We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Learning to play the Guitar is an exciting journey that combines creativity with technical skill. It begins with understanding the instrument's anatomy, including strings, frets, and tuning pegs. Mastering basic chords and strumming patterns forms the foundation of Guitar playing. Whether you aspire to strum along to your favourite songs or create your melodies, read this blog, which will help you learn How to Learn Guitar through a step-by-step process.
Table of Contents
1) Learn How to Play Guitar
a) Choose the appropriate Guitar
b) Know about the Guitar parts
c) Learn how to hold the Guitar
d) Understand the Guitar Strings and fretboard
e) Adjust your Guitar's tuning
f) Perform fundamental Guitar chords
g) Learn the art of Guitar chord strumming
h) Interpret Guitar tablature
i) Practice picking and the use of a Guitar pick
j) Learn minor and major scales
k) Begin performing your preferred songs
l) Engage in consistent practice
2) Conclusion
Learn How to Play Guitar
Here are some detailed steps that will help you learn Guitar easily. Let’s have a look:
1) Choose the appropriate Guitar
Selecting the right Guitar is the first crucial step in your journey to becoming a Guitarist. The type of Guitar you choose should align with the style of music you are interested in. There are primarily three types:
a) Classical Guitars with nylon strings, which are softer on the fingers and produce a mellow sound.
b) Steel-string acoustic Guitars, known for their bright and loud tone, are suitable for folk, pop, and rock.
c) Electric Guitars are versatile for many genres, including rock, jass, and blues when connected to an amplifier.
Consider the Guitar’s size and shape for comfort and playability, especially if you are a beginner or a younger player. Full-sized Guitars might be cumbersome for children, so ½ or ¾ sized Guitars are recommended. The action (distance between the strings and the fretboard) is also essential. Lower action is generally easier to play but might cause bussing if it is too low.
As a beginner, you might want to start with an affordable model. As you progress, you can invest in a higher-quality instrument. Visiting a music store and trying out different Guitars can help you make an informed decision based on feel and sound.
2) Know about the Guitar parts
Understanding the parts of a Guitar is essential for learning how to play it. The main parts include the headstock, which holds the tuning pegs; the neck, comprising the fretboard, frets, and strings; and the body, which consists of the sound hole (in acoustic Guitars) or pickups (in electric Guitars).
In the fretboard, you press the strings to create different notes and chords. The frets are the metal strips that divide the fretboard. The strings are typically numbered from 1 to 6, with 1 being the thinnest string (highest in pitch) and 6 the thickest (lowest in pitch).
In acoustic Guitars, the sound hole amplifies the sound produced by the strings. Electric Guitars have pickups that convert the strings' vibration into electrical signals, which are amplified.
3) Learn how to hold the Guitar
Holding the Guitar correctly is crucial for playing comfortably and effectively. Sit straight on a chair and rest the Guitar on your right thigh (if you’re right-handed) or left thigh (if left-handed). The neck of the Guitar should be slightly upwards, and the body should be snug against your torso.
Your strumming/picking hand should be relaxed over the Guitar’s body, with your arm resting so your hand is over the sound hole or pickups. Your fretting hand should come around the neck, with your thumb positioned at the back for support. Ensure your wrist is relaxed and not overly bent to avoid strain.
4) Understand the Guitar strings and fretboard
Guitar strings are typically numbered from 1 to 6, with 1 being the high E string and 6 being the low E string. Each fret on the fretboard represents a half step in the musical scale. Pressing a string against a fret shortens the string's vibrating length, raising the pitch.
Learning the notes on the fretboard is crucial for navigating the Guitar. Start by memorising the notes on the low E and A strings, often used as reference points—practice finding and playing notes in different positions and octaves to understand the fretboard layout comprehensively.
5) Adjust your Guitar's tuning
Tuning your Guitar is essential for it to sound correct and harmonious. The standard tuning for a Guitar from the thickest to the thinnest string is E, A, D, G, B, and E. You can tune your Guitar using an electronic tuner, a tuning app, or by ear if you have a reference note for the E string.
Beginners should start with standard tuning to familiarise themselves with the basic sound and layout of the Guitar. As you progress, you can explore alternate tunings to achieve different sounds and play specific types of music.
Regularly check your tuning before playing, as environmental factors like temperature and humidity can affect the tuning. Properly tuning your Guitar is crucial for developing a good ear and ensuring you practice correctly.
