We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Organisations today must keep up with the latest digital innovations to maintain a competitive edge over counterparts. One of the frameworks that facilitates technological innovation in an IT organisation is the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL). However, the ITIL has gone through multiple evolutions over time, giving rise to the latest edition called the ITIL®4. Hence, in this blog, we will go through a few ITIL®4 Key Concepts.
Moreover, a 2020 ITSM tools survey revealed that 20% organisations were using ITIL4, while 32.5% were planning for the same. ITIL4 primarily expands the previous version of ITILV3, providing a flexible framework to help organisations for a digital transformation. Delve into ITIL®4 Key Concepts and practices to advance your understanding and implementation in digital transformation.
Table of Contents
1) An introduction to ITIL®4
2) ITIL Key Concepts
a) Creating value through services
b) The ITIL®4 Service Value System (SVS)
c) The Four Dimensions Model of Service Management
d) The ITIL®4 guiding principles
3) What are the ITIL®4 Management practices?
4) Conclusion
An introduction to ITIL®4
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) was introduced by the UK Government in 1980s. This specifically ensures that IT expenditures are allocated for necessary items and budgets are spent usefully.
The ITIL Framework is universally recognised as a vital tool for provision of IT services and the overall IT industry. Additionally, the Version ITIL4 is a lot more sophisticated compared to the earlier versions. With the passage of time, Lean, Agile, and DevOps have successfully implicated various IT and business organisations.
The two most apparent changes that manifested with ITIL 4 are the Service Value System and Service Value Chain. These approaches play a crucial role in construing the value of many factors and procedures of value creation.
Moreover, in ITIL 4, one must understand the entire business process, as detailed in the ITIL 4 Digital and IT Strategy Guide, to effectively align IT strategies with organizational goals. That process includes starting from spotting the value proposition to the elimination of non-value-adding activities. This version of ITIL is precious because it helps an organisation to understand the specifics of their surroundings. Furthermore, it allows team members to make quality choices in support of their organisation under any given circumstance.
ITIL®4 Key Concepts
Let’s delve deeper into some ITIL 4 Key Concepts that have been implemented in the latest edition of ITIL:
Creating value through service
IT is at the heart of every organisation today. It connects an organisation with its employees and clients, facilitates operations and improves efficiency. On one hand, this evolving nature allows an organisation gain access to changing features and facilitate continual improvement in its services. On the other hand, it means that IT organisations can be left behind in the race if they do not continuously adapt to the new standards.
ITIL has developed into the most widely used and accepted framework for Information Technology Service Management (ITSM) in the USA. The framework is a structured approach to ITSM that eases Risk Management for government organisations and businesses. ITIL also improves customer relationships, defines cost-effective operations, and stabilises the IT environment. The popularity of ITIL is because it allows for growth, scale, and change – three integral elements for any organisation in any industry.
The framework has been tried, tested, and implemented over the past two decades in the USA, and most government organisations currently use some form of ITIL-based Service Management.
Learn all you need to know about ITIL®4 by exploring our ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course - join today!
The ITIL®4 Service Value System (SVS)
The ITIL 4 Service Value System (SVS) is a key component of the latest ITIL edition, defining how components and activities combine to co-create value. It is an ecosystem that creates value for organisations, their customers, and stakeholders.
The SVS converts customer demand into value through a chain of activities, and its goal is to ensure continuous co-creation of value with all stakeholders. Failure to observe key elements of the system can lead to a risk of not delivering intended value. The SVS consists of five elements and is tasked with facilitating the transition from potential to final value creation through an interdependent cycle of activities. Here's how ITIL 4 SVS works:

a) Guiding principles
The ITIL 4 Guiding Principles are recommendations that facilitate flexible work for employees in the organisation, regardless of circumstances. They guide decisions and actions so that the organisation can generate the highest amount of value with effectiveness and efficiency.
b) Governance
Governance in the SVS directs and manages an organisation, aligning activities with objectives. The approach to governance varies depending on the organisation's culture and goals. Governance should be adaptable and continuously evaluate its strategy to meet changing business circumstances. Continual improvement applies to service management at all levels, including governance.
c) The Service Value Chain (SVC)
The Service Value Chain (SVC) is a flexible model at the heart of the Service Value System, that describe six key activities to create and manage products and services. The SVC offers flexibility for organisations to react to evolving stakeholder demands and complement their service management strategy.
