We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +41 315281584 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In today's fast-moving business environment, understanding the distinctions between Kanban vs Scrum — two key frameworks in the Agile — is vital. The comparison of Kanban and Scrum offers iterative and flexible approaches to Project Management that allow teams to deliver value quickly while maintaining adaptability and transparency.
According to the State of Kanban Report of 2022, approximately 85 per cent of project teams find the Kanban Board more effective than other methods. Additionally, the report highlights that 90 per cent of respondents implement Scrum methodologies in their projects. Explore this blog to uncover the nuances of each framework and determine which method, Kanban vs Scrum, might be best suited for your project needs.
Table of Contents
1) What is Kanban?
2) What is Scrum?
3) Key differences between Kanban vs Scrum
4) Synergy between Kanban and Scrum
5) Conclusion
What is Kanban?
Kanban is a lean Project Management tool designed to enhance efficiency through visual management. Originating in Japanese manufacturing circles at Toyota, it is now widely applied across various industries for managing work at every stage of production. At its core, Kanban helps teams visualise their workflow, limit work-in-progress, and maximise efficiency.
The process involves using a Kanban Board, typically segmented into columns such as "To Do," "In Progress," and "Completed." This method fosters better team collaboration and continuous process improvement, making it an effective strategy for teams seeking a flexible and transparent approach to Project Management.
What is Scrum?
Scrum is a structured framework for managing complex projects in Software Development and other fields. It breaks down large projects into smaller, manageable chunks known as sprints, typically lasting two to four weeks. Each sprint starts with a planning meeting where team members commit to delivering specific pieces of work.
The process is facilitated by key roles: the Product Owner, the Scrum Master and the Development Team. This framework emphasises accountability, teamwork, and iterative progress toward a well-defined goal, making it highly effective for projects where requirements are rapidly changing.
Gain knowledge of various Scrum Master techniques with our Scrum Master Certification Course – join today!
Key differences between Kanban and Scrum
When it comes to Project Management, Kanban and Scrum lead the pack, especially in the realm of Agile development. Both are popular for their efficiency in handling projects but cater to different types of workflows and team dynamics. Here is the detailed distinction:
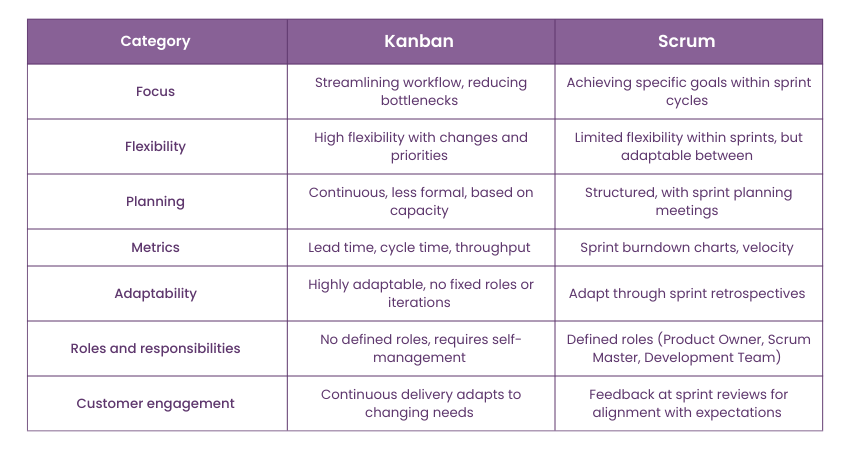
Focus
Kanban focuses on streamlining and improving the flow of work by emphasising the reduction of bottlenecks, managing work in progress, and visualising tasks through a Kanban Board. By using tools like Kanban in OneNote, this approach allows for a smoother workflow and quick identification of blockages.
On the other hand, Scrum workflow concentrates on achieving specific goals within each sprint cycle. It is designed to handle complex projects that benefit from incremental development and frequent reassessment of tasks.
Flexibility
Flexibility is where Kanban shines. It adapts to changes in priority or scope without disrupting the current flow of work, making it ideal for environments where requirements can change rapidly.
In contrast, Scrum is less flexible in terms of scope changes during sprints but offers flexibility through its regular sprint reviews and retrospectives, which allow teams to pivot and adjust before the next sprint begins.
Planning
In Kanban, planning is continuous and less formal. Tasks are pulled from a backlog and moved onto the board as capacity allows, which supports just-in-time delivery of features.
On the other hand, Scrum involves more structured planning, primarily through sprint planning meetings where the team commits to specific tasks for the upcoming sprint, aiming to deliver a potentially shippable product increment at the end.
Metrics
Kanban utilises metrics such as lead time, cycle time, and throughput to measure the flow of work and efficiency. These metrics help teams understand their productivity and identify areas for improvement.
In contrast, Scrum focuses on sprint burndown charts and velocity as key metrics, which help gauge the team's speed and predict future performance based on historical data.
Adaptability
Kanban is highly adaptable due to its lack of prescribed roles or iterations. This makes it easy to integrate with other practices and to be tailored to the specific needs of a team.
On the other hand, Scrum is adaptable but through its sprint retrospectives. Teams can discuss what worked, what did not, and how processes can be improved for better results in the next iteration.
Learn how to use Kanban Board with the Kanban Practitioner Certification – join today!
Roles and responsibilities
Scrum has defined roles: the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team. Each role has specific responsibilities, making it clear who is accountable for what.
In contrast, Kanban does not have defined roles, offering more flexibility but requiring a higher level of maturity and self-management from the team members to ensure everyone contributes effectively.
