We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In the modern business landscape, operational inefficiencies and waste cost organisations millions each year. This is where Lean Six Sigma proves invaluable. But what is Lean Six Sigma? Lean Six Sigma, a framework combining Lean’s waste reduction and Six Sigma’s quality improvement, addresses these challenges by streamlining operations and eliminating defects.
Research from the American Society for Quality (ASQ) highlights that organisations adopting Lean Six Sigma have achieved up to a 20% improvement in process efficiency and 13% in cost savings.
In this blog, we will explore What is Lean Six Sigma, how it originated, its core principles, essential phases, and widespread benefits. Besides, we will also discuss into the detailed overview of the various certification levels associated with Lean Six Sigma.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Lean Six Sigma
2) History of Lean Six Sigma
3) Core Principles of Lean Six Sigma
4) How to Apply Lean Six Sigma in Your Organisation?
5) Lean Six Sigma Levels
6) Benefits of Lean Six Sigma Methodology
7) Conclusion
Understanding What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma refers to the methodologies that combine the principles of Lean and Six Sigma to increase the efficiency of business processes, reduce waste, and improve quality. It leverages the benefits of eliminating waste and maximising activity flow with structured frameworks to deliver quality and high customer satisfaction.
It uses structured frameworks such as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control) and DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyse, Design, Verify) to improve processes and design. These frameworks help guide teams in identifying the real cause of problems and implementing efficient solutions to ensure sustainable improvement over time.
Furthermore, by focusing on data-driven decision-making, continuous process improvement, and customer-oriented thinking, Lean Six Sigma methods can help firms streamline operations, and productivity, and ensure sustainable business growth.
History of Lean Six Sigma
The history of Lean Six Sigma is a fascinating journey that combines two powerful methodologies aimed at improving processes and enhancing quality. Below are key points that outline its evolution and significance:
1) Origins of Six Sigma: The Lean Six Sigma methodology originated in the late 20th century when Motorola developed the Six Sigma approach in the 1980s. This initiative aimed to enhance manufacturing processes and significantly reduce defects, setting a foundation for quality improvement.
2) Development of Lean Principles: Lean principles were refined and popularised by Toyota throughout the 20th century, particularly through the Toyota Production System. This system emphasised waste reduction and operational efficiency, which became crucial for competitive advantage in manufacturing.
3) Fusion into Lean Six Sigma: In the 1990s, Lean and Six Sigma methodologies merged to form Lean Six Sigma. This combination integrated the data-driven focus of Six Sigma with Lean's emphasis on eliminating waste, creating a comprehensive approach to process improvement.
4) Adoption by Major Corporations: General Electric, under the leadership of Jack Welch in the 1990s, extensively adopted Six Sigma to enhance quality and efficiency. This corporate endorsement helped popularise Lean Six Sigma as a combined methodology across various sectors.
5) Ongoing Evolution: The methodology continues to evolve with ongoing refinements and adaptations. Organisations are increasingly tailoring Lean Six Sigma to meet the dynamic needs of modern business environments, striving for operational excellence and sustainable growth.
Core Principles of Lean Six Sigma
By adhering to the foundational principles of Lean Six Sigma, organisations can achieve streamlined processes, reduced waste, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Let’s delve into the crucial Lean Six Sigma Principles:
1) Focus on the Customer
A strong commitment to meeting and understanding customer needs and expectations serves as the base of Lean Six Sigma. By prioritising customer satisfaction, organisations can position their processes and initiatives to deliver great value and improve the overall customer experience.
2) Measure the Value Stream and Find Your Problem
Lean Six Sigma relies on an approach to process exhaustive improvement, which entails measuring every aspect of the value stream. An organisation can, therefore, identify inefficiency, waste, and areas that may require improvement from every activity measure with great authority within the process.
3) Remove Waste to Create a Flow
The core idea of Lean Six Sigma is to eliminate waste to make the process smoother, valuable, and uninterrupted. By eliminating bottlenecks, delays, and steps, businesses can improve their efficiency, productivity, and clients’ satisfaction.
4) Eliminate Variations
Process variation can cause inconsistency, defects, and waste accumulation. Reducing variation is among the key approaches of Lean Six Sigma, which focuses on creating stable and well-controlled processes that bring predictable and reliable results.
5) Undertake Improvements in a Systematic Process
Lean Six Sigma systematically drives process improvement by streamlining methodologies like the DMAIC model. It ensures that methodical changes are thoroughly data-driven and align with the business goals. Thus, organisations can produce sustainable outcomes and continuous improvement.
