We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) is a transformative enterprise software solution used by 425,000+ organisations worldwide to empower them to enhance productivity and streamline operations. Notably, SAP reported generating £26 billion in 2023 alone, highlighting its dominance in the enterprise software market. From financial management to supply chain optimisation, SAP caters to diverse levels of industry needs while integrating technologies such as AI and Cloud Computing.
In this blog, we will explore What is SAP, covering its history, key features, essential skills for professionals, core benefits, various modules, and real-world use cases that illustrate its impact on modern business. Let’s begin!
Table of Contents
1) What is SAP?
2) History of SAP
3) What SAP skills should every professional have?
4) The Benefits of SAP
5) What are the modules in SAP?
6) Conclusion
What is SAP?
SAP is a software system that helps organisations manage their operations effectively. Its modular structure allows businesses to purchase only the section of the software they need, and it can be personalised to fit the organisational needs.
SAP serves customers across a wide range of industries, including retail, finance, manufacturing, and healthcare. It has also evolved over the years to incorporate new technology such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Cloud Computing.
History of SAP
SAP has a diverse history of innovation and growth since it was founded in the early 1970s. Here are the key milestones:
1) Founding and Early Goals (1972): SAP was established in 1972 by five IBM employees in Mannheim, Germany, with the aim of providing clients seamless access to a shared corporate database for real-time interactions across various applications.
2) Introduction of R/1 (1973): SAP introduced R/1, a Financial Accounting system designed for IBM servers and Disk Operating Systems (DOS). R/1 featured a single-tier architecture, consolidating presentation, applications, and data on one platform.
3) Launch of R/2 (1979): SAP unveiled R/2, a mainframe system that revolutionised real-time data processing across domains such as accounting, manufacturing, supply chain, and Human Resources. R/2 adopted a two-tier architecture, separating presentation from applications and data, and attracted around 200 new clients.
4) Release of R/3 (1992): The release of R/3 marked a shift from mainframe computing to the client-server model, transitioning to a three-tier architecture with separate layers for presentation, applications, and data. R/3 was pivotal in propelling SAP onto the global stage.
5) Introduction of SAP NetWeaver (2004): SAP NetWeaver was introduced as the first fully interoperable, web-based, cross-application platform, capable of developing both SAP and third-party applications.
6) SAP Business Suite 7 (2009): SAP Business Suite 7 was launched worldwide, employing a service-oriented architecture to enhance business processes.
7) Launch of SAP HANA (2011): SAP introduced SAP HANA, an in-memory database platform that became a major milestone for the company, poised to replace traditional databases used in its business applications.
Master industry-leading SAP solutions and become a certified SAP professional – join our SAP Training now!
What SAP skills should every professional have?
Several companies utilise SAP for their regular business operations. But to fully utilise SAP, you must have certain skills. Some of those skills are:
1) Managing Transactions: SAP is a Financial Management System in SAP that also serves as a Data Management System. It enables organizations to access data anytime, from anywhere. Both employees and management can leverage this data for sales-related transactions.
2) Human Resource: SAP is also essential in the recruitment of employees in the company. It comprises several recruiting models, which can quickly analyse a candidate’s profile and manage both the application and recruiting process.
3) Managerial Functionality: SAP also has numerous models that can be used for CRM and other management responsibilities.
4) Finance and Accounting: The improved and new SAP module is essential for handling finance and accounting departments in an organisation. Some modules help in accounting for several transactions, budgets, etc. This allows the company to make effective decisions on their budgeting and other financial transactions.
Ready to ace your next interview? Check out our expert SAP Interview Questions and Answers to boost your confidence and performance.
The Benefits of SAP
There are several Benefits of SAP across different industries and functional areas. Listed below are a few key benefits of SAP implementation:

1) Enhanced efficiency: SAP is a system application package that enhances the performance patterns of an organisation. Essentially, it offers a central interface to handle several operations and functions like inventory, sales, accounts, and procurement of resources. It works to supplant large categories of document-intensive manual activities, minimises mistakes and redundancies, and provides instant analysis. This results in increased efficiency and quick decision-making, among other benefits.
2) Improved Visibility: SAP offers timely access to basic business information flows, which helps internal and external users to track, analyse, and control functions. This further allows businesses to monitor their finances, sales, inventories, and production in real-time.