a) It also encourages co-creation of value through the creation and ITIL change management of products and services. The ITIL Change Management aspect within the Service Value Chain (SVC) plays a pivotal role in fostering adaptability for organisations. The following are some key elements included within SVC:
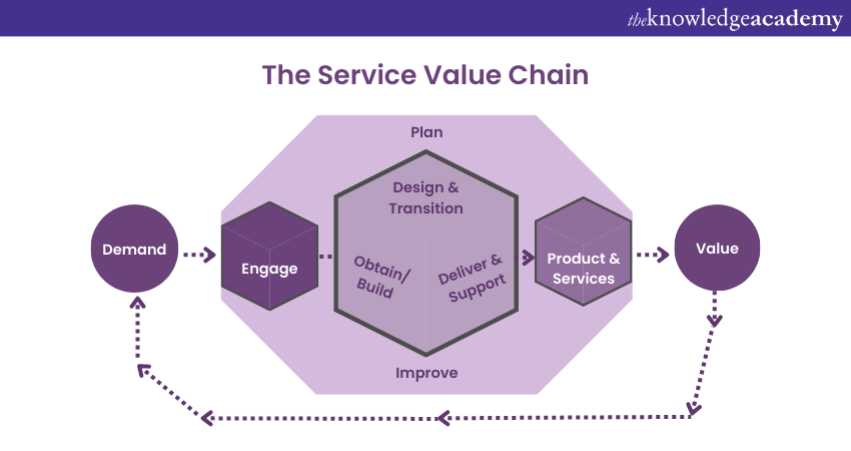
a) Practices: Practices are a set of organisational resources, including existing processes, designed to achieve organisational goals or objectives. This element of the Service Value System is one of the Key Concept in ITIL®4, representing an evolution from the processes in the previous edition. ITIL has transitioned from a limiting process-based perspective to a more holistic practice-based approach. ITIL®4 presents 34 of these practices as an upgrade from the 26 processes included in ITIL®V3. Adopting a holistic approach is required for implementing all these practices.
b) Continual improvement: Continual improvement refers to a repetitive organisational activity that is performed at all levels to facilitate continuous improvement. This repetitive process helps an organisation cater to customer demands as well as stakeholder expectations. To optimise the Service Management process of an organisation, continual improvement should be applied across all levels of service management - from governance and strategy to operations. This element of the SVS encourages collaboration, transparency and an active approach to do things better.
Improve your IT service delivery with the ITIL 4 Create, Deliver, and Support PDF. Get it now!
The Four Dimensions Model of Service Management
Another important element of the latest edition of ITIL®4 is its implementation of a holistic approach. ITIL®4 incorporates four dimensions that are essential to the successful generation of value for customers and stakeholders, providing a structure for efficient ITSM capabilities.
These four dimensions are relevant to the SVS and establish key areas that need to be emphasised to ensure high-quality product delivery according to required standards and intended value. Each dimension requires sufficient focus to facilitate effective value of the product or delivery.
By implementing these dimensions, a holistic approach to ITIL service management can be achieved, as they are applicable to the service value system in general and specific services. The four dimensions are as follows:

a) Organisations and people: An objective-oriented work culture with the appropriate quotient of competency amongst its ranks.
b) Information and technology: The resources required for efficient management of services, namely – information, knowledge and technologies.
c) Partners and suppliers: This element refers to the relationships with other organisations/businesses concerning design, delivery, deployment and continual improvement of services.
d) Value streams and processes: This element refers to how various departments in an organisation working in a coordinated manner are integral in facilitating value creation through services.
The ITIL 4 guiding principles
ITIL 4 guiding principles draw inspiration from modern IT service technologies such as Lean, Agile, and DevOps. They enable efficient integration of different practices into an overall service management approach.
a) The principles support IT professionals at every stage of the service delivery process and promote continual improvement at all levels. They are universal and can be used by anyone aiming to deliver value in the form of services. Those guiding principles are discussed in the following points:

a) Start where you are: Assess the current situation before making changes to avoid losing progress.
b) Focus on value: Deliver value to stakeholders by understanding their needs and experiences.
c) Progress iteratively with framework: Continuously improve by breaking down work into smaller iterations as well as re-evaluating and revising them.
d) Collaborate and promote visibility: Encourage transparency, collaboration, and defined responsibilities for high-quality output.
e) Think and work holistically: Connect all departments and practices to align with organisational objectives and create high-quality service.
f) Keep it simple and practical: Promote simplicity by clearly defining exceptions and asking if processes/practices contribute to value creation.
g) Optimise and automate: Maximise value by automating frequent tasks to ease workload, freeing human resources for complex tasks that create value.
