We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Are you intrigued by the concept of Accounting Principles and their influence on financial reporting? Grasping these principles is vital for maintaining consistency and reliability in financial statements across various organisations. These guidelines ensure comparability and trustworthiness, enabling businesses to present transparent and precise financial information.
By following these principles, companies can provide clear and accurate financial data, which is crucial for stakeholders making informed decisions. Dive into this blog to uncover what Accounting Principles are and why they are essential for strong business practices. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
1) What are Accounting Principles?
2) Role of Accounting Principles
3) Types of Principles of Accounting
4) Features of Accounting Principles
5) Drawbacks of Accounting Principles
6) Accounting Principles vs Accounting Concepts: Key Differences
7) Conclusion
What are Accounting Principles?
Accounting Principles are foundational rules and guidelines designed to ensure that financial reporting is consistent, accurate, and reliable. These principles help standardise how financial statements are prepared and presented, making it simpler to compare financial data across different organisations. Following these principles enhances transparency and trust, enabling stakeholders to make well-informed decisions based on clear and comparable financial information.
Role of Accounting Principles
Accounting Principles play an important role in ensuring consistency and accuracy in financial records and statements. They enable investors to easily interpret and analyse essential financial information. By upholding these principles, businesses can prevent fraud, maintain transparency, and identify any discrepancies. This allows accurate comparison of financial details over time.
Learn the foundational skills in Financial Management with our Accounting Courses – Register today!
Types of Principles of Accounting
Accounting Principles provide a framework for financial reporting, ensuring that financial statements are accurate and reliable. These principles guide how transactions and events are recorded and reported, maintaining consistency and transparency in financial reporting. Here are the key principles:
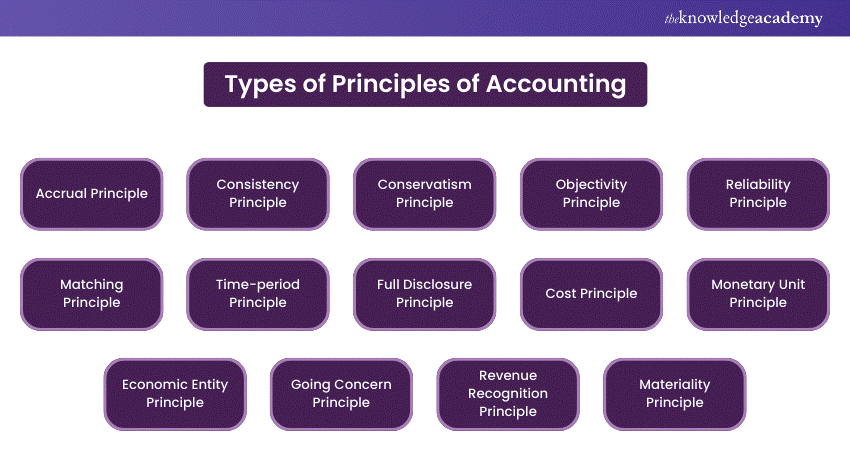
1) Accrual Principle
Records revenues and expenses when they arise, not when cash is exchanged, to provide a more accurate financial picture.
2) Consistency Principle
Requires organisations to use the same accounting methods and principles from one period to the next to ensure comparability.
3) Conservatism Principle
It suggests that uncertainties and risks should be accounted for conservatively by recognising expenses and liabilities as soon as possible.
4) Objectivity Principle
Ensures that financial statements are based on objective evidence and verifiable data rather than personal opinions.
5) Reliability Principle
Financial information should be accurate and dependable, based on factual and unbiased data.
6) Matching Principle
Expenses should be matched with related revenues in the same period to accurately measure profitability.
7) Time-period Principle
Requires financial reporting to be done in specific time periods, such as monthly or yearly, to track performance consistently.
8) Full Disclosure Principle
Mandates that all relevant financial information must be disclosed in financial statements to provide a complete view.
