We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Have you ever wondered how a three-dimensional world transforms into a flat masterpiece in your hands? That's where our story begins! What is Cartography? It isn’t just about drawing lines on paper – it’s about capturing Earth’s grand waltz and freezing it in time. It's where mathematics meets artistry, where science holds hands with creativity, and where every line tells a story of human exploration.
In this blog, we’ll uncover What is Cartography and how it has evolved. From key map design elements to different types of maps, you'll discover how this craft has shaped our understanding of the world. Ready to explore the art behind every map? Let’s navigate this fascinating world of mapmaking!
Table of Contents
1) What is Cartography?
2) What Does a Cartographer Do?
3) Different Types of Maps and Cartographic Representations
4) Key Elements of Cartographic Design
5) Requirements to Become a Cartographer
6) The Connection Between Geography and Cartography
7) Conclusion
What is Cartography?
Cartography is the practice of designing, creating, and interpreting maps. It merges geography, artistry, and technology to visually represent spatial information. While traditional Cartography centred on physical and printed maps, modern methods now use digital tools and interactive maps for more dynamic visualisation.
Maps have evolved from simple cave drawings to advanced digital renderings that provide real-time data on locations, weather, and traffic. Beyond just depicting geographic features, Cartography involves the careful arrangement of elements to effectively communicate spatial information.
What Does a Cartographer Do?
A Cartographer is a professional who specialises in creating maps, blending science and art to visually represent geographic data. They use both traditional methods and modern tools, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), to develop maps for various purposes. These include topographic maps that show physical features and thematic maps that illustrate data like climate patterns.
Cartographers gather and analyse data from sources like satellite imagery, aerial photos, and surveys to craft accurate and informative maps. Their work requires attention to detail, precision, and a strong grasp of spatial relationships. They must carefully select scale, projections, and symbols to ensure the map effectively communicates its intended information.
Master animation techniques to create visually stunning designs with our Animation Course – join now!
Different Types of Maps and Cartographic Representations
