We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +41 315281584 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Have you ever wondered what separates thriving businesses from those that crumble under pressure? Imagine trying to drive through a winding, foggy road without headlights- scary, right? That’s what it's like for organisations without a solid Risk Management strategy- unseen threats waiting to disrupt operations. This is where the Risk Management Process steps in, helping foresee and tackle threats before they escalate into disruptions.
But what are the key steps, and how do they keep companies on track? In this blog, we’ll take you through the five crucial steps of the Risk Management Process. Curious about how this process can help your organisation steer clear of trouble while opening doors to new opportunities? Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
1) What is the Risk Management Process?
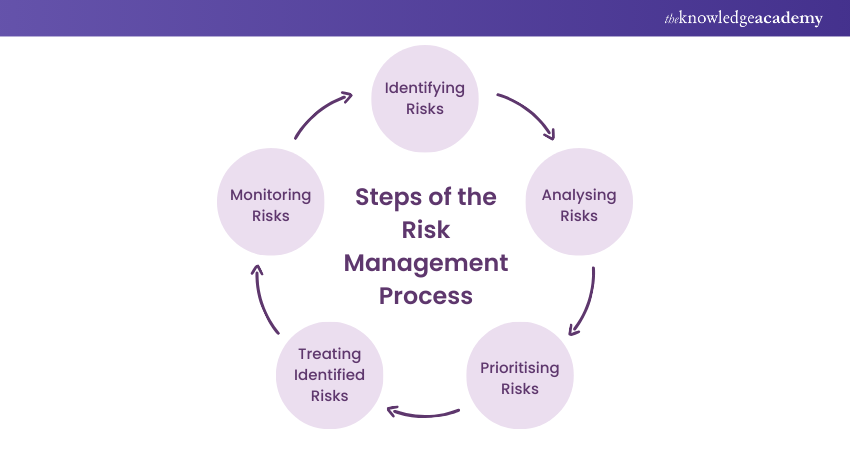
2) What are the Steps of the Risk Management Process?
a) Identifying Risks
b) Analysing Risks
c) Prioritising Rrisks
d) Treating identified Risks
e) Monitoring Risks
3) Conclusion
What is the Risk Management Process?
The Risk Management Process is a systematic strategy that assists organisations and individuals in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. It ensures that possible risks are taken care of before they escalate, helping firms to efficiently manage uncertainty. Additionally, this proactive strategy aids in the identification of possibilities to improve operations or project outcomes.
a) Proactive Culture: Risk Management promotes ongoing monitoring and informed decision-making, increasing organisational resilience.
b) Adaptability: The procedure can be modified for particular industries, sectors, initiatives, or individual objectives.
c) Preparedness: By implementing Risk Management principles, businesses and individuals can improve their capacity to deal with uncertainty.
What are the Steps of the Risk Management Process?
Understanding the Risk Management Process helps managers and their teams perform better by taking care of the many risks that come with the projects. This process involves following a framework which determines the actions that are required to be taken to resolve any errors and risks. This framework is as follows:
1) Identifying Risks
The initial step in Risk Management is to identify potential hazards that could disrupt or negatively impact the firm. This process covers all aspects of the business, including finance, operations, technology, legal requirements, and human resources.
1) Techniques for Identifying Risks:
a) Brainstorming:
Gathering important stakeholders to discuss potential hazards in their areas of expertise.
b) SWOT Analysis:
Analysing an organisation's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and risks may identify areas of vulnerability.
c) Risk Checklists:
Use a checklist based on previous projects or industry standards to identify prevalent hazards.
d) Interviews and Surveys:
Collecting insights from employees, clients, and other stakeholders regarding potential risks.
2) Types of Risks:
a) Operational Risks:
Arising from internal systems, processes, or human error.
b) Financial Risks:
Linked to financial losses, market changes, or economic downturns.
c) Strategic Risks:
Relating to the organisation's long-term goals and planning.
d) Compliance Risks:
Resulting from violations of laws, regulations, or industry standards.
Interested to learn more about Risk Management? Sign up for our Risk Management Black Belt Course now!
2 Analysing Risks
Once risks are identified, they need to be analysed for their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. This step can be broken down into two main approaches:
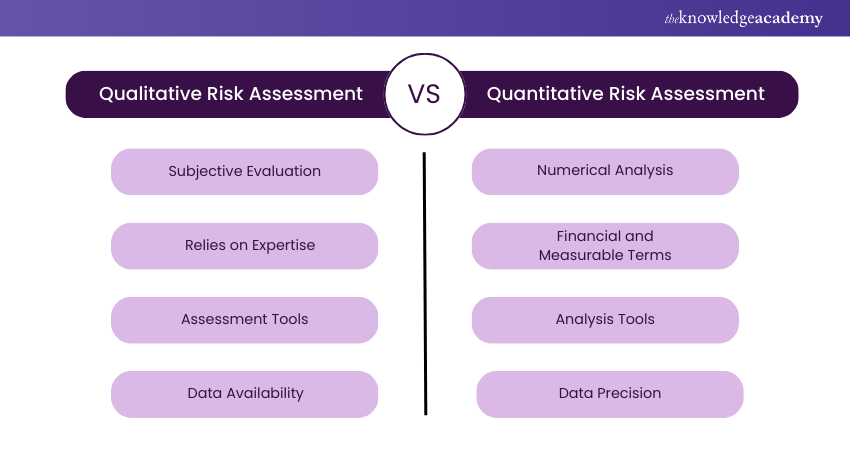
1) Qualitative Risk Assessment:
a) Involves subjective evaluation using non-numerical data.
b) Relies on expert judgment, experience, and historical information.
c) Uses tools like risk matrices and rating scales (e.g., high, medium, low).
d) Ideal when numerical data is limited or unavailable.
2) Quantitative Risk Assessment
a) Involves analysis using numerical data and statistical models.
b) Measures risks in financial or measurable terms.
c) Utilises tools like cost-benefit analysis and probability distributions.
d) Ideal for precise predictions and when detailed data is available.
3) Prioritising risks
Risks need to be prioritised according to their severity and probability of occurrence once they have been identified and analysed. Organisations should prioritise managing the most severe risks by allocating their resources accordingly, as not all risks are equally critical.
1) Criteria for Prioritisation:
a) Impact on Business Objectives:
Risks that could severely impact the organisation's goals, such as financial stability or market position, should be given higher priority.