They can avoid obstacles and adjust to evolving market conditions more effectively. It further aids in keeping items competitive and reaching market adaptability in a global environment that is rising at an alarming rate. To gain deeper insights into managing such challenges, a SAP S/4HANA Guide can provide valuable strategies for optimising business processes and enhancing market responsiveness.
3) Scalability: Its flexibility makes it well-suited for both small businesses and large MNCs. The SAP Road Map highlights the additional flexibility and extensibility of the software, enabling organizations to adapt to evolving demands and needs. This approach also allows enterprises to incorporate or exclude users, modules, and related functions without compromising the system's stability and performance.
4) Enriched Customer Experience: Another critical aspect of SAP solutions is that they allow companies to enhance customer experience. One appropriate example is the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software, which helps firms keep records of their interactions with the clients and the subsequent customer's experiences. SAP also facilitates e-commerce functionalities that allow organisations to sell products and services online. Essentially, it improves customers’ buying experience by allowing them to utilise multiple channels seamlessly.
5) Data Analytics: SAP offers solutions that help the organisation to capture, process, interpret and use data in a seamless manner. This makes it possible for organisations to gather, accommodate and process huge amounts of data from several sources. Additionally, advanced software analysis tools help companies make well-informed decisions in real-time, ensuring they maintain a competitive edge. Incorporating resources like the SAP Cheat Sheet Guide can further enhance understanding and efficiency.
6) Compliance and Security: SAP is designed to meet compliance and security requirements for various industries. The software provides features like an audit trail, access controls, and encryption. These ensure that business data is secure and compliant with regulations. It also provides tools to help businesses comply with industry-specific regulations such as GDPR and SOX.
7) Improved Collaboration: SAP provides collaboration tools that enable teams to work together efficiently. The software offers Project Management, document sharing, and task management features. This enables teams to collaborate and communicate effectively. It also allows teams to work from anywhere at any time.
8) Integration: SAP can integrate with other systems, allowing businesses to connect with suppliers, customers and other stakeholders involved in the process. For example, SAP can integrate with CRM, allowing for a streamlined and efficient customer experience. In addition, the software can also be integrated with Supply Chain Management systems, improving the organisation’s overall efficiency.
Advance your IT career with our SAP BASIS Course! Acquire essential skills in system administration and support for SAP environments.
What are the modules in SAP?
SAP is a highly versatile software with various applications designed to meet specific business needs. SAP modules are primarily divided into functional and technical categories. Let's review the different modules within SAP.
1) Functional modules
The Functional Modules in SAP offer capabilities such as human resource management, finance management, production planning, and other operational processes to support the day-to-day operations of an organisation. Let's now examine the various SAP functional modules and their purposes.
a) Human Capital Management (SAP HCM)
The Human Capital Management (SAP HCM) module facilitates the management of human resource processes, including recruitment, onboarding, performance evaluation, payroll, promotions, and more.
b) Production Planning (SAP PP)
The production planning module in SAP utilises master data to process manufacturing, sales, and distribution data, aiding in production planning and management.
c) Materials Management (SAP MM)
The SAP Material Management (SAP MM) module assists in optimising and planning materials, inventory, and warehouse capabilities.
d) Project System (SAP PS)
The Project System (SAP PS) module involves project structuring, time scheduling, budgeting, reporting, project process analysis, and cost planning to manage the lifecycle of a business project.
e) Sales and Distribution (SAP SD)
The Sales and Distribution (SAP SD) module helps manage processes such as selling, shipping, and billing within an organisation by integrating various sales transactions.
f) Plant Maintenance (SAP PM)
The Plant Management (SAP PM) module oversees the inspection, maintenance, and technical repair of products or services.
g) Financial Accounting (SAP FI)
The SAP Financial Accounting (SAP FI) module aids in analysing financial data by integrating other financial modules and components such as inventory, tax accounting, and financial statements. Using an SAP Financial Accounting Guide can provide deeper insights into optimizing these integrations for better financial management.
h) Quality Management (SAP QM)
Quality Management (SAP QM) assists organisations in managing quality production by integrating sales, procurement, production, audit management, and more.
i) Controlling (SAP CO)
The Controlling (SAP CO) module focuses on decision-making processes within an organisation to enhance financial and monetary functions.
Gain a comprehensive understanding of how Financial Accounting and SAP can co-exist by joining our SAP Financial Accounting Course!