Maps come in all shapes and sizes, each designed to tell a unique story about the world. Here’s a look at the different types of maps and cartographic representations and how they help us understand the world:
1) Thematic Maps
a) Focus on specific themes like population, climate, or economic activity
b) Used to display trends and patterns in various data sets
c) Great for comparing data across different regions
2) Nautical and Aeronautical Charts
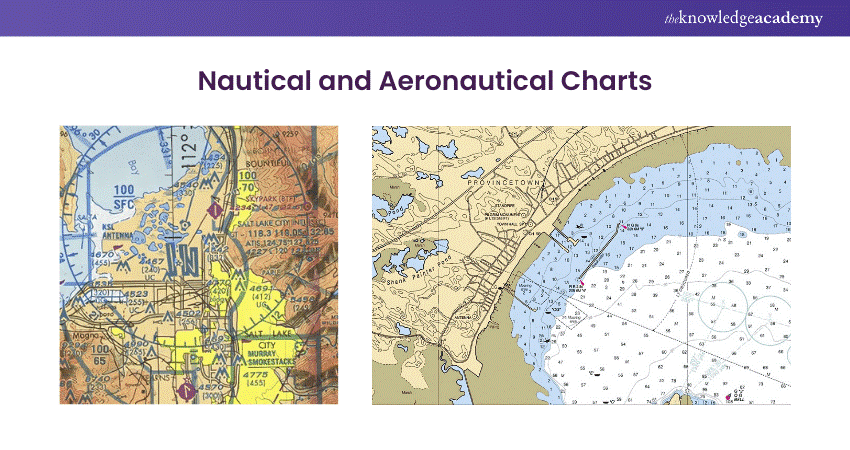
a) Provide navigation information for sailors and pilots
b) Show sea depths, coastal features, and navigational hazards for water routes
c) Aeronautical charts display airways, airports, and airspace data for pilots
3) Topographic Maps
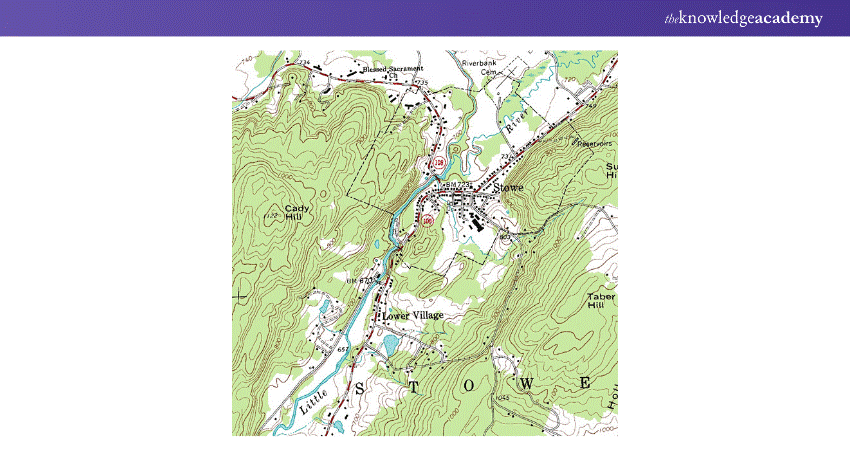
a) Depict terrain and landforms using contour lines to show elevation
b) Essential for activities like hiking, construction, and geological surveys
c) Offer a detailed, 3D-like view of landscapes
4) Digital and Interactive Maps
a) Interactive tools that allow real-time navigation (e.g., Google Maps)
b) Provide features like Zoom, live traffic updates, and directions
c) Useful for everyday navigation and advanced Geographic Analysis
5) Geospatial Data Visualisation
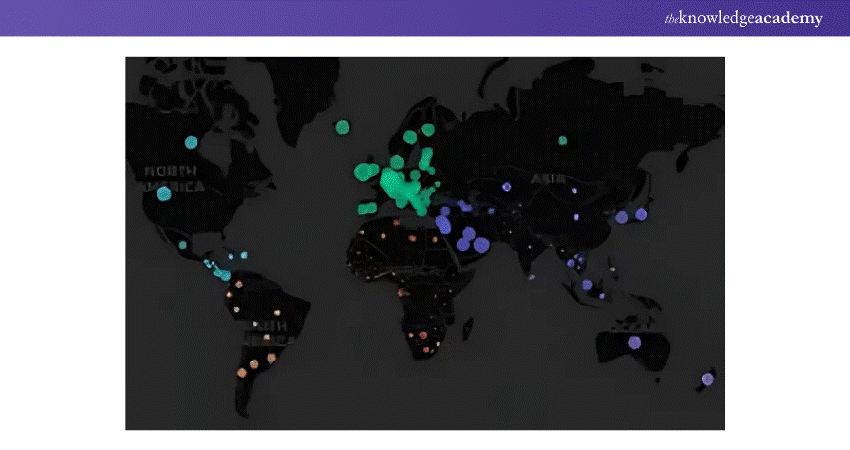
a) Combines large datasets with geography for dynamic mapping
b) Used in urban planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster response
c) Helps in visualising complex spatial trends and relationships
6) Political Maps
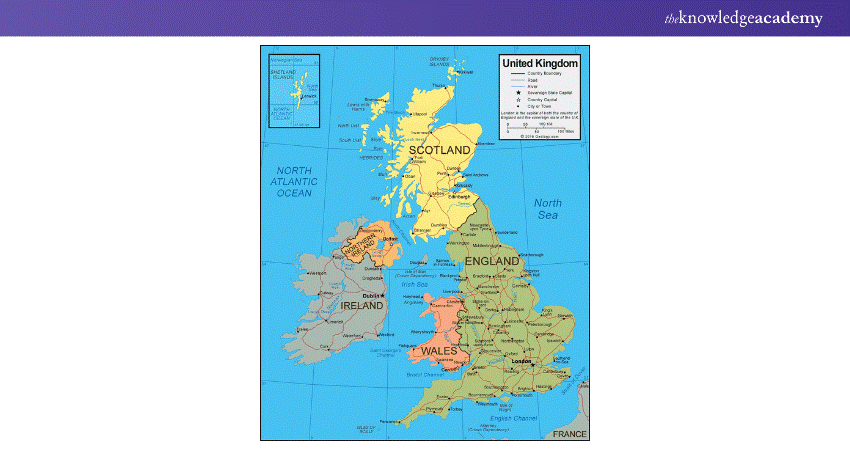
a) Display country borders, cities, and important political divisions
b) Commonly used to understand global political relationships and geography
c) Helpful for studying the boundaries between nations and regions
7) Physical Maps
a) Showcase natural features such as mountains, rivers, and deserts
b) Use colours and shading to represent different elevations and terrain types
c) Focus on the Earth’s physical landscape, which is ideal for geography studies
8) Choropleth Maps
a) A type of thematic map that uses colour gradients to represent data
b) Often used to display demographic information, like population density or income
c) Provides an easy way to compare data visually across regions
Explore CorelDRAW tools and transform your ideas into eye-catching, professional-grade graphic designs with our CorelDRAW Training – sign up now!
Key Elements of Cartographic Design
Cartographic design involves creating maps that effectively communicate spatial information. Here are the key elements of cartographic design:
1) Visual Hierarchy: This refers to the arrangement of elements so that important information stands out. It’s achieved by varying the size, colour, and position of map features to highlight key details.