6) Equip People in Processes
Lean Six Sigma addresses the importance of training, empowerment, and organisational engagement at hierarchy levels. Organisations can harness the expertise and creativity of their workforce towards innovation and improvement if they inculcate a culture of continuous learning and participation.
7) Understand the Real Workflow
Lean Six Sigma enables organisations to perceive their operational workflow and processes at a profound level by transcending beyond reductant surface appearances. Scrutinising helps to discover hidden opportunities, addresses the root causes of the issues, and leverages informed decisions as catalysts to drive substantial change and enhancement.
Streamline your process improvement techniques with our Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Course - register today!
How to Apply Lean Six Sigma in Your Organisation?
The Lean Six Sigma methodology primarily comprises five critical phases. Each phase is designed to guide organisations toward streamlined operations through targeted business improvements.
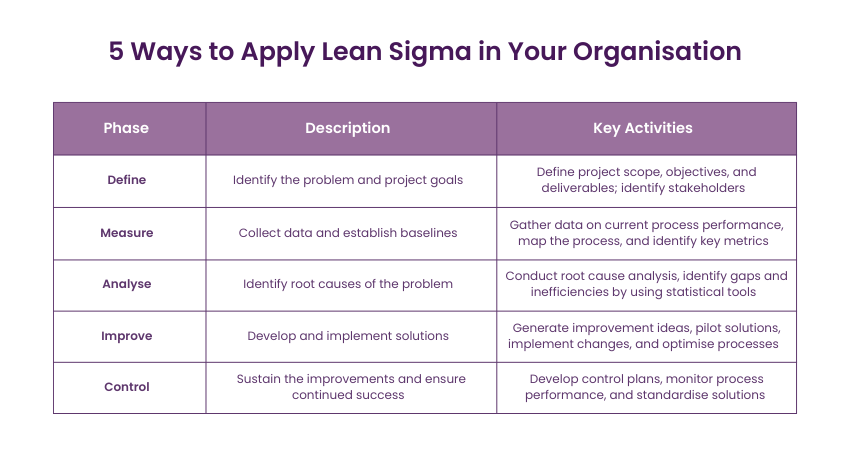
1) Define
To start with, you must first clearly define the project goals and the scope of the improvement initiatives. Some of the key activities within this step include identifying the project’s purpose, stakeholders, and deliverables and clearly defining the customer’s requirements and expectations. A clearly defined problem and the project's desired outcomes can help connect with the project along with the strategic purposes of the organisation.
2) Measure
The ‘Measure’ phase involves data collection and assessment regarding the current process state. It includes identifying relevant metrics, developing measurement systems, and collecting data that describes performance in a quantified manner. This measurement helps set a clear baseline, provide an objective with a clear understanding of process capability, and identify improvement areas.
3) Analyse
In the ‘Analysis’ stage, the collected data is analysed deeply, with a strong focus on the root causes of inefficiencies and defects arising from the operation. Teams analyse large datasets using various statistical tools and methods to identify patterns, trends, and correlations that may reveal underlying issues with process performance.
4) Improve
The ‘Improve’ phrase primarily shifts the focus to resolving the identified issues and efficiently meeting process improvement goals. This often involves generating and evaluating potential solutions, choosing the best, and implementing modifications.
5) Control
The ‘Control’ is the final phase of the Lean Six Sigma implementation that ensures the improvements achieved are sustainable over time. This is achieved by developing control plans, implementing continuous performance measurements, and setting up monitoring systems to track process performance.
These measures allow the organisation to set an easy standardisation of improvements, assess quick detection, and attain resolution of new problems, as well as lasting benefits from the Lean Six Sigma efforts.
Master your problem-solving skills with our Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Upgrade Course - register today!
Lean Six Sigma Levels
The Lean Six Sigma methodology consists of a skill level progression, each tailored to different degrees of proficiency and responsibility in improving the process. Here are six levels of Six Sigma:
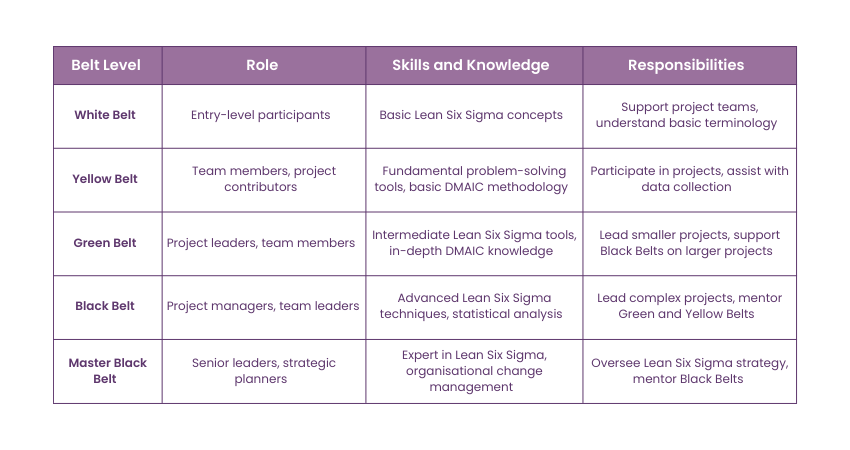
1) Lean Six Sigma White Belt
This foundational awareness level covers the fundamental principles of Lean Six Sigma. These include process improvements, focus on waste removal and the customer’s goals. Such participants typically undergo support work with more experienced practitioners, working on projects by delivering valuable contributions and assistance.
2) Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt
This level provides deeper coverage of tools and concepts compared to the White Belt level. The training at this level covers topics such as process mapping, data collection, and fundamental statistical analysis. Yellow Belts are often front-line employees who actively contribute to improving projects and collaborate with Green or Black Belts leaders to implement the necessary improvements.
3) Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
This is the capability level where a practitioner receives more comprehensive training in Lean Six Sigma methodologies. These include statistical analysis and Project Management. Green Belts run improvement projects independently, ranging from defining the project scope to implementing viable solutions. They normally balance this role with their usual job responsibilities by dedicating part of their time to process improvement.
4) Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
The Black Belt is an advanced-level certification within the Lean Six Sigma framework. These practitioners undergo intensive training to perform advanced statistical analysis and leadership skills to lead complex improvement projects and mentor Green as well as Yellow Belts.
5) Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt
Master Black Belts are at the peak of the Lean Six Sigma skillset. These individuals possess vast experience and are known as strategic thinkers and leaders. They mentor Black Belts and help senior leadership monitor strategic initiatives to meet business objectives.
Become the driving force behind organisational excellence with our Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt Certification – Register today!
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma Methodology
Implementing Lean Six Sigma offers organisations a powerful framework to streamline operations, enhance quality, and drive measurable improvements across processes. Here are some essential Benefits of Lean Six Sigma:
1) Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
Lean Six Sigma simplifies processes, removes unnecessary steps, and improves workflows while increasing efficiency and productivity. By identifying activities that do not add value, organisations can reduce cycle times and achieve better output with existing resources. This increased efficiency enables employees to work more effectively by freeing time and resources to focus on valuable tasks and strategic initiatives.
2) Elevated Quality Standards
The main objective of Lean Six Sigma is to elevate quality by diminishing defects and process variability. By implementing rigorous process controls, standardising procedures, and continuously improving, organisations can achieve higher quality standards and consistently exceed customer expectations. Additionally, preparing for Six Sigma Interview Questions helps professionals understand the critical role of quality in organisational success. Enhanced quality bolsters customer satisfaction, curtails rework, scrap, and warranty expenses, thereby augmenting profitability and market competitiveness.
3) Cost Reduction
Lean Six Sigma initiatives helps in reducing costs through waste abatement, process refinement, and efficiency enhancements. By eliminating the redundant steps, minimising inventory, and optimising resource deployment, organisations can reduce operating costs, improve profit margins, and boost profitability.
4) Better Customer Satisfaction
Lean Six Sigma emphasises the importance of understanding customer needs and expectations. By delivering high-quality, reliable, and responsive services, an organisation can achieve customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to repeat business, referrals, and increased market share.
Satisfied customers are more likely to remain loyal, make repeat purchases, and advocate for the brand. This ultimately supports the long-term growth and success of the business.
Conclusion
We hope you understood this overview on What is Lean Six Sigma. By combining the Principles of Lean and Six Sigma quality management, businesses can streamline processes, reduce waste, and achieve higher levels of quality and customer satisfaction. With this knowledge, organisations can derive their full potential and unlock their sustainable and long-term success.
Improve your organisational efficiency through our Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Course - join today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Aim of Lean & Six Sigma?

The main goal of Lean Six Sigma is to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance quality in various industries through Lean integration. This can be achieved by streamlining production processes, optimising the supply chain, and minimising errors.
What are the Lean Six Sigma Methodologies?

The crucial Lean Six Sigma methodologies combine the benefits of minimising waste with Six Sigma’s emphasis on reducing defects and process variability. It also uses tools like DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control) and DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyse, Design, Verify) to guide teams in improving processes.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Lean Six Sigma Certification Training, including Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Course, Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Course and Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Six Sigma Belts.
Our Business Improvement Blogs cover a range of topics related to Lean Six Sigma, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Lean Six Sigma skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt
Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Thu 10th Jul 2025
Thu 11th Sep 2025
Thu 6th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


