We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

A Cash Budget is your financial roadmap, guiding and driving your business through the unpredictable path of cash flow management. More than mere numbers, it’s your foolproof strategy to ensure that every pound works its magic even amidst the storm of economic uncertainties. This blog explores the art of crafting the perfect Cash Budget that will help you battle financial challenges and seize new business opportunities!
Table of Contents
1) What is Cash Budget?
2) Importance of Cash Budgets
3) How Does a Cash Budget Work?
4) How to Create a Cash Budget?
5) Best Practices for Cash Budgeting
6) Examples of Cash Budgets
7) Challenges in Cash Budgeting
8) Conclusion
What is Cash Budget?
A Cash Budget estimates a business's cash flows over a specific period, such as a weekly, monthly, quarterly, or annual budget. It is used to assess whether the entity has sufficient cash to continue operating over the given time frame. The Cash Budget provides a company with insight into its cash needs (and surplus) and helps determine an efficient cash allocation.
Importance of Cash Budgets
Cash Budgets serve several purposes for finance teams. For most organisations, cash is a vital component of daily operations. Even those business models that are not cash-intensive can benefit greatly from Cash Budgeting practices.
1) Useful Insights: Cash Budgets are beneficial because they can highlight and provide helpful insight into potential cash deficits. This enables business leaders to plan accordingly and adjust costs, so cash balances don’t run too low.
2) Effective Use of Capital: Similarly, cash projections can identify periods when excess cash balances are generated, helping financial planners effectively use working capital.
3) Regulating Expenses: Another useful byproduct of Cash Budgets is that they help expense regulation by identifying periods when expenses run higher than others.
This enables financial analysts to review and explore ways to reduce expenses. They can also use Cash Budgets to develop plans to spread the burden of the costs out over a longer period.
4) Sources and Usage of Cash: Because Cash Budgets are designed using receipts for income and expenses, they create a valuable map of cash sources and uses.
These sources and uses can be utilised to create efficiencies in processes.
For example, suppose revenue is high during the same period when cash collections are low. In this case, the cbudget alerts business leaders to better address collection cycles and manage receivables.
5) Adhering to a Financial Plan: Creating a Cash Budget reinforces the principles of adhering to a financial plan. Highlighting cash sources and uses and identifying potential times when cash balances might run low steers the organisation toward more fiscally responsible practices.
Looking for guidance regarding sustaining your business’ financial stability? Sign up for our Cash Cycle Management Training now!
How Does a Cash Budget Work?
Companies leverage sales and production forecasts to create a Cash Budget and assumptions about necessary spending and accounts receivable collections. A Cash Budget is essential for assessing whether a company will have enough cash to continue operations. If a company lacks liquidity, it must raise capital by issuing stock or taking on more debt.
A cash roll-forward computes the cash inflows and outflows for a month and uses the ending balance as the beginning balance for the following month. This process allows the company to forecast cash needs throughout the year and adjust the cash balances for all future months by changing the roll-forward.
How to Create a Cash Budget?
Now that you've learned about the critical role of Cash Budgets in financial health let's move on to the practical steps involved in creating one. Before starting a Cash Budget, you should remember that it differs from an overall financial budget in that it's strictly concerned with cash receipts and outflows. Here are the essential steps to create a Cash Budget
1) Determine the Starting Balance
First, determine the starting balance that will be used to roll the projected cash balance. If the Cash Budget is for one quarter, the starting balance must equal the previous quarter's ending balance. This works for any given period. Always tie the beginning cash balance to a source, such as a bank statement.
2) Define the Budgeting Period
Cash Budgets can be built on a weekly, monthly, quarterly, and annual basis. If the organisation is cash-intensive, the budget can even be made daily. It would help if you chose an appropriate timeframe to manage daily cash balances while providing enough future insight to detect any potential issues.
3) List All Cash Inflows and Outflows
You must identify every source and cash usage over time and group them in an itemised list. Cash inflows are positive, while cash outflows are negative. Positive cash inflows can include loans, revenue from sales, and investments. Conversely, cash outflows include expenses such as utilities, payroll, rent, and inventory purchases.
4) Calculate Net Cash Flow Against the Starting Balance
Add all the sources of cash to the starting cash balance for the period and then reduce it by the expense amount to determine your net cash position.
5) Address Deficits and Surpluses with a Strategic Plan
After rolling over your starting balance for the period, you will see the cash surpluses or deficits. Analyse the factors contributing to these balances. If the budget shows a deficit, explore options to reduce expenses or boost cash receipts. Consider how the extra cash can support the organisation’s financial KPIs if there's a surplus.
Gain a deeper understanding of the cash flow system for business growth in our Cash Flow Training – Register now!