2) Technical modules
The technical modules within SAP are focused on ensuring seamless operations within the SAP landscape. Let's review the various technical modules and their purposes.
a) SAP Basis
SAP Basis involves system administration and provides the technical foundation necessary for the smooth functioning of the SAP system.
b) SAP ABAP
SAP Advanced Business Application Programming (SAP ABAP) is a high-level programming language used for developing business applications within the SAP environment.
c) SAP NetWeaver
SAP NetWeaver facilitates real-time integration of business users with SAP software, enabling the monitoring of various processes and modules.
d)Information Systems Management (SAP IS)
Information Systems Management (SAP IS) facilitates the collection and analysis of functional modules, aiding businesses in identifying and rectifying problems.
e) Exchange Infrastructure (SAP XI)
Exchange Infrastructure is responsible for implementing cross-system processes across different versions from various vendors.
f) High-Performance Analytic Appliance (SAP HANA)
SAP HANA employs in-memory computing to store compressed data directly into RAM, instead of using relational databases on disk drives.
3) SAP Use Cases
Listed below are three situations where organisations use SAP, along with the modules that are used for each industry mentioned:
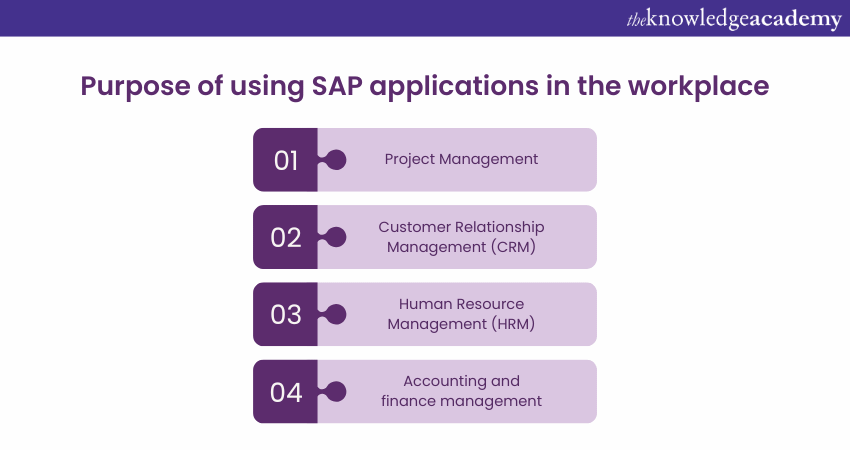
4) Financial Management
SAP's financial management software offers comprehensive solutions to enhance efficiency and compliance. Here are the key points:
a) Integration of Financial Processes
SAP’s financial management software integrates invoicing, billing, and cash flow analysis, streamlining operations and improving efficiency.
b) Spend Management Modules
Modules like SAP Ariba and SAP Fieldglass utilise generative AI and market data to increase the accuracy of cost estimates and identify errors, enhancing spend management.
c) Improved Compliance
The integration and automation capabilities of SAP’s financial tools simplify compliance with regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of errors.
d) Advanced Analytics
By leveraging advanced analytics, SAP’s financial management solutions provide deeper insights into financial data, supporting better decision-making.
5) Supply Chain Management
SAP Supply Chain Management (SAP SCM) provides robust tools for optimising logistics and manufacturing processes. Here are the key points:
a) Logistics and Manufacturing Planning
Companies use SAP SCM to effectively plan logistics and manufacturing operations, ensuring smooth and efficient workflows.
b) Lifecycle Prediction
The module helps predict the lifecycles of various pieces of equipment, allowing for better maintenance planning and resource allocation.
c) Enhanced Visibility
SAP SCM offers enhanced visibility into the supply chain, which enables businesses to monitor and manage their operations in real time.
d) Data-Driven Decision Making
By leveraging advanced analytics, SAP SCM supports data-driven decision-making, helping companies respond proactively to changes and disruptions.
6) Customer Experience and CRM
SAP’s customer experiences modules provide powerful tools for enhancing customer relationships by unifying sales, marketing, and service data. Here are the key points:
a) Unified Data for Improved Relationships
SAP’s customer experiences modules allow companies to unify their sales, marketing, and service data, leading to more cohesive and effective customer relationship management.
b) Personalised Engagement Models
For example, an e-commerce company can use SAP to deliver a unique engagement model based on existing customer data, tailoring interactions to individual preferences and behaviours.
c) Enhanced User Experience
Companies can also improve the user experience of their business by leveraging customer feedback collected through SAP’s modules, ensuring that services and products meet customer expectations.
d) Comprehensive Customer Insights
By integrating various data sources, SAP provides comprehensive insights into customer behaviour, enabling more informed decision-making and strategic planning.