9) Cost Principle
Assets should be recorded at their original cost rather than their market value to ensure reliability.
10) Monetary Unit Principle
Assumes that all transactions can be quantified in monetary terms, without accounting for inflation or deflation effects.
11) Economic Entity Principle
Requires that a business's financial activities be kept separate from those of its owners or other businesses.
12) Going Concern Principle
Assumes that a business will continue working indefinitely unless there is evidence to suggest otherwise.
13) Revenue Recognition Principle
Revenue should be recognised when it is earned and realisable, regardless of when cash is received.
14) Materiality Principle
Allows for minor deviations from Accounting Principles if they do not significantly impact the financial statements.
Do you want to acquire skills in budgeting, financial reporting, and effective accounting practices? Sign up with our Accounting Course now!
Features of Accounting Principles
Accounting Principles are essential for consistent financial reporting. There are three main features of Accounting Principles. They are:
a) Usefulness: Accounting Principles are designed to be relevant and valuable to their users. They ensure that accountants and stakeholders receive the essential information needed for accurate financial analysis and decision-making.
b) Feasibility: Accounting Principles are adaptable to changing conditions. For instance, if costs fluctuate due to market price changes, the principles allow for flexible adjustments, ensuring accurate financial records despite variable conditions.
c) Objectivity: Accounting Principles emphasise the use of precise, factual data without personal biases or external influences. This objectivity ensures that financial information is reliable and meets the business’s reporting needs.
Drawbacks of Accounting Principles
While Accounting Principles ensure consistency and reliability in financial reporting, they are not without limitations. Here are some drawbacks:
1) Inflexibility
Accounting Principles can be rigid and may not accommodate unique or rapidly changing business conditions, leading to less relevant financial reporting.
2) Complexity
Adhering to various Accounting Principles can make financial reporting complex and difficult to understand, particularly for small businesses with limited resources.
3) Judgment and Bias
Despite the aim for objectivity, some Accounting Principles involve subjective judgment, which can introduce biases or inconsistencies in financial statements.
4) Cost of Compliance
Implementing and maintaining compliance with Accounting Principles can be costly and resource-intensive, particularly for businesses with limited budgets.
5) Lag in Information
Certain principles, such as the accrual principle, may result in financial statements that do not reflect the current financial situation of a business, causing delays in decision-making.
6) Lack of Flexibility
Principles such as the cost principle can prevent businesses from reflecting current market values, potentially leading to outdated financial information.
Learn the basic principle of Project Accounting with our Project Accounting Course - Join now!
Accounting Principles vs Accounting Concepts: Key Differences
Accounting Principles and accounting concepts are foundational to financial reporting, but they serve different purposes and functions. Here’s a concise comparison to highlight their distinctions:
Conclusion
Understanding and adhering to Accounting Principles is fundamental for any business aiming to maintain transparency and accuracy in its financial reporting. These principles not only ensure consistency and comparability across financial statements but also build trust with stakeholders, enabling them to make well-informed decisions. By embracing these guidelines, businesses can foster robust financial practices that support their long-term success and credibility
Become familiar with Cash Management to create and sustain a company's financial stability with our Cash Cycle Management Training – Register now!
Frequently Asked Questions

The three golden rules of accounting include:
1) Debit the receiver, credit the giver—applies to personal accounts.
2) Debit all expenses and losses, credit all income and gains—applies to nominal accounts.
3) Debit what comes in, credit what goes out—applies to real accounts.

The two major types of accounting are Financial Accounting and Management Accounting. Financial accounting focuses on preparing financial statements for external stakeholders, while management accounting provides internal reports to help management make informed decisions.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Accounting Courses, including Accounting Course, Inventory Accounting and Costing Course and Accounting and Financial Statement Analysis Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is Corporate Finance.
Our Accounting and Finance Resources cover a range of topics related to Accounting, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Accounting and Finance Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Accounting and Finance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Accounting Course
Accounting Course
Fri 6th Dec 2024
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 8th Aug 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