b) Probability of Occurrence:
Risks that are more likely to occur should be prioritised over less probable risks.
c) Cost of Mitigation:
It's necessary to balance the possible advantages of risk mitigation against its expense. There are risks that the organisation may choose to accept because they are too expensive to address.
2) Prioritisation Tools:
a) Risk Heat Maps:
Visual tools that categorise risks based on their severity and probability. High-severity, high-probability risks appear in the "red" zone, indicating that they require immediate action.
b) Risk Register:
A central document listing all identified risks, along with their analysis and prioritisation. It is continuously updated as new risks arise or old ones are resolved.
4) Treating identified Risks
Once the risks have been prioritised, the next step is to determine how to treat or respond to them. Risk treatment involves developing strategies to minimise, mitigate, or eliminate the impact of the risks.
1) Common Risk Treatment Strategies:
a) Avoidance:
Involves changing the project plan or business strategy to avoid the risk entirely. For example, avoiding investing in a highly volatile market to reduce financial risk.
b) Mitigation:
Taking actions to lessen the likelihood or severity of the risk. For example, more security measures should be added to prevent data breaches.
c) Transfer:
Transferring risk to a third party through outsourcing. This lowers the organisation's direct exposure to the risk.
d) Acceptance:
In some circumstances, the expense of minimising risk may outweigh the possible benefit. In such cases, the organisation may decide to accept the risk, particularly if it has a low chance or modest repercussions.
2) Developing a Risk Treatment Plan:
A risk treatment plan outlines the specific actions that will be taken to address each recognised risk. This plan should include:
a) The chosen strategy (avoidance, mitigation, transfer, or acceptance).
b) The resources required to implement the strategy.
c) A timeline for implementing the risk treatment.
d) Responsibilities for managing the treatment plan.
5) Monitoring Risks
Risk Management is a continuous process, and monitoring is required to ensure that risk treatments work. New risks could arise throughout time, while current risks may become more severe or likely. Regular monitoring enables businesses to keep ahead of possible challenges and adapt their plans accordingly.
1) Steps for Monitoring Risks:
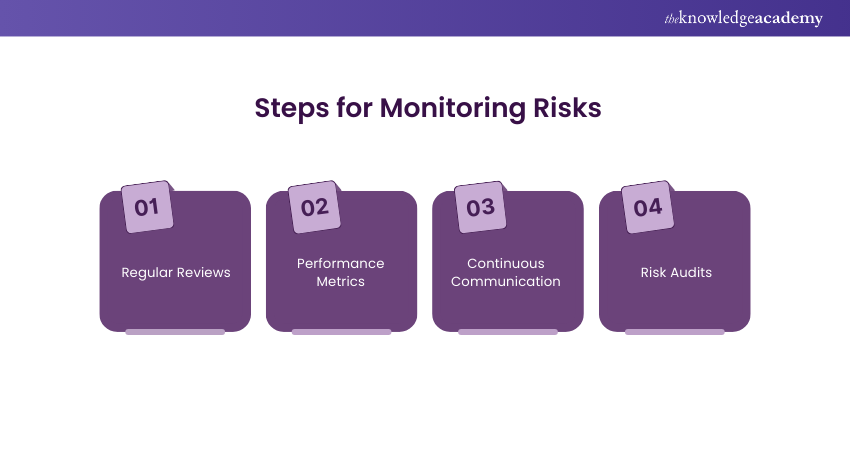
a) Regular Reviews:
Periodically reviewing the risk register and treatment plans to ensure they are up to date and relevant.
b) Performance Metrics:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are used to measure the effectiveness of risk treatments.
c) Continuous Communication:
Ensuring that stakeholders are kept informed of Risk Management activities and any changes in risk status.
d) Risk Audits:
Conduct internal or external audits to determine the effectiveness of the process of risk management and identify areas for improvement.
2) Adapting to Changes:
a) The variety and intensity of hazards may vary as the business environment changes.
b) The organisation remains flexible and adaptable to new challenges by regularly improving its Risk Management approach.
Enhance your knowledge of Risk Management with our Risk Management Green Belt Course - join now!
Conclusion
Mastering the Risk Management Process is like having a powerful toolkit to navigate through business storms. By identifying, analysing, prioritising, treating, and monitoring risks, you turn potential risks into opportunities for growth. Use these steps to steer your organisation confidently towards a future filled with success and stability!
Improve your Project Management skills with Project Management Courses - join now!
Frequently Asked Questions

The highest salary for a Risk Manager may differ according to factors such as location, experience, and the specific industry. According to Glassdoor, the highest salaries for Risk Managers can reach up to £99,000 per year.

A degree in Risk Management or a similar field is ideal for a career in Risk Management. Here are some of the best degrees to consider:
a) Bachelor’s Degree in Risk Management
b) Bachelor’s Degree in Finance or Business Administration
c) Master’s Degree in Risk Management

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Project Management Courses, including Project Risk Management Course, Risk Management Black Belt, Project Management Certification Course and Project Management Black Belt. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Risk Management Resume.
Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to Risk Management, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Project Management Course
Introduction to Project Management Course
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