7) Talent Management and HCM
SAP offers robust tools for Talent Management and Human Capital Management (HCM) through solutions like SAP SuccessFactors. Here are the key points:
a) Workforce Planning and Management
Tools such as SAP SuccessFactors are used to plan and manage workforce tasks, ensuring that companies can effectively allocate resources and streamline operations.
b) Talent Discovery
The software helps companies discover new talent, enhancing their ability to recruit and retain skilled employees.
c) Understanding Employee Motivation
Companies deploy SAP SuccessFactors to better understand what motivates employees, allowing them to implement strategies to improve efficiency and job satisfaction.
d) Leveraging Payroll and Recruiting Data
By leveraging payroll and recruiting data, companies can strategically plan for future growth or changing workforce needs, ensuring they are prepared for evolving business demands.
e) Strategic Workforce Planning
The suite supports Strategic Workforce Planning, helping companies align their human resources with long-term business goals and objectives.
8) Contracts and Procurements
SAP software offers powerful tools for streamlining contracts and procurement processes. Here are the key points:
a) Streamlined Procurement Process
Using SAP software, businesses can streamline the procurement process through a single, unified mechanism, reducing complexity and improving efficiency.
b) Centralised Collaboration Hub
The software facilitates collaboration between suppliers and buyers in a centralised hub, enhancing communication and coordination.
c) Improved Supplier Relationships
By centralising procurement activities, SAP helps businesses build stronger relationships with suppliers, ensuring better terms and more reliable supply chains.
d) Enhanced Transparency
SAP provides enhanced transparency in procurement processes, allowing businesses to track and manage contracts and orders more effectively.
Need expert insights on SAP Cloud Platform? Download the SAP Cloud Platform Integration PDF today and streamline your cloud integration process effectively!
Cloud Solutions
SAP provides a variety of cloud solutions that offer flexibility and advanced capabilities for businesses. Here are the key points:
a) Range of Cloud Options
SAP customers have a range of options for utilising cloud computing in their operations, allowing for tailored solutions that meet specific business needs.
b) Remote Logistics Tracking
Companies can track logistics remotely using sensors connected to the Internet of Things (IoT), providing visibility in real-time and control over supply chain activities.
c) Advanced Predictive Analysis
By incorporating Machine Learning and AI, SAP cloud solutions enable advanced Predictive Analysis, helping businesses forecast trends and make data-driven decisions.
d) Automation Capabilities
SAP’s cloud solutions also support the automation of various processes, improving efficiency and reducing the potential for human error.
Transform your HR capabilities with SAP SuccessFactors Training! Gain insights into effective employee management and recruitment strategies.
Conclusion
We hope this blog has illuminated the depths of "What is SAP" and showcased its transformative impact on modern business landscapes. SAP's versatility is evident across diverse use cases, from optimising operations to fostering innovation. Understanding SAP's role is not just beneficial but essential for driving sustained success and growth. For those preparing for an SAP-related role, reviewing resources on SAP Interview Questions can help you gain a deeper understanding of how to apply SAP concepts effectively in real-world scenarios.
Attain in-depth knowledge of how SAP helps in managing supply chain systems with SAP Supply Chain Management Training. Join now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is SAP a good career?

Yes, SAP is a great career choice. With high demand for skilled professionals, competitive salaries, and global opportunities, it offers significant growth potential. Moreover, the constant evolution of SAP technologies ensures continuous learning and diverse career paths across various industries.
Is Sap Easy for Beginners?

No, SAP is not typically easy for beginners. Due to its vast complexity and the required specialised knowledge, it can be challenging to master. However, with dedicated training and hands-on experience, beginners can gradually develop the skills to navigate and use SAP effectively.
What Are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by the Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What Is the Knowledge Pass, and How Does It Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What Are Related Courses and Blogs Provided by the Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various SAP Courses, including SAP Financial Accounting, SAP Cloud Platform, and SAP Business ByDesign. These courses cater to different skill levels and provide comprehensive insights into the SAP Financial Management System.
Our IT Infrastructure & Networking Blogs cover a range of topics, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Networking skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 SAP Finance and Controlling FICO Training
SAP Finance and Controlling FICO Training
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


