feedback, and make necessary adjustments. A well-refined and finalised Financial Model is a valuable tool for strategic decision-making.
Unlock your potential in finance: Discover our comprehensive range of Accounting & Finance Training!
Benefits of Building a Financial Model
Building a Financial Model is not just a numerical exercise; it offers profound benefits that can transform a business's strategy, planning, and decision-making approach. Two of the most significant benefits are enhancing the comprehension of the business and pinpointing areas for allocating funds.
Enhances Comprehension of the Business
A Financial Model acts as a mirror reflecting the inner workings of a business in numbers. It provides a structured way to analyse a company’s operations, making it an indispensable tool for business owners, managers, and Investors. By translating complex business activities into financial forecasts and statements, a Financial Model enables a deeper understanding of the business in several ways:
a) Strategic Insight: Financial Models allow users to see the impact of past decisions and how future decisions could affect the company. Businesses can make informed strategic choices by analysing various scenarios and their outcomes. For instance, a model can reveal how expanding into a new market or launching a product may affect the company’s bottom line.
b) Operational Understanding: It breaks down the company's revenue streams and cost structures, providing insights into which areas are most profitable and which are costing the company. This understanding is crucial for operational efficiency and can lead to effective cost management and optimisation of resources.
c) Risk Management: A Financial Model helps understand the business's potential risks and uncertainties by including different assumptions and scenarios. It allows companies to prepare contingency plans and develop strategies to mitigate these risks.
d) Communication Tool: Financial Models are vital for communicating with stakeholders, including Investors, creditors, and employees. They provide a clear, quantitative view of the company's prospects and performance, making it easier to secure investments, loans, or buy-in from internal stakeholders.
Pinpoint Areas for Allocating Funds
A critical advantage of Financial Modelling is its ability to highlight where funds should be allocated for maximum effectiveness and growth. This benefit is crucial for several reasons:
a) Resource Optimisation: By understanding the financial impacts of different business areas, companies can allocate resources more efficiently. Financial Models show where investment can lead to growth and where it may not be as effective. It can help prioritise investment in high-return areas such as new product development, marketing strategies, or market expansion.
b) Budgeting and Forecasting: Financial Models are essential for budgeting and forecasting. They enable businesses to plan their financials systematically, ensuring that funds are allocated to align with both short-term and long-term strategic goals.
c) Investment Decisions: For businesses looking to invest in new projects or acquisitions, Financial Models provide a framework for evaluating the risks associated with these investments. It ensures that capital is invested in projects most likely to yield favourable returns.
d) Financial Health: Understanding where to allocate funds helps maintain and improve the company's financial health. Effective fund allocation can lead to better cash flow management, debt reduction, and financial stability.
Elevate your career with top-tier Financial Modelling Skills – Sign up for our Financial Modelling Course !
Conclusion
Building a Financial Model is a skill that can help you analyse, plan, and evaluate your business, project, or investment. It can help you make better decisions, communicate your ideas, and achieve your goals. In this blog, we have shown you How to Build a Financial Model in 14 easy steps, using a simple example of a lemonade stand business. We hope this blog has inspired you to learn more about building a Financial Model and applying it to your own situation.
Master the language of business: Sign up for our premier Accounting Training!
Frequently Asked Questions

There are many Financial Modelling Software to choose from such as Finmark, Quantrix, Oracle BI, Synario, IBM Cognos, Mosaic, Jirav and Hyperion

Both CFA and Financial modelling has their merits. CFA prioritises advanced financial topics and Financial Modelling creates detailed plans for organisations.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Accounting & Finance Courses, including Financial Modelling, Payroll and Financial Management. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Financial Management.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Financial Management, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Financial Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Accounting and Finance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Financial Modelling Course
Financial Modelling Course
Fri 6th Dec 2024
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 28th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