Customer engagement
Kanban involves the customer primarily through the continuous delivery of work items, which can quickly adapt to changing customer needs. This ongoing interaction ensures that the product evolves in close alignment with what the customer wants.
On the other hand, Scrum engages customers at the end of each sprint during the sprint review, where stakeholders can provide feedback on the increment delivered, ensuring the product is developed according to their expectations.
Unlock your potential by reviewing top Kanban Interview Questions and Answers. Start preparing now!
Synergy between Kanban and Scrum
While Kanban and Scrum play different roles in distinct Project Management, many organisations find value in combining elements of both to create a more adaptable and efficient workflow. This hybrid approach, often referred to as Scrumban, leverages the strengths of each method to enhance team productivity and Project Management. The commonalities between these two are mentioned below:
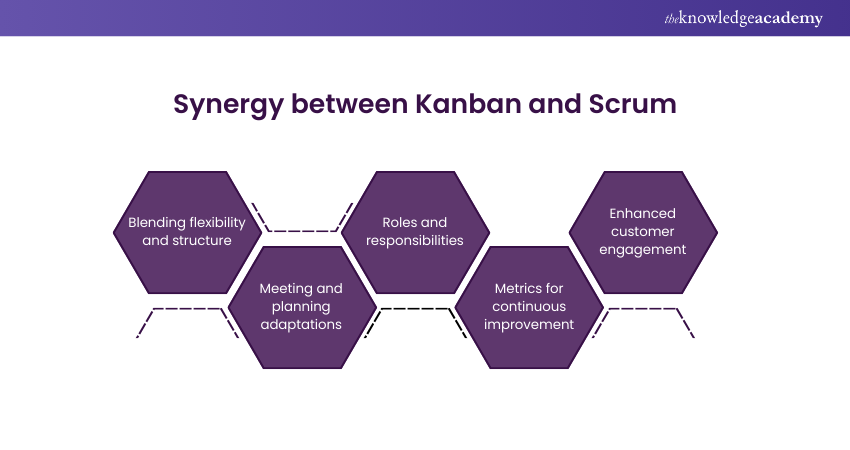
a) Blending flexibility and structure: Scrumban uses the flexible approach of Kanban within the structured framework of Scrum. This allows teams to plan sprints as in Scrum, but with the ability to update and adapt their task boards as work progresses, akin to Kanban. This blend helps manage both the predictable and the unpredictable aspects of projects, ensuring more consistent delivery of value.
b) Meeting and planning adaptations: Scrumban typically involves the regular sprint planning meetings of Scrum but integrates the continuous workflow of Kanban. This means while there may be a set plan for the sprint, the team can dynamically adjust their workload based on immediate needs and blockages, much like in Kanban.
c) Roles and responsibilities: In Scrumban, the defined roles of Scrum (Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team) are often maintained to keep clarity of responsibilities, but flexibility in role definitions from Kanban is also adopted. This allows team members to be more versatile and to take on various tasks as needed.
d) Metrics for continuous improvement: By combining Kanban's metrics like cycle time and throughput with Scrum's focus on sprint goals and Scrum Velocity, Scrumban provides a comprehensive view of both individual workflow efficiencies and overall project progress. This dual approach helps teams measure and optimise their process continuously.
e) Enhanced customer engagement: The synergy of Kanban and Scrum also improves the way teams engage with customers. Like in Scrum, regular reviews keep the project aligned with customer needs, while Kanban's continuous delivery ensures that any changes or feedback can be quickly incorporated into the project without waiting for the next sprint cycle.
Also learn about the difference between Kanban and Agile in Kanban vs Agile blog.
Conclusion
By understanding the key differences and strengths of both Scrum and Kanban, as outlined in our blog "Kanban vs Scrum," teams can make informed choices that best suit their operational goals. Additionally, the synergy between Kanban and Scrum can offer teams a versatile and dynamic framework, combining structured planning with flexibility in execution. This approach can be the solution for teams looking to enhance their productivity and streamline their Project Management processes effectively.
Gain insights into Agile principles and continuous improvement practices with our Scrum for Teams Course – join today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Kanban have sprints?

Kanban does not use sprints as it is built around continuous flow and incremental improvements. However, some teams adapt Kanban to include sprint-like cycles for specific projects, creating a hybrid approach that incorporates elements of Scrum.
When should one use Scrum, and when should one use Kanban?

Scrum is best suited for complex projects requiring feedback and structured phases, making it ideal for environments like Software Development. Kanban is more appropriate for projects that need continuous delivery and flexibility, such as maintenance or operations, where priorities can frequently change.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is the Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are related courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Scrum Certification Training, including Scrum Master Certification Course, Scrum Product Owner Training and Scrum Developer Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Agile Project Management With Scrum.
Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to Scrum, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Improvement skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Scrum Master Certification
Scrum Master Certification
Thu 24th Apr 2025
Thu 1st May 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 5th Jun 2025
Thu 19th Jun 2025
Thu 3rd Jul 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 31st Jul 2025
Thu 14th Aug 2025
Thu 11th Sep 2025
Thu 25th Sep 2025
Thu 2nd Oct 2025
Thu 9th Oct 2025
Thu 16th Oct 2025
Thu 23rd Oct 2025
Thu 30th Oct 2025
Thu 6th Nov 2025
Thu 13th Nov 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025
Thu 27th Nov 2025
Thu 4th Dec 2025
Thu 11th Dec 2025
Thu 18th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