Best Practices for Cash Budgeting
Best practices in Cash Budgeting are strategic approaches adopted to emphasise efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability in your business. They involve creating budgets based on conservative estimates and realistic assumptions. The following best practices will help you monitor your cash flow and financial stability.
1) Regular Monitoring and Updates
Periodic monitoring of cash flows is essential. Comparing the budget to actuals periodically will help integrate variance analysis into cash reporting practices. It can highlight opportunities for
a) Optimising cash flow
b) Identifying spending patterns
c) Identifying growth limitations within your business
Updating the budget regularly ensures it remains aligned with the business's actual financial trajectory. This practice allows for timely updates, ensuring the budget stays realistic and adaptable.
2) Use Conservative Estimates
Adopting conservative assumptions when estimating revenues and forecasting expenses can help mitigate unexpected financial challenges. It’s essential to be cautious, ensuring the budget isn't overtly reliant on optimistic projections.
3) Plan for Unexpected Events
Setting aside emergency funds within the budget is a powerful safety net during unforeseen circumstances. A contingency plan enables the business to respond promptly and swiftly to unexpected events, preventing disruptions in operations and maintaining cash flow stability.
4) Utilise Financial Tools
Using advanced financial tools and software streamlines the Cash Budgeting process. These tools perform functions such as:
a) Automate calculations
b) Generate real-time reports
c) Provide insightful analyses
Technology elevates the efficiency, accuracy, and overall effectiveness of budgeting efforts.
Examples of Cash Budgets
Here’s an example of a Cash Budget for a small business:
ABC Enterprises - Cash Budget for [Month], [Year]
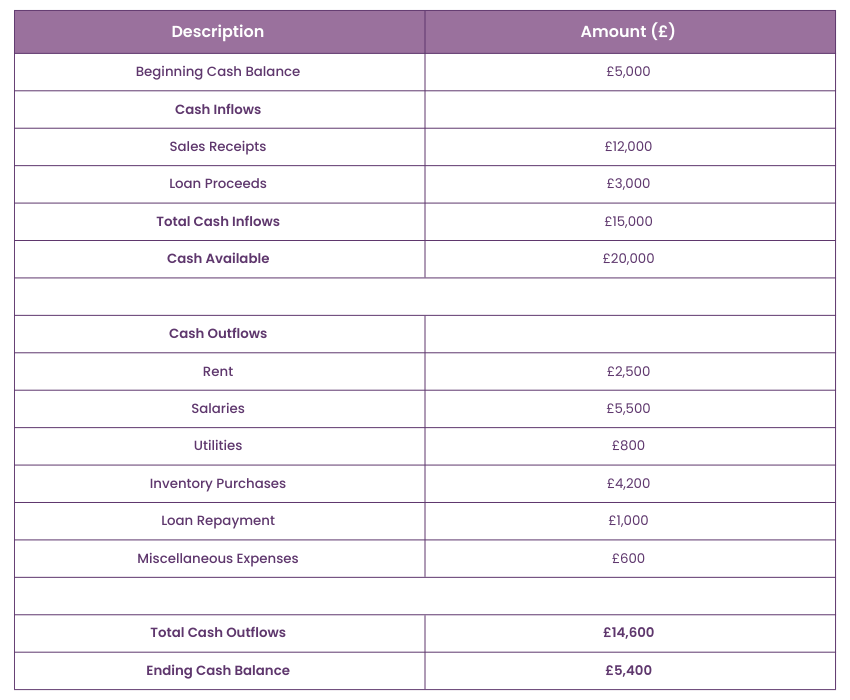
In this example, ABC enterprises begins with £5,000 in cash. After accounting for all inflows and outflows, they end the month with £5,400, which indicates a slight increase in cash reserves.
Learn about effective Asset Management in our comprehensive Fixed Assets Accounting and Management Course - Sign up now!
Challenges in Cash Budgeting
Navigating the path of Cash Budgeting can expose businesses to various challenges. Overcoming these challenges requires implementing best practices to ensure the Cash Budget remains resilient amidst organisational complexities. Let’s explore some of these challenges.
1) Economic Uncertainty
Cash Budgeting can become complex through unpredictable economic factors. A business’s profitability is significantly impacted by factors such as:
a) Inflation
b) Fluctuating interest rates
c) Currency value changes
Constant vigilance and strategic planning will enable the Cash Budget to adapt to such economic uncertainties.
2) Inaccurate Sales Forecasts
The accuracy of sales forecasts is one of the biggest Cash Budget problems. Overestimating sales can result in overcommitting of resources, while underestimating can lead to missed opportunities. To ensure perfect alignment of Cash Budget with the revenue streams, you need to balance these projections with:
a) Consumer behaviour
b) Market demand
c) Industry trends
3) Overlooked Unexpected Expenses
Cash Budgets often fumble due to unforeseen expenses. While regular operating costs are accounted for, financial resources can be strained due to unexpected events such as:
a) Legal issues
b) Equipment breakdowns
c) Sudden regulatory changes
Failing to anticipate these unforeseen expenses can create significant gaps in the cash flow, which will disrupt the budgeting plan.
4) Managing Cash Flow
Cash flow gaps occur when cash outflows exceed inflows which pose a significant challenge in Cash Budgeting. These gaps can lead to:
a) Strained supplier relationships
b) Missed payments
c) abysmal day-to-day operations
Managing these gaps necessitates proactive measures like:
a) Negotiating extended payment terms
b) Securing short-term financing
c) Maintaining a cash reserve for emergencies
Addressing these gaps ensures the business stays financially resilient despite periodic imbalances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a Cash Budget is an essential financial tool that helps businesses and companies manage their cash flow effectively. Forecasting income and expenses ensures that your business meets its obligations, and growth plans and avoids cash shortfalls. It's the key to financial stability and success.
Elevate your Financial Management skills with our Inventory Accounting and Costing Course - Register now!
Frequently Asked Questions

The three objectives of Cash Budget are:
a) Ensuring liquidity
b) Minimising idle cash
c) Planning for shortfalls and surpluses

The techniques of preparing a Cash Budget include:
a) Receipt and payment method.
b) Adjusted profit and Loss Method (or cash flow) method.
c) Balance sheet method.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Accounting Courses Courses, including the Accounting Course and the Cash Cycle Management Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is Wealth Management.
Our Accounting and Finance Blogs cover a range of topics related to Cash Budget, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cash Budget skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Accounting and Finance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Cash Cycle Management Training
Cash Cycle Management Training
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 21st Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 6th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 26th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