Become an ITIL®4 Strategist by joining our ITIL®4 Strategist: Direct, Plan and Improve DPI Course!
What are the ITIL 4 Management practices?
The ITIL 4 comprises 34 management practices that work in the current business scenario. It considers the integrated facets of an organisation such as invention, and the promptness in advertising products.
Moreover, ITIL Service Management in ITIL 4 deals with handling IT service through techniques like DevOps, Agile, Lean, and several others. The ITIL Service Delivery Guide emphasizes that management practices denote administrative workings and create a solid base for the implementation of organizational goals. The ITIL 4 Practices deal with performing work or accomplishing an objective and can be divided into three parts. Now, let’s take a look at those three sections:
General management practices
General management practices refer to the 14 practices that support system or an entire organisation. This is because, such practices allegedly underlie the supply of all goods and services. Some of those practices are listed below:
1) Strategy management
3) Architecture management
4) Service financial management
5) Workforce and talent management
6) Continual improvement
7) Measurement and reporting
8) Risk management
9) Information security management
10) Knowledge management
11) Organisational change management
13) Relationship management
14) Supplier management
Service Management practices
Service Management practices, as the name suggests comprises 17 attributes of guaranteeing service quality for all the sectors. Those practices are newsworthy and can assist in finding answers to casual questions such as marketing, services, or products. Below are listed some of those practices:
2) Service catalogue management
3) Service design
4) Service level management
5) Availability management
6) Capacity and performance managaement
7) Service continuity management
8) Monitoring and event management
9) Service desk
10) Incident management
11) Service request management
12) Problem management
14) Change enablement
15) Service validation and testing
16) Service configuration management
Technical Management practices
The Technical Management practices have two-folded functions in common: for both manufacturing and services. The three technical management practices derived from the domain of technology management include the following:
1) Deployment management
2) Infrastructure and platform management
3) Software development and management
Don’t miss your chance to pass! Reschedule your ITIL® 4 Foundation Exam today and take the next step in your career.
Conclusion
ITIL 4 redefines IT Service Management practices and introduces new concepts such as SVS and the four Dimensions Model. Understanding these concepts is essential, and reviewing ITIL Interview Questions related to ITIL 4 can help you better grasp how to apply them effectively. These ITIL 4 Key Concepts help organisations gain a better understanding of how to achieve their service management objectives, while providing governance, stability, and clarity about their customers, products, and services. By embracing these concepts, organisations can fully realise the Benefits of IT Service Management, improving service delivery and ensuring long-term success.
Realise your dream of becoming an ITIL®4 Specialist by signing up for our ITIL®4 Specialist: High Velocity IT Training course!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are ITIL Practices, and how do they relate to Service Management?

The ITIL includes around 34 management practices that supports and guarantees service management inside an organisation. Moreover, these practices are categorised into general, service and technical domains. All of them collaboratively provide guidelines for numerous ITSM aspects.
What is the Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA
What are related courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various ITIL Certification Courses, including the ITIL®4 Foundation Course, Root Cause Analysis Course, and Certified IT Service Manager (CITSM) Course.
Our IT Service Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to ITIL, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Service Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Course
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Wed 2nd Apr 2025
Sat 5th Apr 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Wed 9th Apr 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Wed 16th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Wed 30th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Sat 10th May 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Wed 14th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Wed 21st May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Wed 4th Jun 2025
Sat 7th Jun 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Wed 11th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Wed 18th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Wed 25th Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Wed 2nd Jul 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Wed 9th Jul 2025
Sat 12th Jul 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Wed 16th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Wed 23rd Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Wed 30th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Wed 6th Aug 2025
Sat 9th Aug 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Wed 13th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Wed 20th Aug 2025
Mon 25th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Wed 3rd Sep 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Wed 10th Sep 2025
Sat 13th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Wed 17th Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Wed 24th Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Wed 1st Oct 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Wed 8th Oct 2025
Sat 11th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Wed 15th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Wed 22nd Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Wed 29th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Wed 5th Nov 2025
Sat 8th Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Wed 12th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Wed 19th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Wed 26th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Wed 3rd Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Wed 10th Dec 2025
Sat 13th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025
Wed 17th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