2) Balance: A well-balanced map ensures that all elements (like the title, legend, and data) are evenly distributed, preventing any section from feeling too crowded or too empty.
3) Typography: Choosing the right font size, style, and placement of text is essential for readability and aesthetics. Labels for different features should be distinct yet unobtrusive.
4) Colour: The use of colour helps in distinguishing different types of information on a map, enhancing readability and visual appeal. It's crucial to select a colour scheme that is both informative and accessible, including considerations for colour blindness.
5) Scale: Maps should have an appropriate scale bar that reflects the distance between features. This helps users understand the relationship between real-world distances and the map’s dimensions.
6) Legend: The legend is essential for interpreting symbols, colours, and other representations on a map. It must be clear and concise.
7) Symbology: Symbols used for different geographic features need to be consistent and easily recognisable. For example, rivers are typically shown with lines, while cities might be represented with dots.
8) Clarity: The map should avoid clutter and maintain simplicity so that the data can be interpreted quickly and easily. Overcomplicating the design reduces the effectiveness of communication.
9) Projection: The choice of map projection (how the 3D surface of the Earth is translated onto a 2D map) is important as it affects the accuracy of distances, shapes, and areas on the map.
Transform your imagination into stunning animations with our comprehensive 2D Animation Course – join now!
Requirements to Become a Cartographer
Let’s explore the essential skills, education, and experience needed to master the art and science of mapmaking:
Educational Background
a) Bachelor’s Degree: A degree in geography, Cartography, geomatics, geographic information systems (GIS), or a related field is typically required. Courses in physical geography, mapmaking, and Spatial Analysis are helpful.
b) Advanced Degrees: Some Cartographers pursue a master's degree in Cartography, GIS, or remote sensing for higher-level roles or specialised areas.
Relevant Work Experience
a) Internships or Apprenticeships: Practical experience through internships or entry-level positions in GIS or Cartography can provide essential hands-on training.
b) On-the-job Training: Many Cartographers gain advanced skills through job-specific training and working on a variety of mapping projects.
Essential Skills
a) Proficiency in GIS Software: Strong knowledge of GIS tools like ArcGIS or QGIS is essential for modern Cartographers to create, analyse, and manipulate spatial data.
b) Remote Sensing Knowledge: Familiarity with remote sensing technologies (like satellite imagery) and photogrammetry is beneficial for creating detailed maps.
c) Data Analysis: Cartographers should be skilled in interpreting data, analysing patterns, and visualising information effectively through maps.
d) Cartographic Design: Understanding the principles of cartographic design, such as visual hierarchy, balance, and symbolisation, is crucial for producing clear and functional maps.
e) Attention to Detail: Accuracy is essential, as small errors can have a major impact on the final map's usability and reliability.
f) Problem-solving: Cartographers often need to solve complex spatial problems, requiring logical thinking and creativity.
g) Communication Skills: The ability to clearly convey geographic data and findings to non-expert audiences is important in many Cartography roles.
Certification Requirements
a) Certification: Although not always required, certification in GIS or Cartography can enhance credibility and job prospects.
Licensing (Optional)
a) Some Cartographers may need a surveyor's license.
b) Required exams include Fundamentals of Surveying (FS), Principles and Practice of Surveying (PS) and Region-specific exams.
Transform your artistic abilities with our engaging Drawing Course – join now!
The Connection Between Geography and Cartography
Cartography and geography are deeply intertwined. While geography is the study of places, spaces, and environments, Cartography provides the tools to represent these concepts visually.
Cartographers use geographic theories and data to create maps that reflect the Earth’s physical and cultural landscapes. The maps produced by Cartographers are essential tools for geographers, helping them analyse spatial relationships and explore patterns across different scales.
Turn your designs into powerful motion graphics with the Motion Graphics Course – join now!
Conclusion
In essence, What is Cartography, if not a beautiful fusion of art and science? It transforms complex data into accessible, visually stunning maps that guide and inform us. Next time you use a map, remember the intricate craftsmanship behind it, making our world more navigable and understandable.
Transform your creative potential through our Animation and Design Training for professionals!
Frequently Asked Questions

GPS is used in Cartography to collect accurate geographic data, pinpoint locations, and create precise maps. It enhances map accuracy, aids in navigation, and supports real-time data integration for digital maps.

The theory of Cartography focuses on the principles and methods of representing geographic data visually. It involves understanding spatial relationships, scale, projection, and design to create accurate and effective maps.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable . Course Bundles of TKA

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Animation and Design Training, including Motion Graphics Course, Animation Course, Drawing Course and Digital Painting Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Motion Graphics.
Our Office Applications Blogs cover a range of topics related to Cartography, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Animation and Design skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Office Applications Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Motion Graphics Course
Motion Graphics Course
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