6) Perform fundamental Guitar chords
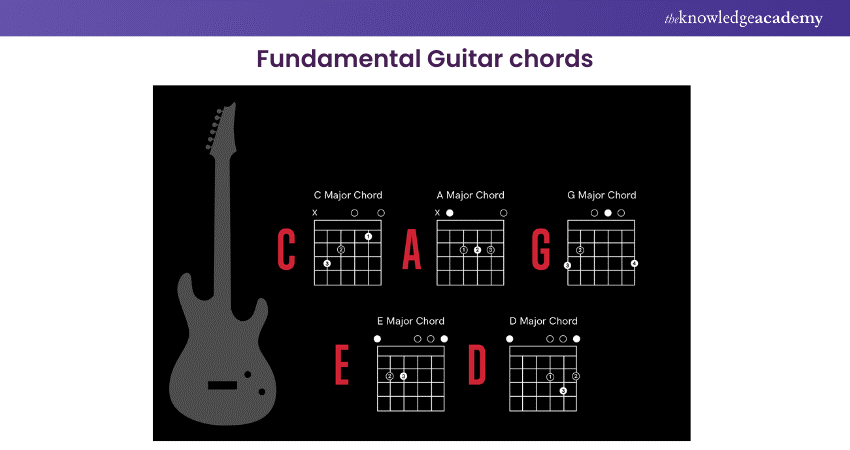
Learning fundamental Guitar chords is a cornerstone of playing the Guitar. Chords are a group of notes played simultaneously, forming the basis of most songs. As a beginner, focus on learning the open chords, played using at least one empty string (not fretted). These typically include major chords like C, A, G, E, and D, and minor chords like Am, Dm, and Em.
Start by learning the shape of each chord. Place your fingers on the correct frets and strings as per chord diagrams, which visually represent the Guitar neck. Ensure each finger is placed just behind the frets, not on top of them. Apply enough pressure to prevent bussing sounds but not so much that it causes discomfort.
Practicing chord transitions is crucial. Start slowly, moving from one chord to another and focus on smooth, clean transitions. It's common for beginners to struggle with specific chord shapes or transitions, but regular practice will improve muscle memory and skill.
Incorporate a metronome into your practice to develop a sense of timing and rhythm. Initially, the changes will be slow, but you can switch chords quickly and seamlessly with consistent practice.
Are you interested to explore the different types of hobbies for all-round development? Register now for our Hobbies & Interests course today!
7) Learn the art of Guitar chord strumming
Strumming is brushing your fingers or picking across the Guitar strings to produce sound. It's essential for giving rhythm to the music. First, learn the basic downstroke (strumming downwards towards the floor) and upstroke (strumming upwards towards the ceiling).
Developing a consistent strumming pattern is critical. Common patterns include alternating downstrokes and upstrokes or more complex rhythms involving muted strums or different emphases on specific beats. Start with simple patterns and gradually increase complexity as you become more comfortable.
Your strumming hand should be relaxed, and the movement should come from the wrist, not the entire arm. Practising with a metronome or along with songs can help maintain a steady rhythm.
Strumming isn't just about hitting all the strings; it's also about dynamics and accentuating certain strums to bring life to a song. Listen to how different strumming patterns affect the feel of a song and experiment with creating your own.
8) Interpret Guitar tablature
Guitar tablature, or “tabs,” is a musical notation specifically for Guitar. It’s a simpler alternative to reading music and is popular among Guitarists. A tab shows six horizontal lines representing the strings of the Guitar, with the top line being the high E string and the bottom line being the low E string. Numbers on these lines indicate which fret to play.
For instance, a “3” on the bottom line means you should play the third fret on the low E string. Chords and melodies can be easily read and played using tabs. However, tabs have limitations; they don’t usually indicate each note's rhythm or duration. It's often helpful to listen to the piece of music while you follow the tab to understand the timing. Learning to read tabs can vastly expand your repertoire and is invaluable for learning new songs and techniques.
9) Practice picking and the use of a Guitar pick
Picking involves plucking individual strings to play melodies, riffs, or parts of chords. It can be done with fingers (fingerpicking) or with a pick (flatpicking). A pick, or plectrum, is a small plastic between the thumb and index finger to strike the strings. When starting with a pick, focus on keeping it correctly – not too tight or loose – and practice basic downstrokes and upstrokes on individual strings.
Start slowly and aim for clean, clear notes. Try playing simple melodies or scales to improve your skill as you become more comfortable. Fingerpicking uses the fingers of the strumming hand to pluck the strings. Each finger is assigned to a specific string. This technique is widely used in genres like classical, folk, and flamenco.
10) Learn minor and major scales
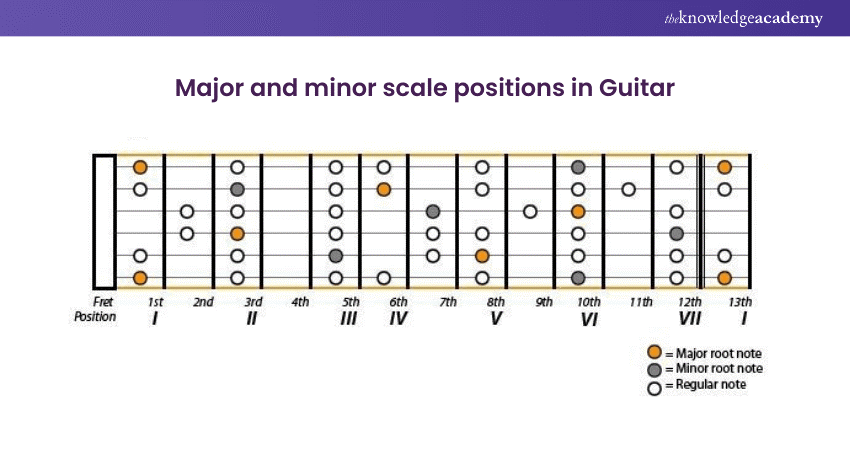
Scales are sequences of notes played in ascending and descending order. They are the building blocks of melodies and solos. The major scale has a bright, happy sound, while the minor is more profound and often perceived as sad or reflective. To start, learn the C major scale, which has no sharp or flat notes. Practice playing it slowly, focusing on clean notes and even timing.
Then, move on to other significant scales and their relative minor scales. Understanding scales is crucial for improvisation and songwriting. They help develop an ear for music and understand how different notes interact. Practice scales regularly and try incorporating them into simple solos or melodies to understand their practical applications.
Learn How to Play Guitar like a professional – sign up for our Guitar Course now!
11) Begin performing your preferred songs
One of the most rewarding aspects of learning Guitar is the ability to play your favourite songs. Start with simple songs with basic chords and strumming patterns you already know. This approach makes the learning process enjoyable and less daunting. Choose songs with slower tempos and straightforward chord progressions initially.
These are easier to follow and allow you to focus on your technique and timing. Gradually introduce songs with more complex structures, faster tempos, and varied strumming patterns as you improve. Learning songs from different genres can expose you to diverse playing styles and techniques.
Playing with the original track or a metronome can help you develop a sense of timing and rhythm. It also provides a reference to ensure you’re correctly playing the chords and melody. If you find a song too challenging, don't hesitate to simplify it. You can slow the tempo, simplify the strumming pattern, or even transpose the song to a more accessible key.
12) Engage in consistent practice
Regular practice helps develop muscle memory, improves dexterity, and deepens your understanding of the instrument. Set aside dedicated time each day for practice, even if it’s just for a short period. Consistent, focused practice is more effective than sporadic, lengthy sessions.
Start your practice with a warm-up. This could be simple scales, chord progressions, or strumming patterns. Warming up prepares your fingers and mind for more complex tasks and reduces the risk of injury. Following your warm-up, work on specific skills or songs you are learning. Break down difficult sections into smaller parts and practice them slowly until you can play them seamlessly.
Incorporate a variety of exercises into your practice sessions. This could include chord transitions, scale runs, fingerpicking patterns, or new strumming techniques. Variety not only keeps practice interesting but also ensures a well-rounded skill set. Use tools like a metronome to improve your timing and rhythm, which are crucial for playing music effectively.
Recording your practice sessions can be beneficial. Listening to your playbacks can help identify areas that need improvement and track your progress over time. Don’t avoid challenges; tackling complex pieces or techniques can lead to significant improvements.
Do you want to learn the different techniques of mixing audio? Register now for our Music Production Course!
Conclusion
We hope that you understood How to Play Guitar from this blog. In this blog, we discussed learning to Play Guitar is a fulfilling journey that blends technical skill with artistic expression. Consistent practice and dedication are essential, from choosing the right Guitar to mastering chords, strumming, and songs.
Learn how to play piano using various advanced techniques with our Piano Course – join now!
Frequently Asked Questions

The time it takes to learn Guitar varies widely depending on practice frequency and goals. Beginners can play basic chords and songs within a few weeks, but mastering the instrument requires ongoing practice. Consistently practising for at least 30 minutes daily can lead to noticeable progress over several months.

Both acoustic and electric Guitars have their advantages for beginners. Acoustic Guitars are often recommended for their simplicity and portability. They help develop finger strength and technique due to their thicker strings. Electric Guitars, with lighter strings and a slimmer neck, might be easier to play initially. The choice depends on personal musical preferences and comfort.

Many people successfully learn Guitar independently using online resources, books, and practice. However, lessons with a skilled teacher can provide personalised feedback and structured learning and help overcome specific challenges. Beginners can benefit from lessons to ensure they develop correct techniques, but self-learning is also a viable and rewarding path.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Hobbies and Interest courses, including Guitar Course, Music Production Course, and Piano Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Music Production.
Our Hobbies and Interests blogs covers a range of topics related to Music Production, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Guitar skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


